Abstract
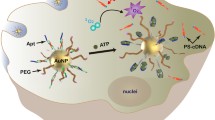
We present here a pH-responsive activatable aptamer probe for targeted cancer imaging based on i-motif-driven conformation alteration. This pH-responsive activatable aptamer probe is composed of two single-stranded DNA. One was used for target recognition, containing a central, target specific aptamer sequence at the 3'-end and an extension sequence at the 5'-end with 5-carboxytetramethylrhodamine (TAMRA) label (denoted as strand A). The other (strand I), being competent to work on the formation of i-motif structure, contained four stretches of the cytosine (C) rich domain and was labeled with a Black Hole Quencher 2 (BHQ2) at the 3'-end. At neutral or slightly alkaline pH, strand I was hybridized to the extension sequence of strand A to form a double-stranded DNA probe, termed i-motif-based activatable aptamer probe (I-AAP). Because of proximityinduced energy transfer, the I-AAP was in a “signal off” state. The slightly acidic pH enforced the strand I to form an intramolecular i-motif and then initiated the dehybridization of I-AAP, leading to fluorescence readout in the target recognition. As a demonstration, AS1411 aptamer was used for MCF-7 cells imaging. It was displayed that the I-AAP could be carried out for target cancer cells imaging after being activated in slightly acidic environment. The applicability of I-AAP for tumor tissues imaging has been also investigated by using the isolated MCF-7 tumor tissues. These results implied the I-AAP strategy is promising as a novel approach for cancer imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker A, Hessenius C, Licha K, Ebert B, Sukowski U, Semmler W, Wiedenmann B, Grötzinger C. Nat Biotechnol, 2001, 19: 327–331
Cerchia L, Franciscis VD. Trends Biotechnol, 2010, 28: 517–525
Tan WH, Michael JD, Jiang JH. Chem Rev, 2013, 113: 2842–2862
Schmidt KS, Borkowski SJ, Stephens AW, Bald R, Hecht M, Friebe M, Dinkelborg L, Erdmann VA. Nucleic Acids Res, 2004, 32: 5757–5765
Hicke BJ, Stephens AW, Gould T, Chang YF, Lynott CK, Heil J, Borkowski S, Hilger CS, Cook G, Warren S, Schmidt PG. J Nucl Med, 2006, 47: 668–678
Yu MK, Kim D, Lee IH, So JS, Jeong YY, Jon S. Small, 2011, 7: 2241–2249
Zhang CL, Ji XH, Zhang Y, Zhou GH, Ke XL, Wang HZ, Tinnefeld P, He ZK. Anal Chem, 2013, 85: 5843–5849
Shi H, He XX, Wang KM, Wu X, Ye XS, Guo QP, Tan WH, Qing ZH, Yang XH, Zhou B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108: 3900–3905
Yan LA, Shi H, He XX, Wang KM, Tang JL, Chen M, Ye XS, Xu FZ, Lei YL. Anal Chem, 2014, 86: 9271–9277
Medley CD, Smith JE, Tang ZW, Wu YR, Bamrungsap S, Tan WH. Anal Chem, 2008, 80: 1067–1072
Leroy JL. Nucleic Acids Res, 2009, 37: 4127–4134
Song GT, Ren JS. Chem Commun, 2010, 46: 7283–7294
Chen LF, Di JC, Cao CY, Zhao Y, Ma Y, Luo J, Wen YQ, Song WG, Song YL, Jiang L. Chem Commun, 2011, 47: 2850–2852
Li W, Wang JS, Ren JS, Qu XG. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2013, 52: 6726–6730
Nesterova IV, Nesterov EE. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136: 8843–8846
Dembska A, Juskowiak B. Spectroc Acta Pt A: Molec Biomolec Spectr, 2015, 150: 928–933
Li T, Famulok M. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 136: 1593–1599
Wang C, Huang Z, Lin Y, Ren J, Qu X. Adv Mater, 2010, 22: 2792–2798
Li J, Huang YQ, Qin WS, Liu XF, Huang W. Polym Chem, 2011, 2: 1341–1346
Pu F, Wang CY, Hu D, Huang ZZ, Ren JS, Wang S, Qu XG. Mol BioSyst, 2010, 6: 1928–1932
Huang J, Ying L, Yang XH, Yang YJ, Quan K, Wang H, Xie NL, Ou M, Zhou QF, Wang KM. Anal Chem, 2015, 87: 8724–8731
Surana S, Bhat JM, Koushika SP, Krishnan Y. Nat Commun, 2011, 2:340
Modi S, Nizak C, Surana S, Halder S, Krishnan Y. Nat Nanotech, 2013, 8: 459–467
Zhou J, Wei CY, Jia GQ, Wang XL, Feng ZC, Li C. Mol BioSyst, 2010, 6: 580–586
Bates PJ, Laber DA, Miller DM, Thomas SD, Trent JO. Exp Mol Pathol, 2009, 86: 151–164
Choi J, Kim S, Tachikawa T, Fujitsuka M, Majima T. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 16146–16153
Dong YC, Yang ZQ, Liu DS. Acc Chem Res, 2014, 47: 1853–1860
Kato Y, Ozawa S, Miyamoto C, Maehata Y, Atsuko Suzuki A, Maeda T. Cancer Cell Int, 2013, 13: 89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, L., Shi, H., He, D. et al. A pH-responsive activatable aptamer probe for targeted cancer imaging based on i-motif-driven conformation alteration. Sci. China Chem. 59, 802–808 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-016-5575-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-016-5575-2