Abstract
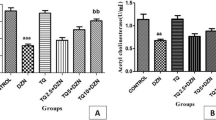
Currently, public pay more attention to the adverse effect of organophosphate pesticides on human and animal health and on the environment in developing nations. Vitamin E may protect the hepatocyte and increase the function of liver. The study was to investigate the effects of phoxim-induced hepatotoxicity on Sprague Dawley (SD) rats and the protection of vitamin E. SD rats received by gavage 180 mg kg−1 (per body weight) of phoxim, 200 mg kg−1 (per body weight) of vitamin E, and phoxim + vitamin E. The results showed that exposure to phoxim elevated liver coefficient; glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin, total bile acid, and alanine aminotransferase in the serum; ROS in the liver; and the expression of p53, Bax, CYP2E1, ROS, caspase-9, caspase-8, and caspase-3, while phoxim caused a reduction of total protein, albumin, and cholinesterase in the serum; acetylcholinesterase, total antioxidant capacity, glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione in the liver; and the expression of Bcl-2. Vitamin E modified the phoxim-induced hepatotoxicity by reducing the GGT in the serum, malondialdehyde in the liver, and the expression of CYP2E1 significantly. There were no significant changes of globulin in the serum, the activity of catalase in the liver, as well as expression levels of Fas and Bad in the liver. Overall, subacute exposure to phoxim induced hepatic injury, oxidative stress damage, and cell apoptosis. Vitamin E modified phoxim-induced hepatotoxicity slightly. And, vitamin E minimized oxidative stress damage and ultrastructural changes in rat hepatocytes notably.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdeldaim MM, Abuzead SM, Halawa SM (2013) Protective role of Spirulina platensis against acute deltamethrin-induced toxicity in rats. PLoS One 8:e72991. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072991
Androutsopoulos VP, Hernandez AF, Liesivuori J, Tsatsakis AM (2013) A mechanistic overview of health associated effects of low levels of organochlorine and organophosphorous pesticides. Toxicology 307:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2012.09.011
Armagan I, Bayram D, Candan IA, Yigit A, Celik E, Armagan HH, Uğuz AC (2015) Effects of pentoxifylline and alpha lipoic acid on methotrexate-induced damage in liver and kidney of rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39:1122–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.04.003
Banerjee BD, Seth V, Ahmed RS (2011) Pesticide-induced oxidative stress: perspectives and trends. Rev Environ Health 16:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1515/REVEH.2001.16.1.1
Catalgol B, Ozer NK (2012) Protective effects of vitamin E against hypercholesterolemia-induced age-related diseases. Genes Nutr 7:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-011-0235-9
Celik I, Yilmaz Z, Turkoglu V (2009) Hematotoxic and hepatotoxic effects of dichlorvos at sublethal dosages in rats. Environ Toxicol 24:128–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20390
Cemek M, Büyükben A, Büyükokuroğlu ME, Aymelek F, Tür L (2010a) Protective roles of vitamin E (α-tocopherol), selenium and vitamin E plus selenium in organophosphate toxicity in vivo: a comparative study. Pestic Biochem Phys 96:113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2009.09.009
Cemek M, Büyükokuroğlu ME, Büyükben A, Aymelek F, Özcan L (2010b) Effects of vitamin E and selenium on tissue bioelement status in organophosphate toxicity of rats. Pestic Biochem Phys 98:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2010.04.003
Chen Q, Galleano M, Cederbaum AI (1997) Cytotoxicity and apoptosis produced by arachidonic acid in Hep G2 cells overexpressing human cytochrome P4502E1. J Biol Chem 272(23):14532–14541. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.23.14532
Costa LG (2006) Current issues in organophosphate toxicology. Clin Chim Acta 366:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2005.10.008
Dalaklioglu S, Genc GE, Aksoy NH, Akcit F, Gumuslu S (2013) Resveratrol ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via inhibition of lipid peroxidation. Hum Exp Toxicol 32:662–671. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327112468178
Dirican EK, Kalender Y (2012) Dichlorvos-induced testicular toxicity in male rats and the protective role of vitamins C and E. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64(7):821–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2011.03.002
Gavelle DE, Lauzon-Guillain DB, Charles MA, Chevrier C, Hulin M, Sirot V, Merlo M, Nougadère A (2016) Chronic dietary exposure to pesticide residues and associated risk in the French ELFE cohort of pregnant women. Environ Int 92:533–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.04.007
Elahi E, Zhang L, Abid M, Javed MT, Xinru H (2017) Direct and indirect effects of wastewater use and herd environment on the occurrence of animal diseases and animal health in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut R:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8423-9
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Erkekoğlu P, Rachidi W, Yüzügüllü OG, Giray B, Oztürk M, Favier A, Hıncal F (2011) Induction of ROS, p53, p21 in DEHP- and MEHP-exposed LNCaP cells-protection by selenium compounds. Food Chem Toxicol 49:1565–1571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2011.04.001
Fakhri-Bafghi MS, Ghasemi-Niri SF, Mostafalou S, Navaei-Nigjeh M, Baeeri M, Mohammadirad A, Abdollahi M (2016) Protective effect of selenium-based medicines on toxicity of three common organophosphorus compounds in human erythrocytes in vitro. Cell J 17:740–747. 10.22074/cellj.2016.3846
Fu Y, Li M, Liu C, Qu J, Zhu W, Xing H, Xu S, Li S (2013) Effect of atrazine and chlorpyrifos exposure on cytochrome P450 contents and enzyme activities in common carp gills. Ecotox Environ Safe 94:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.04.018
Gu ZY, Li FC, Wang BB, Xu KZ, Ni M, Zhang H, Shen WD, Li B (2015) Differentially expressed genes in the fat body of Bombyx mior in response to phoxim insecticide. Pestic Biochem Physiol 117:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.10.007
Hadi NR, Al-Amran FG, Swadi A (2012) Metformin ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Pharmacother 3:248–253. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500X.99426
Hamza RZ, Al-Harbi MS, El-Shenawy NS (2017) Ameliorative effect of vitamin E and selenium against oxidative stress induced by sodium azide in liver, kidney, testis and heart of male mice. Biomed Pharmacother 91:602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.122
Han Y, Song S, Wu H, Zhang J, Ma E (2017) Antioxidant enzymes and their role in phoxim and carbaryl stress in Caenorhabditis elegans. Pestic Biochem Phys 138:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2017.02.005
Halliwell B (2006) Reactive species and antioxidants. Redox biology is a fundamental theme of aerobic life. Plant Physiol 141:312–322. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.077073
Jaeschke H, Gores GJ, Cederbaum AI, Hinson JA, Pessayre D, Lemasters JJ (2002) Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 65:166–176. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/65.2.166
Joshi SC, Mathur R, Gajraj A, Sharma T (2003) Influence of methyl parathion on reproductive parameters in male rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 14:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1382-6689(03)00043-7
Jia Y, Jing Q, Niu H, Huang B (2017) Ameliorative effect of vitamin E on hepatic oxidative stress and hypoimmunity induced by high-fat diet in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Shellfish Immun 67:634–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.06.056
Jin Y, Wu S, Zeng Z, Fu Z (2017) Effects of environmental pollutants on gut microbiota. Environ Pollut 222:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.045
Jin Y, Zhang X, Shu L, Chen L, Sun L, Qian H, Liu W, Fu Z (2010) Oxidative stress response and gene expression with atrazine exposure in adult female zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 78:846–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.11.044
Kalender S, Kalender Y, Durak D, Ogutcu A, Uzunhisarcikli M, Cevrimli BM, Yildirim M (2007) Methyl parathion induced nephrotoxicity in male rats and protective role of vitamins C and E. Pestic Biochem Phys 88:213–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.11.00
Kalender S, Ogutcu A, Uzunhisarcikli M, Açikgoz F, Durak D, Ulusoy Y, Kalender Y (2005b) Diazinon-induced hepatotoxicity and protective effect of vitamin E on some biochemical indices and ultrastructural changes. Toxicology 211:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2005.03.007
Kalender S, Uzun FG, Durak D, Demir F, Kalender Y (2010) Malathion-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: the effects of vitamins C and E. Food Chem Toxicol 48:633–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.11.044
Kalender Y, Yel M, Kalender S (2005a) Doxorubicin hepatotoxicity and hepatic free radical metabolism in rats: the effects of vitamin E and catechin. Toxicology 209:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2004.12.003
Lasram MM, Lamine AJ, Dhouib IB, Bouzid K, Annabi A, Belhadjhmida N, Ahmed MB, El Fazaa S, Abdelmoula J, Gharbi N (2014) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of N-acetylcysteine against malathion-induced liver damages and immunotoxicity in rats. Life Sci 107:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2014.04.033
Li F, Hu J, Tian J, Xu K, Ni M, Wang B, Shen W, Li B (2016) Effects of phoxim on nutrient metabolism and insulin signaling pathway in silkworm midgut. Chemosphere 146:478–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.032
Li S, Tan HY, Wang N, Zhang ZJ, Lao L, Wong CW, Feng Y (2015) The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16:26087–26124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125942
Mansour SA, Mossa ATH (2010) Oxidative damage, biochemical and histopathological alterations in rats exposed to chlorpyrifos and the antioxidant role of zinc. Pestic Biochem Phys 96:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2009.08.008
Masella R, Benedetto RD, Varì R, Filesi C, Giovannini C (2005) Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological systems: involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. J Nutr Biochem 16:577–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2005.05.013
Mehany HA, Abo-Youssef AM, Ahmed LA, Arafa A, Abd HA (2013) Protective effect of vitamin E and atorvastatin against potassium dichromate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. BJBAS 2:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjbas.2013.02.002
Meyer-Kühling B, Pfister K, Müller-Lindloff J, Heine J (2007) Field efficacy of phoxim 50% (ByeMite®) against the poultry red mite Dermanyssus gallinae in battery cages stocked with laying hens. Vet Parasitol 147:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.04.012
Mohamed E, El-Hack A, Mahrose K, Arif M, Chaudhry MT, Saadeldin IM, Saeed M, Soomro RN, Abbasi IHR, Rehman ZU (2017) Alleviating the environmental heat burden on laying hens by feeding on diets enriched with certain antioxidants (vitamin E and selenium) individually or combined. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8690-5
Mostafalou S, Abdollahi M (2017) Pesticides: an update of human exposure and toxicity. Arch of Toxicol 91:549–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1849-x
Muriel P (2009) Role of free radicals in liver diseases. Hepatol Int 3:526–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-009-9158-6
Noh JR, Kim YH, Hwang JH, Choi DH, Kim KS, Oh WK, Lee CH (2015) Sulforaphane protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 80:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2015.03.020
Ogutcu A, Suludere Z, Kalender Y (2008) Dichlorvos-induced hepatotoxicity in rats and the protective effects of vitamins C and E. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26:355–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2008.07.005
Ogutcu A, Uzunhisarcikli M, Kalender S, Durak D, Bayrakdar F, Kalender Y (2006) The effects of organophosphate insecticide diazinon on malondialdehyde levels and myocardial cells in rat heart tissue and protective role of vitamin E. Pestic Biochem Phys 86(2):93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.01.010
Ourique GM, Saccol EMH, Pês TS, Glanzner WG, Schiefelbein SH, Woehl VM, Baldisserotto B, Pavanato MA, Gonçalves PB, Barreto KP (2016) Protective effect of vitamin E on sperm motility and oxidative stress in valproic acid treated rats. Food Chem Toxicol 95:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.07.011
Petroianu GA, Hasan MY, Nurulain SM, Shafiullah M, Sheen R, Nagelkerke N (2006) Ranitidine in acute high-dose organophosphate exposure in rats: effect of the time-point of administration and comparison with pyridostigmine. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 99:312–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.pto_215.x
Pflaum J, Schlosser S, Müller M (2014) p53 family and cellular stress responses in cancer. Front Oncol 4:285–285. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00285
Soltaninejad K, Abdollahi M (2009) Current opinion on the science of organophosphate pesticides and toxic stress: a systematic review. Med Sci Monit 15:RA75–RA90
Södergren E, Cederberg J, Vessby B, Basu S (2001) Vitamin E reduces lipid peroxidation in experimental hepatotoxicity in rats. Eur J Nutr 40:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00007381
Spodniewska A, Barski D, Giżejewska A (2015) Effect of enrofloxacin and chlorpyrifos on the levels of vitamins A and E in Wistar rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:587–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.08.019
Storm JE, Rozman KK, Doull J (2000) Occupational exposure limits for 30 organophosphate pesticides based on inhibition of red blood cell acetylcholinesterase. Toxicology 150:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(00)00219-5
Traber MG, Atkinson J (2007) Vitamin E, antioxidant and nothing more. Free Radic Biol Med 43:4–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.024
Uzunhisarcikli M, Kalender Y (2011) Protective effects of vitamins C and E against hepatotoxicity induced by methyl parathion in rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:2112–2118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.07.001
Van Haaften RIM, Haenen GRMM, Evelo CTA, Bast A (2003) Effect of vitamin E on glutathione-dependent enzymes. Drug Metab Rev 35:215–253. https://doi.org/10.1081/DMR-120024086
Vaseva AV, Marchenko ND, Ji K, Tsirka SE, Holzmann S, Moll UM (2012) p53 opens the mitochondrial permeability transition pore to trigger necrosis. Cell 149:1536–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.014
Verma RS, Mehta A, Srivastava N (2007) In vivo, chlorpyrifos induced oxidative stress: attenuation by antioxidant vitamins. Pestic Biochem Phys 88:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.11.002
Videla LA (2009) Oxidative stress signaling underlying liver disease and hepatoprotective mechanisms. W World J Hepatol 1:72–78. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v1.i1.72
Vittozzi L, Fabrizi L, Di CE, Testai E (2001) Mechanistic aspects of organophosphorothionate toxicity in fish and humans. Environ Int 26:125–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(00)00102-1
Wang BB, Li FC, Xu KZ, Ni M, Hu JS, Tian JH, Li YY, Shen WD, Li B (2016) Effects of mutations on the structure and function of silkworm type I acetylcholinesterase. Pestic Biochem Physiol 129:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2015.11.003
Wilson N, Dixit VA (2009) Death receptor signal transducers: nodes of coordination in immune signaling networks. Nat Immunol 10:348–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1714
Wu J, Lin L, Luan T, Chan GYS, Lan C (2007) Effects of organophosphorus pesticides and their ozonation byproducts on gap junctional intercellular communication in rat liver cell line. Food Chem Toxicol 45:2057–2063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.05.006
Yang F, Ren L, Zhuo L, Ananda S, Liu L (2011) Involvement of oxidative stress in the mechanism of triptolide-induced acute nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:905–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2011.03.013
Zeng L, Li T, Xu DC, Liu J, Mao G, Cui MZ, Fu X, Xu X (2012) Death receptor 6 induces apoptosis not through type I or type II pathways, but via a unique mitochondria-dependent pathway by interacting with Bax protein. J Biol Che 287:29125–29133. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.362038
Zhang X, Wang M, Gao S, Ren R, Zheng J, Zhang Y (2011) Atrazine-induced apoptosis of splenocytes in BALB/C mice. BMC Med 9:117. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-9-117
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Plan (2016YFD0501207), the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-36), and the National Basic Research Program (2012CB124703).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was performed in strict accordance with the recommendations of the National Research Council Guide (1996), and all of the animal experimental procedures were approved by the Ethical and Animal Welfare Committee of Heilongjiang Province, China (2008).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
All authors have read the manuscript and have agreed to submit it in its current form for consideration for publication in the journal.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Song, W., Sun, Y. et al. Effects of phoxim-induced hepatotoxicity on SD rats and the protection of vitamin E. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 24916–24927 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0104-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0104-1