Abstract
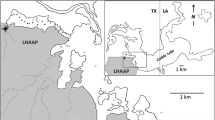
Lake Diefenbaker, on the South Saskatchewan River, Saskatchewan, Canada, receives, on average, 90% of its inflow from snowmelt and rainfall in the Rocky Mountains. The inflowing rivers also receive irrigation return flows and municipal and industrial effluents which may result in the contamination of lake sediments. The sediments were assessed by nematode and algal bioassays.
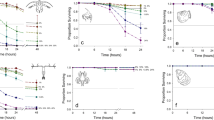
The toxicity of five chemical fractions of the sediment was determined using the nematode Panagrellus redivivus as the test organisms. The results suggest that the sediment chemical fractions frequently inhibit growth and maturation, while lethality was observed at 4 of 12 sites.
Samples from 3 of these sites were further evaluated using conventional elutriate Algal Fractionation Bioassays (AFB) with both natural Lake Diefenbaker phytoplankton and a mixed laboratory grown algal culture. The natural phytoplankton showed inhibition at sediment: water ratios of 10: 1; whereas the algal cultures showed both enhancement and inhibition. Evidently, the sediments are frequently toxic to the species tested except for the algal culture. The AFB assesses the mitigative and synergistic effects of contaminants and nutrients and being a conventional elutriate, is more realistic and potentially more acceptable than the chemical fractionation/nematode bioassay technique which essentially considers potential trace organic contaminant effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birkholz, D. A., G. Nelson, S. Daignault & L. Mulligan, 1983. Measurements of organics in petroleum refinery waste waters. Environmental Protection Services Report, Environment Canada, Edmonton, 83 p.
Blaise, C., N. Bermingham & R. Van Coillie, 1985. The integrated ecotoxicological approach to assessment of ecotoxicity. Wat. Qual. Bull. 10: 3–10, 60.
Cairns, J., 1985. Bioassays as they relate to water quality. Wat. Qual. Bull. 10: 17–20, 58, 59.
Cross, P. M., H. R. Hamilton & S. E. D. Charlton, 1984. The limnological characteristics of the Bow, Oldman and South Saskatchewan Rivers: 1. nutrient and water chemistry. Water Quality Control Branch, Alberta Environment, unpublished report.
Daniels, S. A., M. Munawar & C. I. Mayfield, 1989. An improved elutriation technique for testing the bioavailability of contaminants in sediments. In: M. Munawar, G. Dixon, S. I. Mayfield, T. Reynoldson and M. H. Sadar, Environmental Bioassay Techniques and Their Application. Hydrobiologia. (This volume).
International Joint Commission (I.J.C.), 1986. Evaluation of sediment bioassessment techniques. Report of the Dredging Subcommittee to the Great Lakes Water Quality Board, Windsor, Ontario, 123 pp.
Munawar, M., P. Stadelman & I. F. Munawar, 1974. Phytoplankton biomass, species composition and primary production at a nearshore and midlake station of Lake Ontario during IFYGL. Proc. 17th Conf Great Lakes Res., Internat. Assoc. Great Lakes Res. pp. 629–652.
Munawar, M. & I. F. Munawar, 1982. Phycological studies in Lakes Ontario, Erie, Huron and Superior. Can. J. Botany 60: 1837–1858.
Munawar, M., A. Mudroch, I. F. Munawar & R. L. Thomas, 1983. The impact of sediment-associated contaminants from the Niagara River mouth on various size assemblages of phytoplankton. J. Great Lakes Res. 9: 303–313.
Munawar, M., R. L. Thomas, H. Shear, P. McKee & A. Mudroch, 1984. An overview of sediment-associated contaminants and their bioassessment. Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1253 (i-vi): 1–136.
Munawar, M. & I. F. Munawar, 1987. Phytoplankton bioassays for evaluating toxicity of in situ sediment contaminants. In: R. L. Thomas, R. Evans, A. Hamilton, M. Munawar, T. Reynoldson & H. Sadar (Eds.), Proc. Internat. Workshop on Ecological Effects of In Situ Sediment Contaminants. Hydrobiologia. 149: 87–105.
Munawar, M., I. F. Munawar, P. E. Ross & C. Mayfield, 1987. Differential sensitivity of natural phytoplankton size assemblages to metal mixture toxicity. In M. Munawar (Ed.), Proc. Internat. Symp. on Phycology of Large Lakes of the World. Arch. Hydrobiol., Beih. Ergebn. Limnol., 25: 123–139.
Munawar, M., D. Gregor, S. A. Daniels & W. P. Norwood, 1989. A sensitive screening bioassay technique for the toxicological assessment of small quantities of contaminated bottom or suspended sediments. In: P. G. Sly & B. T. Hart (eds.), Sediment/Interactions. Hydrobiologia. (In press).
Munawar, M. & R. L. Thomas, (1989). Sediment toxicity testing in two areas of concern of the Laurentian Great Lakes: Toronto (Ontario) and Toledo (Ohio) harbours. In: P. G. Sly & B. T. Hart (eds.), Sediment/Interactions. Hydrobiologia. (In press).
Ongley, E. D. & D. Blachford, 1984. Tributary effects on main stream suspended sediment chemistry. Wat. Poll. Res. J. Can. 19: 37–46.
Ongley, E. D., D. A. Birkholz, J. Carey & M. R. Samoiloff, 1988. Is water a relevant sampling medium for toxic chemicals?: an alternative environmental sensing strategy. J. Envir. Qual. 17: 391–401.
Samoiloff, M. R., S. Schulz, Y. Jordan, K. Denich & E. Arnott, 1980. A rapid simple long-term toxicity assay for aquatic contaminants using the nematode Panagrellus redivivus. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 37: 1167–1174.
Samoiloff, M. R., J. Bell, D. A. Birkholz, G. R. B. Webster, E. G. Arnott, R. Pulak & A. Madrid, 1983. Combined bioassay-chemical fractionation scheme for the determination and ranking of toxic chemicals in sediments. Envir. Sci. Tech. 17: 329–334.
Samoiloff, M. R. & T. Bogaert, 1984. The use of nematodes in marine ecotoxicology. In: G. Persoone, E. Jaspers & C. Claus (Eds.), Ecotoxicological Testing for the Marine Environment, State University, Ghent and Inst. Mar. Scient. Res., Bredene, Belgium, vol. 1, 407–425.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregor, D.J., Munawar, M. Assessing toxicity of Lake Diefenbaker (Saskatchewan, Canada) sediments using algal and nematode bioassays. Hydrobiologia 188, 291–300 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00027795
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00027795