Abstract
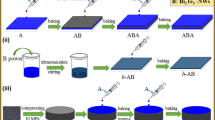
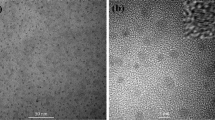
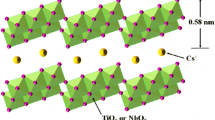
This paper reports on work developing an efficient distributed photovoltaic (PV) sensor using Buckypaper (BP) as working electrodes (WEs). BP is a thin sheet made from an aggregate of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with the advantages of good mechanical properties, high electrical conductivity and flexibility. These advantages enable sensor flexibility and significantly improve the charge transfer speed. In addition to BPs, quantum dots (QD) have recently drawn attention in photoconversion systems due to high absorption coefficient, tunable band gap and multiple exciton generation (MEG) effects. Herein, this work proposes to apply np-TiO2/mp-TiO2/CdS/CdSe/N719 hybrid structure to realize both MEG effects and multiple electron transmission paths. Previous research has confirmed that a liquid electrolyte and glass cladding were also components of the assembly process which additionally improve sensor efficiency. However, the reported efficiency (>5 %) of the solid state sensor is ten times that seen in previous work utilizing metal-cored wire-shaped liquid PV sensor. This article also discusses surface characterization of nanowires and the functionalization of solid-solid interfacial properties. Moreover, the distributed PV sensor construction is the basis of ongoing work towards embedded smart composites with intrinsic triboluminescent/mechanoluminescent (TL/ML) features.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farrar, C.R., Worden, K.: An introduction to structural health monitoring. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 365, 303–315 (2007)
Worden, K., Farrar, C.R., Manson, G., Park, G.: The fundamental axioms of structural health monitoring. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 463, 1639–1664 (2007)
Sage, I., Badcock, R., Humberstone, L., Geddes, N., Kemp, M., Bourhill, G.: Triboluminescent damage sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 8, 504–510 (1999)
Kirikera, G.R., Shinde, V., Schulz, M.J., Ghoshal, A., Sundaresan, M., Allemang, R.: Damage localisation in composite and metallic structures using a structural neural system and simulated acoustic emissions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 21, 280–297 (2007)
Walton, A.J.: Triboluminescence. Adv. Phys. 26, 887–948 (1977)
http://scienceworld.wolfram.com/physics/Triboluminescence.html
Chandra, B.P., Chandra, V.K., Jha, P.: Models for intrinsic and extrinsic fracto-mechanoluminescence of solids. J. Lumin. 135, 139–153 (2013)
Chandra, B.P., Zink, J.I.: Triboluminescence and the dynamics of crystal fracture. Phys. Rev. B 21, 816–826 (1980)
Aggarwal, M.D., Penn, B.G., Miller, J., Sadate, S., Batra, A.K.: Triboluminescent materials for smart optical damage sensors for space applications. In: CASI, NASA, (eds.) NASA/TM-2008-215410, M-1230 (2008)
Becquerel, A.E.: Mémoire sur les effets électriques produits sous l'influence des rayons solaires. Comptes Rendus des Séances Hebdomadaires 9, 561–567 (1839)
Einstein, A.: The Photoelectric Effect. Annalen der Physik, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, Berlin (1905)
Oregan, B., Gratzel, M.: A low-cost, high-efficiency solar-cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal Tio2 films. Nature 353, 737–740 (1991)
Gao, F., Wang, Y., Shi, D., Zhang, J., Wang, M.K., Jing, X.Y., Humphry-Baker, R., Wang, P., Zakeeruddin, S.M., Gratzel, M.: Enhance the optical absorptivity of nanocrystalline TiO(2) film with high molar extinction coefficient ruthenium sensitizers for high performance dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 10720–10728 (2008)
Yu, Q.J., Wang, Y.H., Yi, Z.H., Zu, N.N., Zhang, J., Zhang, M., Wang, P.: High-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells: the influence of lithium ions on exciton dissociation, charge recombination, and surface states. ACS Nano 4, 6032–6038 (2010)
Sauvage, F., Chen, D.H., Comte, P., Huang, F.Z., Heiniger, L.P., Cheng, Y.B., Caruso, R.A., Graetzel, M.: Dye-sensitized solar cells employing a single film of mesoporous TiO2 beads achieve power conversion efficiencies over 10%. ACS Nano 4, 4420–4425 (2010)
Nazeeruddin, M.K., Baranoff, E., Grätzel, M.: Dye-sensitized solar cells: a brief overview. Sol. Energy 85, 1172–1178 (2011)
Uddin, M.J., Dickens, T., Yan, J., Chirayath, R., Olawale, D.O., Okoli, O.I.: Solid state dye-sensitized photovoltaic micro-wires (DSPMs) with carbon nanotubes yarns as counter electrode: synthesis and characterization. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 108, 65–69 (2013)
Fan, X., Chu, Z.Z., Wang, F.Z., Zhang, C., Chen, L., Tang, Y.W., Zou, D.C.: Wire-shaped flexible dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Mater. 20, 592–595 (2008)
Zhang, S., Ji, C.Y., Bian, Z.Q., Liu, R.H., Xia, X.Y., Yun, D.Q., Zhang, L.H., Huang, C.H., Cao, A.Y.: Single-wire dye-sensitized solar cells wrapped by carbon nanotube film electrodes. Nano Lett. 11, 3383–3387 (2011)
Yan, J., Uddin, M.J., Dickens, T.J., Daramola, D.E., Olawale, D.O., Okoli, O.I.: Tailoring the efficiency of 3D wire-shaped photovoltaic cells (WPVCs) by functionalization of solid-liquid interfacial properties. Phys. Status Solidi A 210, 7 (2013)
Yan, J., Uddin, M.J., Dickens,T.J., Daramola, D.E., Okoli, O.I.: 3D wire-shaped dye-sensitized solar cells in solid state using carbon nanotube yarns with hybrid photovoltaic structure. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 1, (2014)
Future planes, cars may be made of ‘buckypaper’. Yahoo! Tech News. 2008-10-17. Retrieved 2008-10-18
Yoshida, H., Sugai, T., Shinohara Fabrication, H.: Purification, and characterization of double-wall carbon nanotubes via pulsed arc discharge. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 19908–19915 (2008)
Kukovecz, A., Smajda, R., Oze, M., Schaefer, B., Haspel, H., Konya, Z., Kiricsi, I.: Multiwall carbon nanotube films surface-doped with electroceramics for sensor applications. Phys. Status Solidi B Basic Solid State Phys. 245, 2331–2334 (2008)
Simien, D., Fagan, J.A., Luo, W., Douglas, J.F., Migler, K., Obrzut, J.: Influence of nanotube length on the optical and conductivity properties of thin single-wall carbon nanotube networks. ACS Nano 2, 1879–1884 (2008)
Pham, G.T., Park, Y.B., Wang, S.R., Liang, Z.Y., Wang, B., Zhang, C., Funchess, P., Kramer, L.: Mechanical and electrical properties of polycarbonate nanotube buckypaper composite sheets. Nanotechnology 19(32), 325705 (2008)
Park, J.G., Li, S., Liang, R., Zhang, C., Wang, B.: Structural changes and Raman analysis of single-walled carbon nanotube buckypaper after high current density induced burning. Carbon 46, 1175–1183 (2008)
Zhu, H.W., Wei, B.Q.: Assembly and applications of carbon nanotube thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 24, 447–456 (2008)
Whitby, R.L.D., Fukuda, T., Maekawa, T., James, S.L., Mikhalovsky, S.V.: Geometric control and tuneable pore size distribution of buckypaper and buckydiscs. Carbon 46, 949–956 (2008)
Enyashin, A.N., Ivanovskii, A.L.: Structural, elastic, and electronic properties of new superhard isotropic cubic crystals of carbon nanotubes. JETP Lett. 87, 321–325 (2008)
Wang, D., Song, P.C., Liu, C.H., Wu, W., Fan, S.S.: Highly oriented carbon nanotube papers made of aligned carbon nanotubes. Nanotechnology 19(7), 075609 (2008)
Han, J.T., Jeong, H.J., Lee, G.W.: Buckypaper from thin multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Proc. SPIE 7037, 703717 (2008)
Zhu, W., Zheng, J.P., Liang, R., Wang, B., Zhang, C., Walsh, S., Au, G., Plichta, E.J.: Highly-efficient buckypaper-based electrodes for PEMFC. Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells 8, Pts 1 and 2 16, 1615–1626 (2008)
Lee, Y.-L., Chi, C.-F., Liau, S.-Y.: CdS/CdSe co-sensitized TiO2 photoelectrode for efficient hydrogen generation in a photoelectrochemical cell. Chem. Mater. 22, 922–927 (2009)
Lee, Y.-L., Huang, B.-M., Chien, H.-T.: Highly efficient CdSe-sensitized TiO2 photoelectrode for quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell applications. Chem. Mater. 20, 6903–6905 (2008)
Uddin, M.J., Davies, B., Dickens, T.J., Okoli, O.I.: Self-aligned carbon nanotubes yarns (CNY) with efficient optoelectronic interface for microyarn shaped 3D photovoltaic cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 115, 166–171 (2013)
Yan, J., Uddin, M.J., Dickens, T.J., Okoli, O.I.: Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) enrich the solar cells. Sol. Energy 96, 239–252 (2013)
Olawale, D.O., Sullivan, G., Dickens, T., Tsalickis, S., Okoli, O.I., Sobanjo, J.O., Wang, B.: Development of a triboluminescence-based sensor system for concrete structures. Struct. Health Monit. 11, 139–147 (2012)
Olawale, D.O., Dickens, T., Uddin, M.J., Okoli, O.O.: Triboluminescence multifunctional cementitious composites with in situ damage sensing capability. Proc. SPIE 834538 (2012)
Ito, S., Ha, N.L.C., Rothenberger, G., Liska, P., Comte, P., Zakeeruddin, S.M., Pechy, P., Nazeeruddin, M.K., Gratzel, M.: High-efficiency (7.2%) flexible dye-sensitized solar cells with Ti-metal substrate for nanocrystalline-TiO2 photoanode. Chem. Commun. 38, 4004–4006 (2006)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation through grant ID CMMI-0969413 and Air Force Research Laboratory. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Zhiyong (Richard) Liang (High-Performance Materials Institute, Florida, USA) for providing both random and aligned Buckypapers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 The Society for Experimental Mechanics, Inc.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yan, J., Daramola, D.E., Antolinez, J.M., Okoli, N., Dickens, T.J., Okoli, O.I. (2016). Buckypaper-Cored Novel Photovoltaic Sensors for In-Situ Structural Health Monitoring of Composite Materials Using Hybrid Quantum Dots. In: Ralph, C., Silberstein, M., Thakre, P., Singh, R. (eds) Mechanics of Composite and Multi-functional Materials, Volume 7. Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21762-8_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21762-8_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-21761-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-21762-8
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)