Abstract
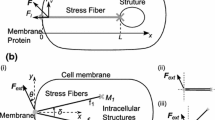
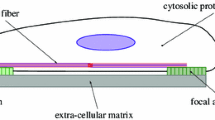
Hemodynamic forces affect endothelial cell morphology and function. In particular, circumferential cyclic stretch of blood vessels, due to pressure changes during the cardiac cycle, is known to affect the endothelial cell shape, mediating the alignment of the cells in the direction perpendicular to stretch. This change in cell shape proceeds a drastic reorganization at the internal level. The cellular scaffolding, mainly composed of actin filaments, reorganize in the direction which later becomes the cell’s long axis. How this external mechanical stimulus is ’sensed’ and transduced into the cell is still unknown. Here, we develop a mathematical model depicting the dynamics of actin filaments, and the influence of the cyclic stretch of the substratum based on the experimental evidence that external stimuli may be transduced inside the cell via transmembrane proteins which are coupled with actin filaments on the cytoplasmic side. Based on this view, we investigate two approaches describing the formulation of the transduction mechanisms involving the coupling between filaments and the membrane proteins. As a result, we find that the mechanical stimulus could cause the experimentally observed reorganization of the entire cytoskeleton simply by altering the dynamics of the filaments connected with the integral membrane proteins, as described in our model. Comparison of our results with previous studies of cytoskeletal dynamics reveals that the cytoskeleton, which, in the absence of the effect of stretch would maintain its isotropic distribution, slowly aligns with the precise direction set by the external stimulus. It is found that even a feeble stimulus, coupled with a strong internal dynamics, is sufficient to align actin filaments perpendicular to the direction of stretch.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alt, W. (1987). Mathematical models in actin-myosin interaction, in Nature and Function of Cytoskeletal Proteins in Motility and Transport, K. E. Wohlfarth-Bottermann (Ed.), Gustav Fisher: Stuttgart.
Ben-Avraham, D. and M. Tirion (1995). Dynamic and elastic properties of F-actin: A normal modes analysis. Biophys. J. 68, 1231–1245.
Burridge, K., G Nuckolls, C. Otey, F. Pavalko, K. Simon and C. Turner (1990). Actin-membrane interaction in focal adhesions. Cell Diff. Dev. 32, 337–342.
Civelekoglu, G. and L. Edelstein-Keshet (1994). Modeling the dynamics of F-actin in the cell. Bull. Math. Biol. 56, 587–616.
Davies, P. F. (1989). How do vascular endothelial cells respond to flow? NIPS 4, 22–25.
Davies, P. F., and K. A. Barbee (1994). Endothelial cell surface imaging: insights into hemodynamic force transduction. News Physiol. Sci. 9, 153–157.
Davies, P. F., and S. C. Tripathi (1993). Mechanical stress mechanisms of the cell, an endothelial paradigm. Circ. Res. 72, 239–245.
Dembo, M. (1989). Field theory of the cytoplasm. Com. Theor. Biol. 1–3, 159–177.
Dewey, C. F. Jr., S. R. Bussolari, and M. A. Gimbrone (1981). The dynamic response of vascular endotheliun cells to fluid shear stress. J. Biomech. Eng. 103, 177–185.
Dufort, P. A. and C. J. Lumsden (1993). Cellular automaton model of the actin cytoskeleton. Cell Mot. Cytoskel. 25, 87–104.
Fry, D. L. (1968). Acute vascular endothelial changes associated with increased blood velocity gradients. Circ. Res. 22, 165–197.
Girard, P. G. and R. M. Nerem (1995). Shear stress modulates endothelial cell morphology and F-actin organization through the regulation of focal adhesion-associated proteins. J. Cell Physiol. 163, 179–193.
Harrigan, T. P. (1990). Transduction of stress to cellular signals, in First World Congress in Biomech. University of C. San Diego. Vol. 2, p. 51.
Iba, T. and B. E. Sumpio (1991). Morphological response of human endothelial cells subjected to cyclic strain in vitro. Microvasc. Res. 42, 245–254.
Ingber, D. (1991). Integrins as mechanochemical transducers. Curr. Op. Cell Biol. 3, 841–848.
Ives, C. L., S. G. Eskin and L. V. McIntire (1986). Mechanical effects on endothelial cell morphology: in vitro assessment. In vivo Cell Dev. Biol. 22, 500–507.
Kim, D. W. A. I. Gotlieb and B. L. Langille (1989). In vivo modulation of endothelial F-actin microfilaments by experimental alterations in shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 9, 439–445.
Kishino, A. and T. Yanagida (1988). Force measurements by micromanipulation of a single actin filament by glass needles. Nature 334, 74–76.
Kojima, H., A. Ishijima and T. Yanagida (1994). Direct measurements of stiffness of single actin filaments with and without tropomyosin by in vitro nanomanipulation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 91, 12962–12966.
Ku, D. N., C. K. Giddens, C. K. Zarins and S. Glagov (1985). Pulsative flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Arteriosclerosis. 5, 293–302.
Kusumi, A., S. Yasushi and Y. Mutsuya (1993). Confined lateral diffusion of membrane receptors as studied by single particle tracking. Effects of calcium-induced differentiation in cultured epithelial cells. Biophys. J. 65, 2021–2040.
Levesque, M. J., D. Liepsch, S. Moravec and R. M. Nerem (1986). Correlation of endothelial cell shape and wall shear stress in a stenosed dog aorta. Arteriosclerosis 6, 220–229.
Meyer, R. K. and U. Aebi (1990). Bundling of actin filaments by alpha-actin depends on its molecular length. J. Cell Biol. 110, 2013–2024.
Moore, J. E. Jr., E. Brki, A. Suciu, S. Zhao, M. Burnier, H. R. Brunner and J. J. Meister (1994). A device for subjecting vascular endothelial cells to both fluid shear stress and circumferential cyclic stretch. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 22, 416–422.
Morita, T., H. Kurihara, K. Maemura, M. Yoshizumi, R. Nagai and Y. Yazaki (1994). Role of Ca2+ and protein kinase C in shear stress-induced actin depolymerization and endothelin 1 gene expression. Circ. Res. 75, 630–636.
Ookawa, K., M. Sato and N. Ohshima (1993). Time course changes in cytoskeletal structures of cultured endothelial cells. Front. Med. Biol. Eng. 5, 121–125.
Osol, G. (1995). Mechanotransduction by vascular smooth muscle. J. Vasc. Res. 32, 275–292.
Oster, G. F. and G. M. Odell. (1984). Mechanics of cytogels I: oscillations in physarum. Cell Motil. 4, 464–503.
Petrov, A. G. and P. N. R. Usherwood (1994). Mechanosensitivity of cell membranes. Eur. Biophys. J. 23, 1–19.
Pollard, T. D. and J. A. Cooper (1986). Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 55, 987–1035.
Resnick, N., T., Collins, W., Atkinson, D. T. Bonthron, C. F. Jr. Dewey and M. A. Gimbrone (1993). Platelet-derived growth factor B chain promoter contains a cis-acting fluid shear-stress-responsive element. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 4591–4595.
Sachs, F. (1988). Mechanical transduction in biological systems. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 6, 141–169.
Satcher, R. L. Jr. (1993). A mechanical model of vascular endothelium, PhD Thesis, MIT, Cambridge, U.S.A.
Satcher, R. L. Jr and F. Dewey, Jr (1996). Theoretical estimates of mechanical properties of the endothelial cell cytoskeleton. Biophys. J. 71, 109–118.
Schmidt, C. E., T. Chen and D. A. Lauffenburger (1994). Simulation of integrin-cytoskeletal interactions in migrating fibroblasts. Biophys. J. 67, 461–474.
Schmidt, C. E., A. F. Horwitz, D. A. Lauffenburger and M. P. Sheetz (1993). Integrin-cytoskeletal interactions in migrating fibroblasts are dynamic, asymmetric, and regulated. J. Cell Biol. 123, 977–991.
Shen, J., F. W. Luscinskas, A. Connolly, C. F. Dewey Jr and M. A. Gimbrone Jr (1992). Fluid shear stress modulates cytosolic free calcium in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 262, C384–C390.
Sherratt, J. A. and J. Lewis (1993). Stress-induced alignment of actin filaments and the mechanics of cytogel. Bull. Math. Biol. 55, 637–654.
Suciu, A., G. Civelekoglu, Y. Tardy and J. J. Meister (1997). A model for the alignment of actin filaments in endothelial cells subjected to fluid shear stress. Bull. Math. Biol. in press.
Wang, N., J. P. Butler and D. E. Ingber (1993). Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science 260, 1124–1127.
Zarins C. K., D. P. Giddens, B. K. Bharadvaj, V. S. Sottiurai, R. F. Mabon and S. Glagov (1983). Carotid bifurcation atherosclerosis: quantitative correlation of plaque localization with flow velocity profiles and wall shear stress. Circ. Res. 53, 502–514.
Zhao, S., A. Suciu, T. Ziegler, J. E. Jr. Moore, E. Brki, J. J. Meister and H. R. Brunner (1995). Effects of combined fluid shear stress and cyclic circumferential stretch on the morphology and cytoskeleton of vascular endothelial cells. Arterio. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 15, 1781–1786.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Civelekoglu, G., Tardy, Y. & Meister, JJ. Modeling actin filament reorganization in endothelial cells subjected to cyclic stretch. Bull. Math. Biol. 60, 1017–1037 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1006/S0092-8240(98)90001-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/S0092-8240(98)90001-5