Abstract
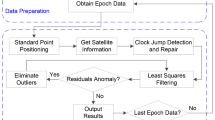
The tracking loop performance of low-cost receiver is poor, and the risk of satellite signal loss increases, resulting in frequent carrier phase cycle slip. The conventional satellite-by-satellite cycle slip processing method initializes the carrier phase ambiguity with cycle slip, decreases precise point positioning performance, and may lead to re-initialization. To avoid the degradation of positioning performance and even PPP re-initialization caused by cycle slip processing of the low-cost receiver, we proposed a method of partial cycle slip fixing based on the time-differenced model for low-cost receiver. In this method, the cycle slip subset is selected by quality control, and then the cycle slip is estimated and fixed by the time-differenced observation. The proposed method is verified with collected BDS and GPS dual-frequency data using a u-blox low-cost receiver, and the results show that the method adopted in this paper can correctly fix the cycle slip and achieve rapid PPP re-initialization, and improve the continuity of PPP high-precision positioning results of the low-cost receiver.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zumberge JF et al (1997) Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J Geophys Res Solid Earth
Ding WW, Ou JK, Li ZS et al (2014) Instantaneous re-initialization method of real time kinematic PPP by adding ionospheric delay constraints. Chin J Geophys (in Chinese) 57(6):1720–1731
Dai Z, Zhang K, Liu P et al (2021) Cycle slip repair strategy of low-cost GNSS receivers. Navig, Position Timing 8(6):125–130
Xiaohong Z, Xingxing L (2012) Instantaneous re-initialization in real-time kinematic PPP with cycle slip fixing. GPS Solutions 16(3):315–327
Li X et al (2013) A method for improving uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixing in real-time precise point positioning. J Geodesy 87:405–416
Zhao QL et al (2015) Real-time detection and repair of cycle slips in triple-frequency GNSS measurements. GPS Solutions 19(3):381–391
Yang F et al (2019) Ionosphere-constrained triple-frequency cycle slip fixing method for the rapid re-initialization of PPP 19(1):117
Chen K et al (2021) An improved TDCP-GNSS/INS integration scheme considering small cycle slip for low-cost land vehicular applications. Meas Sci Technol 32(5):055006
Li X et al (2022) Single-frequency cycle slip detection and repair based on Doppler residuals with inertial aiding for ground-based navigation systems. GPS Solutions 26(4):116
Banville S, Langley RB (2009) Improving real-time kinematic PPP with instantaneous cycle-slip correction. In: Ion GNSS
Xiao G et al (2017) Improved time-differenced cycle slip detect and repair for GNSS undifferenced observations. GPS Solutions 22(1):6
Zhao L, Zhu K, Zhang S (2019) Study on integrated cycle slip handling using GPS/Galileo combined observations. GPS Solutions 23(3):77
Zhang W, Wang J (2021) A real-time cycle slip repair method using the multi-epoch geometry-based model. GPS Solutions 25(2):60
Li T (2016) Real-time cycle slip detection and repair for network multi-GNSS, Multi-frequency data processing
Li D et al (2021) A new cycle-slip repair method for dual-frequency BDS against the disturbances of severe ionospheric variations and pseudoranges with large errors 13(5):1037
Acknowledgements
This research was jointly funded by the National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2021YFB3901300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 62003109, 61773132, 61633008, 61803115), the 145 High-tech Ship Innovation Project sponsored by the Chinese Ministry of Industry and In-formation Technology, the Heilongjiang Province Research Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (No. YQ2020F009), and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (Nos. 3072019CF0401, 3072020CFT0403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Aerospace Information Research Institute
About this paper
Cite this paper
Luo, F., Zhao, L., Yang, F., Sun, Z., Zhang, J. (2024). Analysis of Rapid Re-initialization Performance of Precise Point Positioning for Low-Cost Receiver. In: Yang, C., Xie, J. (eds) China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC 2024) Proceedings. CSNC 2024. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1094. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6944-9_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6944-9_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-6943-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-6944-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)