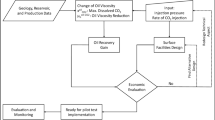
Abstract
Endogenous microbial oil recovery technology has attracted more attention because of its strong adaptability, good compatibility with reservoir and low cost. However, at present, the physical simulation experimental method of microbial oil displacement is quite different from the actual reservoir, and the evaluation method needs to be improved urgently. Therefore, this paper conducted a basic theoretical study on the influencing factors of endogenous microbial model experiment. The computer-aided simulation experiment of endogenous microbial oil displacement is a computer model that simulates the behavior of microorganisms in oil reservoirs. The purpose of this model is to study the effects of different conditions on microorganisms and petroleum hydrocarbons (oil). It can also be used to design remediation strategies for contaminated sites with high microbial activity and low dissolved organic carbon content.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, J., Ying, F.: Research on the construction of virtual simulation experiment teaching center based on computer-aided civil engineering in colleges and universities. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1744(3), 032115 (6p.) (2021)
Chen, L., Li, W., Li, Z.L., et al.: Experiment and simulation analysis of the pressure carrying capacity of ×80 pipe with metal loss defect on the girth weld. Mater. Sci. Forum 1035, 813–818 (2021)
Yu, V.S., Popov, E.A.: Computer-aided simulation of high-dimensional event-continuous systems. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1791(1), 012087 (5p.) (2021)
Langreck, J., Wong, H., Hernandez, A., et al.: Modeling and simulation of future capabilities with an automated computer-aided wargame. J. Defense. Model. Simul. Appl. Methodol. Technol. 18(4), 407–416 (2021)
Moba, B., Akt, C., Rg, D.: Sustainable biorefinery process synthesis, design, and simulation: Systematic computer-aided methods and tools (2022)
Lewandowski, G.A., Klimczuk, T., et al.: Towards Computer-Aided Graphene Covered TiO2-Cu/(CuxOy) Composite Design for the Purpose of Photoinduced Hydrogen Evolution (2021)
Wang, Y., Nault, C., Givens, M., et al.: Computer-Aided Engineering Toolkit For Simulated Testing of Pressure-Controlling Component Designs, US20210342506A1 (2021)
Zhang, J., Lee, C., Farner, M.: Using computer-aided image processing to estimate chemical composition of igneous rocks: a potential tool for large-scale compositional mapping. Solid Earth Sci. 6(1), 21–26 (2021)
Ava, A., Vv, A., Sb, B., et al.: Computer aided cooling curve analysis (CACCA) of ADC-12 alloy (2021)
Oso, M., Regueira, A., Hospido, A., et al.: Fostering the valorization of organic wastes into carboxylates by a computer-aided design tool. Waste Manage. 142, 101–110 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ze, W. (2023). Computer Aided Simulation Experiment of Endogenous Microbial Oil Displacement. In: Hung, J.C., Chang, JW., Pei, Y. (eds) Innovative Computing Vol 2 - Emerging Topics in Future Internet. IC 2023. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1045. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2287-1_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2287-1_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2286-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2287-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)