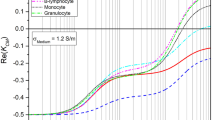
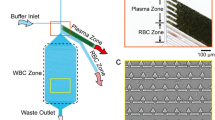
Abstract
The isolation of Red Blood Cells (RBCs) has become a broad area of research in recent times. The early segregation of RBCs from the blood prevents them from lysis. The segregation of RBCs using traditional techniques like centrifugation has become outdated due to the usage of bulky equipment. This paper reviews the functions of RBCs, the age-old techniques that were practically used to distinguish RBCs, and their drawbacks. The assessment of microfluidic devices which are prevalently used in present-day diagnostics that are promised to replace the bottlenecks posed by the traditional methods is also presented. This review aims to project the recent advancements in microfluidics, their applications, and the segregation of microfluidic particles using them. The modern approaches that can separate RBCs virtually using electroosmotic phenomena like di-electrophoresis are also reviewed. The present scenarios for the separation of RBCs with a FEM tool computer-aided design for virtual analysis are also discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waugh A, Grant A (2014) Ross & Wilson anatomy and physiology in health and illness E-book. Elsevier Health Sciences
Pal GK, Pal P, Nanda N (2016) Comprehensive textbook of medical physiology-two volume set. JP Medical Ltd
Pearson HA (1967) Life-span of the fetal red blood cell. J Pediatr 70(2):166–171
Turrigiano G (2007) Homeostatic signaling: the positive side of negative feedback. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17(3):318–324
Bunn HF (2013) Erythropoietin. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3(3):a011619
Saba TM (2018) Fibronectin: role in phagocytic host defense and lung vascular integrity. In: Fibronectin in Health and Disease. pp 49–68
Weaver L, Hamoud AR, Stec DE, Hinds TD Jr (2018) Biliverdin reductase and bilirubin in hepatic disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 314(6):G668–G676
Mitra S, Rahman MH, Prince HA, Rozin EH (2020) Numerical investigation on dielectrophoresis blood cell separation for different applied voltage and red blood cell size. In: 2020 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP). IEEE, pp 730–733
Danon D, Marikovsky Y (1964) Determination of density distribution of red cell population. J Lab Clin Med 64(4):668–674
Piomelli S, Lurinsky G, Wasserman LR (1967) The mechanism of red cell aging. I. Relationship between cell age and specific gravity evaluated by ultracentrifugation in a discontinuous density gradient. J Lab Clin Med 69(4):659–674
Corash LM, Piomelli S, Chen HC, Seaman C, Gross E (1974) Separation of erythrocytes according to age on a simplified density gradient. J Lab Clin Med 84(1):147–151
Vettore L, De Matteis MC, Zampini P (1980) A new density gradient system for the separation of human red blood cells. Am J Hematol 8(3):291–297
Marikovsky Y, Danon D (1971) Agglutination of young and old human red cells by blood group antibodies. Vox Sang 20(2):174–177
Bartos HR, Desforges JF (1967) Enzymes as erythrocyte age reference standards. Am J Med Sci 254(6):862–865
Walter H, Krob EJ, Garza R (1968) Factors in the partition of red blood cells in aqueous dextran-polyethylene glycol two-phase systems. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gen Subj 165(3):507–514
Costa JAV, de Morais MG (2014) An open pond system for microalgal cultivation. In: Biofuels from algae. Elsevier, pp 1–22
Rigas DA, Koler RD (1961) Ultracentrifugal fractionation of human erythrocytes on the basis of cell age. J Lab Clin Med 58:242–246
Boyd EM, Thomas DR, Horton BF, Huisman THJ (1967) The quantities of various minor hemoglobin components in old and young human red blood cells. Clin Chim Acta 16(3):333–341
Pertoft H, Bäck O, Lindahl-Kiessling K (1968) Separation of various blood cells in colloidal silica-polyvinylpyrrolidone gradients. Exp Cell Res 50(2):355–368
Desimone J, Kleve L, Shaeffer J (1974) Isolation of a reticulocyte-rich fraction from normal human blood on renografin gradients. J Lab Clin Med 84(4):517–524
Goebel KM, Goebel FD, Schubotz R, Schneider J (1977) Red cell metabolic and membrane features in haemolytic anaemia of alcoholic liver disease (Zieve’s syndrome). Br J Haematol 35(4):573–585
Danon D, Marikovsky Y (1961) Difference de charge electrique de surface entre erythrocytes jeunes et ages. Comptes Rendus Hebd Seances L Acad Sci 253(12):1271
Mantegazza A, Clavica F, Obrist D (2020) In vitro investigations of red blood cell phase separation in a complex microchannel network. Biomicrofluidics 14(1):014101
Dennison C, Lovrien R (1997) Three phase partitioning: concentration and purification of proteins. Protein Expr Purif 11(2):149–161
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442(7101):368–373
Weibel DB, Whitesides GM (2006) Applications of microfluidics in chemical biology. Curr Opin Chem Biol 10(6):584–591
Beebe DJ, Mensing GA, Walker GM (2002) Physics and applications of microfluidics in biology. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 4(1):261–286
Groisman A, Lobo C, Cho H, Campbell JK, Dufour YS, Stevens AM, Levchenko A (2005) A microfluidic chemostat for experiments with bacterial and yeast cells. Nat Methods 2(9):685–689
Balagaddé FK, You L, Hansen CL, Arnold FH, Quake SR (2005) Long-term monitoring of bacteria undergoing programmed population control in a microchemostat. Science 309(5731):137–140
Lee H, Purdon AM, Chu V, Westervelt RM (2004) Controlled assembly of magnetic nanoparticles from magnetotactic bacteria using microelectromagnets arrays. Nano Lett 4(5):995–998
Weston AD, Hood L (2004) Systems biology, proteomics, and the future of health care: toward predictive, preventative, and personalized medicine. J Proteome Res 3(2):179–196
Reyes DR, Iossifidis D, Auroux PA, Manz A (2002) Micro total analysis systems. 1. Introduction, theory, and technology. Anal Chem 74(12):2623–2636
Gravesen P, Branebjerg J, Jensen OS (1993) Microfluidics-a review. J Micromech Microeng 3(4):168
Whitesides G, Stroock A (2001) Flexible methods for microfluidics. Phys Today 54:42–48
Jakeway SC, de Mello AJ, Russell EL (2000) Miniaturized total analysis systems for biological analysis. Fresenius J Anal Chem 366(6):525–539
Ho CM, Tai YC (1998) Micro-electro-mechanical-systems (MEMS) and fluid flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 30:579–612
Becker H, Gärtner C (2000) Polymer microfabrication methods for microfluidic analytical applications. ELECTROPHORESIS Int J 21(1):12–26
Brody JP, Yager P, Goldstein RE, Austin RH (1996) Biotechnology at low Reynolds numbers. Biophys J 71(6):3430–3441
Purcell EM (1977) Life at low Reynolds number. Am J Phys 45(1):3–11
Flow VF (1991) Frank M. White
Brody JP, Yager P (1997) Diffusion-based extraction in a microfabricated device. Sens Actuat A 58(1):13–18
Hatch A, Kamholz AE, Hawkins KR, Munson MS, Schilling EA, Weigl BH, Yager P (2001) A rapid diffusion immunoassay in a T-sensor. Nat Biotechnol 19(5):461–465
Yeo LY, Chang HC, Chan PP, Friend JR (2011) Microfluidic devices for bioapplications. Small 7(1):12–48
Ren K, Zhou J, Wu H (2013) Materials for microfluidic chip fabrication. Acc Chem Res 46(11):2396–2406
Friend J, Yeo L (2010) Fabrication of microfluidic devices using polydimethylsiloxane. Biomicrofluidics 4(2):026502
Catarino SO, Rodrigues RO, Pinho D, Miranda JM, Minas G, Lima R (2019) Blood cells separation and sorting techniques of passive microfluidic devices: from fabrication to applications. Micromachines 10(9):593
Haeberle S, Zengerle R (2007) Microfluidic platforms for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 7(9):1094–1110
Rife JC, Bell MI, Horwitz JS, Kabler MN, Auyeung RCY, Kim WJ (2000) Miniature valveless ultrasonic pumps and mixers. Sens Actuat A 86(1–2):135–140
Yc F (1997) Biomechanics: circulation
Roselli RJ, Diller KR (2011) Biotransport: principles and applications. Springer, New York, p 139
Mohamed H (2012) Use of microfluidic technology for cell separation. In: Blood cell-an overview of studies in hematology, pp 195–226
Shields CW IV, Reyes CD, López GP (2015) Microfluidic cell sorting: a review of the advances in the separation of cells from debulking to rare cell isolation. Lab Chip 15(5):1230–1249
Kersaudy-Kerhoas M, Sollier E (2013) Micro-scale blood plasma separation: from acoustophoresis to egg-beaters. Lab Chip 13(17):3323–3346
Bharat et al (2020) Modelling of dielectrophoretic separation platelets from red blood cells. ISSN 2394–5125
Pethig R (2010) Dielectrophoresis: Status of the theory, technology, and applications. Biomicrofluidics 4(2):022811
Khoshmanesh K, Nahavandi S, Baratchi S, Mitchell A, Kalantar-zadeh K (2011) Dielectrophoretic platforms for bio-microfluidic systems. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):1800–1814
Demircan Y, Özgür E, Külah H (2013) Dielectrophoresis: applications and future outlook in point of care. Electrophoresis 34(7):1008–1027
Li M, Li WH, Zhang J, Alici G, Wen W (2014) A review of microfabrication techniques and dielectrophoretic microdevices for particle manipulation and separation. J Phys D Appl Phys 47(6):063001
Jubery TZ, Srivastava SK, Dutta P (2014) Dielectrophoretic separation of bioparticles in microdevices: a review. Electrophoresis 35(5):691–713
Sahin O, Kosar A, Yapici MK (2021) Modeling the dielectrophoretic separation of red blood cells (RBCs) from B-Lymphocytes (B-Cells). In: 2021 43rd annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine & biology society (EMBC). IEEE, pp 1238–1241
Salahi A, Honrado C, Rane A, Caselli F, Swami NS (2022) Modified red blood cells as multimodal standards for benchmarking single-cell cytometry and separation based on electrical physiology. Anal Chem 94(6):2865–2872
Praveenkumar S, Srigitha SN, Dinesh RG, Ramesh R (2020) Computational modeling of dielectrophoretic microfluidic channel for simultaneous separation of red blood cells and platelets. Curr Signal Transduct Ther 15(3):243–251
Shirmohammadli V, Manavizadeh N (2019) Application of differential electrodes in a dielectrophoresis-based device for cell separation. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 66(9):4075–4080
Shamloo A, Parast FY (2019) Simulation of blood particle separation in a trapezoidal microfluidic device by acoustic force. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 66(3):1495–1503
Zhao S, Wu M, Yang S, Wu Y, Gu Y, Chen C, Huang TJ (2020) A disposable acoustofluidic chip for nano/microparticle separation using unidirectional acoustic transducers. Lab Chip 20(7):1298–1308
Zhang Y, Chen X (2020) Dielectrophoretic microfluidic device for separation of red blood cells and platelets: a model-based study. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(2):1–11
Chiriac E, Avram M, Bălan C (2020) Dielectrophoretic separation of circulating tumor cells and red blood cells in a microfluidic device. In: 2020 International semiconductor conference (CAS). IEEE, pp 211–214
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College for providing the necessary infrastructure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Turaka, S. et al. (2023). A Review on Recent Trends in the Segregation of Red Blood Cells Using Microfluidic Devices. In: Guha, K., Dutta, G., Biswas, A., Srinivasa Rao, K. (eds) MEMS and Microfluidics in Healthcare. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 989. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8714-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8714-4_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-8713-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-8714-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)