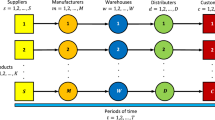
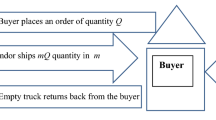
Abstract
The supply chain inventory planning is well studied and analyzed in the literature considering various costs and other factors. However, social factor is largely overlooked although, it is important like cost factors which generally come from sourcing, production, storage and distribution. In the current work, a mathematical model for supply chain inventory was developed with four objectives (i.e., cost, local development, steadiness in employment and investment in green technology). The first objective is related to the total cost, which includes mostly inventory, manufacturing, and re-manufacturing related costs. The other two objectives are related to social aspects which focus on improvement in local development and steadiness in employment. The fourth objective is related to environmental aspect which focuses on the right time to invest in environmentally friendly machinery and technologies. The proposed model has the capability to obtain the optimal number of products to be manufactured and re-manufactured, number of inventories, number of employees to recruit and lay-off within a certain region in each quarter of the year, and decision on time to invest in green technology or pay govt. penalty, considering the upcoming demand in each quarter. The weighted sum method is applied to solve the multi-objective optimization problem.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal S, Singh RK, Murtaza Q (2015) A literature review and perspectives in reverse logistics. Resour Conserv Recycl 97:76–92
Becerra P, Mula J, Sanchis R (2022) Sustainable inventory management in supply chains: trends and further research. Sustainability 14:2613
Berning A, Venter C (2015) Sustainable supply chain engagement in a retail environment. Sustainability 7(5):6246–6263
Bocken N, Short SW, Rana P, Evans S (2014) A literature and practice review to develop sustainable business model archetypes. J Clean Prod 65:42–56
Brandenburg M, Govindan K, Sarkis J, Seuring S (2014) Quantitative models for sustainable supply chain management: developments and directions. Eur J Oper Res 233(2):299–312
Chen CK, Weng TC, Lo CC (2016) Optimal replenishment quantity for new products and return rate of used products for a retailer. Appl Math Model 40(23–24):9754–9766
Chiu SW, Tseng C-T, Wu M-F, Sung P-C (2016) Multi-item EPQ model with scrap, rework and multi-delivery using common cycle policy. J Appl Res Technol 12:615–622
Chiu Y-SP, Wu M-F, Chiu SW, Chang H-H (2015) A simplified approach to the multi-item economic production quantity model with scrap, rework and multi-delivery. J Appl Res Technol 13:472–476
Craig RC, Easton PL (2011) Sustainable supply chain management: evolution and future directions. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 41(1):46–62
Dakov I, Novkov S (2008) Sustainable supply chain management–scope, activities and interrelations with other concepts. In: Proceeding of 5th international conference on business and management 2008, pp 16–17
Fahimnia B, Sarkis J, Eshragh A (2015) A tradeoff model for green supply chain planning: a leanness-versus-greenness analysis. Omega 54:173–190
Galpin T, Whittington JL, Bell G (2015) Is your sustainability strategy sustainable? Creating a culture of sustainability. Corp Gov 15(1):1–17
Ghadge A, Dani S, Kalawsky R (2012) Supply chain risk management: present and future scope. Int J Logist Manag 23(3):313–339
Ghadimi P, Azadnia AH, Heavey C, Dolgui A, Can B (2016) A review on the buyer–supplier dyad relationships in sustainable procurement context: past, present and future. Int J Prod Res 54(5):1443–1462
Ghadimi P, Dargi A, Heavey C (2017) Making sustainable sourcing decisions: practical evidence from the automotive industry. Int J Logist 20(4):297–321
Ghadimi P, Wang C, Lim MK (2019) Sustainable supply chain modeling and analysis: Past debate, present problems and future challenges. Resour Conserv Recycl 140:72–84
Jindal A, Sangwan KS (2017) Multi-objective fuzzy mathematical modelling of closed-loop supply chain considering economical and environmental factors. Ann Oper Res 257(1):95–120
Kannan G, Soleimani H (2017) A review of reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chains: a journal of cleaner production focus. J Clean Prod 142:371–384
Pagell M, Shevchenko A (2014) Why research in sustainable supply chain management should have no future. J Supply Chain Manag 50(1):44–55
Saffari H, Makui A, Mahmoodian V, Pishvaee MS (2015) Multi-objective robust optimization model for social responsible closed-loop supply chain solved by nondominated sorting genetic algorithm. J Ind Syst Eng 8(3):42–58
Sarkis J, Zhu Q (2018) Environmental sustainability and production: taking the road less travelled. Int J Prod Res 56(1–2):743–759
Seuring S, Müller M (2008) From a literature review to a conceptual framework for sustainable supply chain management. J Clean Prod 16(15):1699–1710
Seuring S (2013) A review of modeling approaches for sustainable supply chain management. Decis Support Syst 54(4):1513–1520
Soleymanfar VR, Makui A, Taleizadeh AA, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2022) Sustainable EOQ and EPQ models for a two-echelon multi-product supply chain with return policy. Environ Dev Sustain 24:5317–5343
Validi S, Bhattacharya A, Byrne PJ (2015) A solution method for a two-layer sustainable supply chain distribution model. Comput Oper Res 54:204–217
Zarbakhshnia N, Kannan D, Mavi RK, Soleimani H (2020) A novel sustainable multi-objective optimization model for forward and reverse logistics system under demand uncertainty. Ann Oper Res 295(2):843–880
Zarbakhshnia N, Soleimani H, Goh M, Razavi SS (2019) A novel multi-objective model for green forward and reverse logistics network design. J Clean Prod 208:1304–1316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Dhingra, A., Poonia, V., Kulshrestha, R. (2022). A Multi-objective Mathematical Model for Socially Responsible Supply Chain Inventory Planning. In: Sharma, D.K., Jain, M. (eds) Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence for Inventory and Supply Chain Management. Inventory Optimization. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6337-7_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6337-7_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-6336-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-6337-7
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)