Abstract
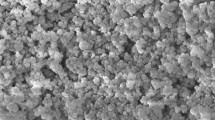
Friction is one of major concern in mechanical movement while the lubricant is one of solution to counter it. The additive of nanoparticles in lubricant may improve its tribological performance. The current study focusses on the effect of SiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles as additive in PVE lubricant. The new solution namely nanolubricant was prepared at three different concentrations. The nanolubricants were characterized using TEM and its stability was evaluated up to 30 days. Four-ball method was used to determine the effect of nanoparticle concentration on coefficient of friction (COF) and wear scar diameter (WSD). The results reveal that nanoparticle additive provide better COF at low volume concentration. The COF for nanolubricant at volume concentration less than 0.010% for TiO2 and less than 0.005% for SiO2 attained lower than pure PVE lubricant. The results for WSD also were in agreement with the trend of COF. Therefore, the nanolubricant has potential to provide better friction coefficient performance for lubrication application.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang H, Wang YM (2012) Tribological Performance of AlN nanoparticles as lubricating oil additive. Adv Res Mater Eng Architectural Eng Informatization 366:238–242
Azmi WH, Sharif MZ, Yusof TM, Mamat R, Redhwan AAM (2017) Potential of nanorefrigerant and nanolubricant on energy saving in refrigeration system—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 69:415–428
Karthick M, Karuppiah SK, Kanthan V (2020) Performance investigation and exergy analysis of vapor compression refrigeration system operated using r600a refrigerant and nanoadditive compressor oil. Therm Sci 24(5A):2977–2989
Kotia A, Rajkhowa P, Rao GS, Ghosh SK (2018) Thermophysical and tribological properties of nanolubricants: a review. Heat Mass Transf 54(11):3493–3508
Kumar R, Singh DK, Chander S (2020) An experimental approach to study thermal and tribology behavior of LPG refrigerant and MO lubricant appended with ZnO nanoparticles in domestic refrigeration cycle. Heat Mass Transf 56(7):2303–2311
Marcucci Pico DF, da Silva LRR, Hernandez Mendoza OS, Bandarra Filho EP (2020) Experimental study on thermal and tribological performance of diamond nanolubricants applied to a refrigeration system using R32. Int J Heat Mass Transf 152:119493
Idemitsu Kosan CL (2020) Characteristics of Daphne hermetic oil. https://www.idemitsu.com/business/lube/pve/daphne.html. Accessed 1 Jan (2020)
Motozawa M, Makida N, Fukuta M (2018) Experimental study on physical properties of CuO—PVE Nano-oil and its mixture with refrigerant. Int Compressor Eng Conf. Purdue
Redhwan AAM, Azmi WH, Sharif MZ, Mamat R, Samykano M, Najafi G (2019) Performance improvement in mobile air conditioning system using Al2O3/PAG nanolubricant. J Therm Anal Calorim 135(2):1299–1310
Sanukrishna SS, Jose Prakash M (2018) Experimental studies on thermal and rheological behaviour of TiO2-PAG nanolubricant for refrigeration system. Int J Refrig 86:356–372
Zawawi NNM, Azmi WH, Sharif MZ, Najafi G (2019) Experimental investigation on stability and thermo-physical properties of Al2O3-SiO2/PAG nanolubricants with different nanoparticle ratios. J Therm Anal Calorim 135(2):1243–1255
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Universiti Malaysia Pahang for financial supports given under RDU213302 and additional financial support under Postgraduate Research grant PGRS2003202. The authors also thank the research team from Centre for Research in Advanced Fluid and Processes (Pusat Bendalir) and Advanced Automotive Liquids Laboratory (AALL), who provided insight and expertise that greatly assisted in the present research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ismail, M.F., Wan Hamzah, W.A. (2023). Tribological Performance Effect of SiO2 and TiO2 Nanoparticles as Lubricating Oil Additives. In: Johari, N.H., Wan Hamzah, W.A., Ghazali, M.F., Setiabudi, H.D., Kumarasamy, S. (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd Energy Security and Chemical Engineering Congress. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4425-3_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4425-3_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-4424-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-4425-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)