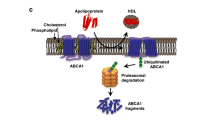
Abstract
In previous chapters, we know that high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) could act at multiple cell lines and then trigger intracellular molecular pathway to prevent several metabolic diseases. Besides the classic genes regulating cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport (RCT), microRNAs (miRNAs) could also affect HDLs biogenesis, metabolism, and functions. This chapter summarizes the miRNAs, which regulate HDLs functions in table. In addition, HDLs are good vectors for miRNAs. They could carry miRNAs in circulation and take them into several cells such as macrophages and endothelial cells. Complete understanding of the miRNAs associated with HDL regulation would give us broader insights to prevent and treat metabolic diseases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Kristo F, Li Y, Shioda T, Cohen DE, Gerszten RE, Näär AM (2010) MicroRNA-33 and the SREBP host genescooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis. Science 328(5985):1566–1569
Rayner KJ, Sheedy FJ, Esau CC, Hussain FN, Temel RE, Parathath S, van Gils JM, Rayner AJ, Chang AN, Suarez Y, Fernandez-Hernando C, Fisher EA, Moore KJ (2011) Antagonism of miR-33 in mice promotes reverse cholesterol transport and regression of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest 121(7):2921–2931
Hoekstra M, van der Sluis RJ, Kuiper J, Van Berkel TJC (2012) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an altered hepatocyte microRNA profile in LDL receptor knockout mice. J Nutr Biochem 23(6):622–628
Meiler S, Baumer Y, Toulmin E, Seng K, Boisvert WA (2015) MicroRNA 302a is a novel modulator of cholesterol homeostasis and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35(2):323–331
Ramirez CM, Dávalos A, Goedeke L, Salerno AG, Warrier N, Cirera-Salinas D, Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C (2011) MicroRNA-758 regulates cholesterol efflux through posttranscriptional repression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(11):2707–2714
Liang B, Wang X, Song X, Bai R, Yang H, Yang Z, Xiao C, Bian Y (2017) MicroRNA-20a/b regulates cholesterol efflux through post-transcriptional repression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1862(9):929–938
Sun D, Zhang J, Xie J, Wei W, Chen M, Zhao X (2012) MiR-26 controls LXR-dependent cholesterol efflux by targeting ABCA1 and ARL7. FEBS Lett 586(10):1472–1479
de Aguiar Vallim TQ, Tarling EJ, Kim T, Civelek M, Baldán Á, Esau C, Edwards PA (2013) MicroRNA-144 regulates hepatic ATP binding cassette transporter A1 and plasma high-density lipoprotein after activation of the nuclear receptor farnesoid X receptor. Circ Res 112(12):1602–1612
Adlakha YK, Khanna S, Singh R, Singh VP, Agrawal A, Saini N (2013) Pro-apoptotic miRNA-128-2 modulates ABCA1, ABCG1 and RXRα expression and cholesterol homeostasis. Cell Death Dis 4(8):e780
Geng S, Chen K, Yuan R, Peng L, Maitra U, Diao N, Chen C, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Qi C, Pierce S, Ling W, Xiong H, Li L (2016) The persistence of low-grade inflammatory monocytes contributes to aggravated atherosclerosis. Nat Commun 7:13436
Ren K, Zhu X, Zheng Z, Mo Z, Peng X, Zeng Y, Ou H, Zhang Q, Qi H, Zhao G, Yi G (2018) MicroRNA-24 aggravates atherosclerosis by inhibiting selective lipid uptake from HDL cholesterol via the post-transcriptional repression of scavenger receptor class B type I. Atherosclerosis 270:57–67
Wang L, Jia X, Jiang H, Du Y, Yang F, Si S, Hong B (2013) MicroRNAs 185, 96, and 223 repress selective high-density lipoprotein cholesterol uptake through posttranscriptional inhibition. Mol Cell Biol 33(10):1956–1964
Vickers KC, Landstreet SR, Levin MG, Shoucri BM, Toth CL, Taylor RC, Palmisano BT, Tabet F, Cui HL, Rye K, Sethupathy P, Remaley AT (2014) MicroRNA-223 coordinates cholesterol homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(40):14518–14523
Hu Z, Shen W, Kraemer FB, Azhar S (2012) MicroRNAs 125a and 455 repress lipoprotein-supported steroidogenesis by targeting scavenger receptor class B type I in steroidogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol 32(24):5035–5045
D’Amore S, Härdfeldt J, Cariello M, Graziano G, Copetti M, Di Tullio G, Piglionica M, Scialpi N, Sabbà C, Palasciano G, Vacca M, Moschetta A (2018) Identification of miR-9-5p as direct regulator of ABCA1 and HDL-driven reverse cholesterol transport in circulating CD14+ cells of patients with metabolic syndrome. Cardiovasc Res 114(8):1154–1164
Kang MH, Zhang L, Wijesekara N, de Haan W, Butland S, Bhattacharjee A, Hayden MR (2013) Regulation of ABCA1 protein expression and function in hepatic and pancreatic islet cells by miR-145. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(12):2724–2732
Sene A, Khan AA, Cox D, Nakamura RE, Santeford A, Kim BM, Sidhu R, Onken MD, Harbour JW, Hagbi-Levi S, Chowers I, Edwards PA, Baldan A, Parks JS, Ory DS, Apte RS (2013) Impaired cholesterol efflux in senescent macrophages promotes age-related macular degeneration. Cell Metab 17(4):549–561
Karunakaran D, Thrush AB, Nguyen M, Richards L, Geoffrion M, Singaravelu R, Ramphos E, Shangari P, Ouimet M, Pezacki JP, Moore KJ, Perisic L, Maegdefessel L, Hedin U, Harper M, Rayner KJ (2015) Macrophage mitochondrial energy status regulates cholesterol efflux and is enhanced by anti-miR33 in atherosclerosis. Circ Res 117(3):266–278
Price NL, Rotllan N, Zhang X, Canfrán-Duque A, Nottoli T, Suarez Y, Fernández-Hernando C (2019) Specific disruption of Abca1 targeting largely mimics the effects of miR-33 knockout on macrophage cholesterol efflux and atherosclerotic plaque development. Circ Res 124(6):874–880
Yang S, Ye Z, Chen S, Luo X, Chen S, Mao L, Li Y, Jin H, Yu C, Xiang F, Xie M, Chang J, Xia Y, Hu B (2018) MicroRNA-23a-5p promotes atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability by repressing ATP-binding cassette transporter A1/G1 in macrophages. J Mol Cell Cardiol 123:139–149
Lv Y, Tang Y, Peng J, Zhao G, Yang J, Yao F, Ouyang X, He P, Xie W, Tan Y, Zhang M, Liu D, Tang D, Cayabyab FS, Zheng X, Zhang D, Tian G, Tang C (2014) MicroRNA-19b promotes macrophage cholesterol accumulation and aortic atherosclerosis by targeting ATP-binding cassette transporter A1. Atherosclerosis 236(1):215–226
Wang D, Xia M, Yan X, Li D, Wang L, Xu Y, Jin T, Ling W (2012) Gut microbiota metabolism of anthocyanin promotes reverse cholesterol transport in mice via repressing miRNA-10b. Circ Res 111(8):967–981
Wang D, Wang W, Lin W, Yang W, Zhang P, Chen M, Ding D, Liu C, Zheng J, Ling W (2018) Apoptotic cell induction of miR-10b in macrophages contributes to advanced atherosclerosis progression in ApoE−/− mice. Cardiovasc Res 114(13):1794–1805
Canfrán-Duque A, Rotllan N, Zhang X, Fernández-Fuertes M, Ramírez-Hidalgo C, Araldi E, Daimiel L, Busto R, Fernández-Hernando C, Suárez Y (2017) Macrophage deficiency of miR-21 promotes apoptosis, plaque necrosis, and vascular inflammation during atherogenesis. EMBO Mol Med 9(9):1244–1262
Santovito D, Marcantonio P, Mastroiacovo D, Natarelli L, Mandolini C, De Nardis V, Paganelli C, De Cesare D, Affaitati G, Giamberardino MA, Stellin L, Pinelli M, Weber C, De Blasis G, Occhiuzzi U, Bucci M, Desideri G, Cipollone F (2020) High dose rosuvastatin increases ABCA1 transporter in human atherosclerotic plaques in a cholesterol-independent fashion. Int J Cardiol 299:249–253
Sala F, Aranda JF, Rotllan N, Ramírez CM, Aryal B, Elia L, Condorelli G, Catapano AL, Fernández-Hernando C, Norata GD (2014) MiR-143/145 deficiency attenuates the progression of atherosclerosis in Ldlr−/− mice. Thromb Haemost 112(4):796–802
Tabet F, Vickers KC, Cuesta Torres LF, Wiese CB, Shoucri BM, Lambert G, Catherinet C, Prado-Lourenco L, Levin MG, Thacker S, Sethupathy P, Barter PJ, Remaley AT, Rye K (2014) HDL-transferred microRNA-223 regulates ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Nat Commun 5:3292
Wagner J, Riwanto M, Besler C, Knau A, Fichtlscherer S, Röxe T, Zeiher AM, Landmesser U, Dimmeler S (2013) Characterization of levels and cellular transfer of circulating lipoprotein-bound MicroRNAs. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(6):1392–1400
Florijn BW, Duijs JMGJ, Levels JH, Dallinga-Thie GM, Wang Y, Boing AN, Yuana Y, Stam W, Limpens RWAL, Au YW, Nieuwland R, Rabelink TJ, Reinders MEJ, van Zonneveld AJ, Bijkerk R (2019) Diabetic nephropathy alters the distribution of circulating Angiogenic MicroRNAs among extracellular vesicles, HDL, and Ago-2. Diabetes 68(12):2287–2300
Riedel S, Radzanowski S, Bowen TS, Werner S, Erbs S, Schuler G, Adams V (2015) Exercise training improves high-density lipoprotein-mediated transcription of proangiogenic microRNA in endothelial cells. Eur J Prev Cardiol 22(7):899–903
Briand O, Touche V, Colin S, Brufau G, Davalos A, Schonewille M, Bovenga F, Carrière V, de Boer JF, Dugardin C, Riveau B, Clavey V, Tailleux A, Moschetta A, Lasunción MA, Groen AK, Staels B, Lestavel S (2016) Liver X receptor regulates triglyceride absorption through intestinal Down-regulation of scavenger receptor class B, type 1. Gastroenterology 150(3):650–658
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Cui, H., Lv, K., Yang, N. (2022). HDL and microRNAs. In: Zheng, L. (eds) HDL Metabolism and Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1377. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1592-5_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1592-5_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-1591-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-1592-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)