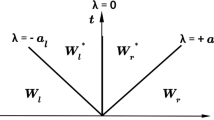
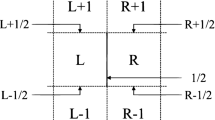
Abstract
The majority of available numerical algorithms for interfacial two-phase flows either treat both fluid phases as incompressible (constant density) or treat both phases as compressible (variable density). This presents a limitation for the prediction of many two-phase flows, as treating both phases as compressible is computationally expensive due to the very stiff pressure–density–temperature coupling of liquids. A framework with the capability of treating one phase compressible and the other phase incompressible, therefore, has a significant potential to improve the computational performance and still capture all important physical mechanisms. We propose a numerical algorithm that can simulate interfacial flows in all Mach number regimes, from \(M=0\) to \(M > 1\), including interfacial flows in which compressible and incompressible fluids interact, within the same pressure-based framework and conservative finite-volume discretisation. For interfacial flows with only incompressible fluids or with only compressible fluids, the presented algorithm reduces to numerical frameworks that have already been presented in the literature. Representative test cases are used to validate the proposed algorithm, including mixed compressible–incompressible interfacial flows with acoustic waves, shock waves and rarefaction fans.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
The term “acoustically-conservative” refers to the acoustic properties of this discretisation method in the context of fully compressible flows and is not indicative of its application to incompressible fluids.
References
Aanjaneya, M., Patkar, S., Fedkiw, R.: A monolithic mass tracking formulation for bubbles in incompressible flow. J. Comput. Phys. 247, 17–61 (2013)
Abgrall, R., Karni, S.: Computations of compressible multifluids. J. Comput. Phys. 169, 594–623 (2001)
Allaire, G., Clerc, S., Kokh, S.: A five-equation model for the simulation of interfaces between compressible fluids. J. Comput. Phys. 181(2), 577–616 (2002)
Anderson, J.D.: Modern Compressible Flow: With a Historical Perspective. McGraw-Hill, New York (2003)
Baer, M., Nunziato, J.: A two-phase mixture theory for the deflagration-to-detonation transition (ddt) in reactive granular materials. Int. J. Multiphase Flow 12(6), 861–889 (1986)
Balay, S., Abhyankar, S., Adams, M.F., Brown, J., Brune, P., Buschelman, K., Dalcin, L., Eijkhout, V., Kaushik, D., Knepley, M.G., May, D.A., McInnes, L.C., Gropp, W.D., Rupp, K., Sanan, P., Smith, B.F., Zampini, S., Zhang, H., Zhang, H.: PETSc Users Manual. Tech. Rep. ANL-95/11 - Revision 3.8, Argonne National Laboratory (2017)
Bartholomew, P., Denner, F., Abdol-Azis, M., Marquis, A., van Wachem, B.: Unified formulation of the momentum-weighted interpolation for collocated variable arrangements. J. Comput. Phys. 375, 177–208 (2018)
Bell, J.B., Colella, P., Glaz, H.M.: A second-order projection method for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 85(2), 257–283 (1989)
Bijl, H., Wesseling, P.: A unified method for computing incompressible and compressible flows in boundary-fitted coordinates. J. Comput. Phys. 141, 153–173 (1998)
Billaud, M., Gallice, G., Nkonga, B.: A simple stabilized finite element method for solving two phase compressible-incompressible interface flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200(9–12), 1272–1290 (2011)
Boger, M., Jaegle, F., Weigand, B., Munz, C.D.: A pressure-based treatment for the direct numerical simulation of compressible multi-phase flow using multiple pressure variables. Comput. Fluids 96, 338–349 (2014)
Brackbill, J., Kothe, D., Zemach, C.: Continuum method for modeling surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 100, 335–354 (1992)
Caiden, R., Fedkiw, R., Anderson, C.: A numerical method for two-phase flow consisting of separate compressible and incompressible regions. J. Comput. Phys. 166, 1–27 (2001)
Caltagirone, J.P., Vincent, S., Caruyer, C.: A multiphase compressible model for the simulation of multiphase flows. Comput. Fluids 50(1), 24–34 (2011)
Chorin, A.J.: A numerical method for solving incompressible viscous flow problems. J. Comput. Phys. 2(1), 12–26 (1967)
Chorin, A.J., Marsden, J.E.: A Mathematical Introduction to Fluid Mechanics. Springer, Berlin (1993)
Coralic, V., Colonius, T.: Finite-volume WENO scheme for viscous compressible multicomponent flows. J. Comput. Phys. 274, 95–121 (2014)
Cordier, F., Degond, P., Kumbaro, A.: An asymptotic-preserving all-speed scheme for the Euler and Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 231(17), 5685–5704 (2012)
Darwish, M., Moukalled, F.: A fully coupled Navier-Stokes solver for fluid flow at all speeds. Numer. Heat Tr. B-Fund. 65(5), 410–444 (2014)
Denner, F.: Fully-coupled pressure-based algorithm for compressible flows: linearisation and iterative solution strategies. Comp. Fluids 175, 53–65 (2018)
Denner, F., Charogiannis, A., Pradas, M., Markides, C.N., van Wachem, B., Kalliadasis, S.: Solitary waves on falling liquid films in the inertia-dominated regime. J. Fluid Mech. 837, 491–519 (2018)
Denner, F., Evrard, F., van Wachem, B.: Conservative finite-volume framework and pressure-based algorithm for flows of incompressible, ideal-gas and real-gas fluids at all speeds. J. Comput. Phys. 409, 109348 (2020)
Denner, F., Evrard, F., van Wachem, B.: Modeling acoustic cavitation using a pressure-based algorithm for polytropic fluids. Fluids 5(2), 69 (2020)
Denner, F., Paré, G., Zaleski, S.: Dispersion and viscous attenuation of capillary waves with finite amplitude. Euro. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 226, 1229–1238 (2017)
Denner, F., van Wachem, B.: Compressive VOF method with skewness correction to capture sharp interfaces on arbitrary meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 279, 127–144 (2014)
Denner, F., van Wachem, B.: Fully-coupled balanced-force VOF framework for arbitrary meshes with least-squares curvature evaluation from volume fractions. Numer. Heat Tr. B-Fund. 65(3), 218–255 (2014)
Denner, F., van Wachem, B.: Numerical time-step restrictions as a result of capillary waves. J. Comput. Phys. 285, 24–40 (2015)
Denner, F., van Wachem, B.: TVD differencing on three-dimensional unstructured meshes with monotonicity-preserving correction of mesh skewness. J. Comput. Phys. 298, 466–479 (2015)
Denner, F., Xiao, C.N., van Wachem, B.: Pressure-based algorithm for compressible interfacial flows with acoustically-conservative interface discretisation. J. Comput. Phys. 367, 192–234 (2018)
Evrard, F., Denner, F., van Wachem, B.: Height-function curvature estimation with arbitrary order on non-uniform Cartesian grids. J. Comput. Phys.: X 7, 100060 (2020)
Fedkiw, R., Aslam, T., Merriman, B., Osher, S.: A non-oscillatory Eulerian approach to interfaces in multimaterial flows (the ghost fluid method). J. Comput. Phys. 152(2), 457–492 (1999)
Ferziger, J.: Interfacial transfer in Tryggvason’s method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 41, 551–560 (2003)
Ferziger, J., Perić, M.: Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Ferziger, J.H., Peric, M., Street, R.L.: Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, 4th edn. Springer International Publishing, Berlin (2020)
Fuster, D., Popinet, S.: An all-Mach method for the simulation of bubble dynamics problems in the presence of surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 374, 752–768 (2018)
Garrick, D.P., Owkes, M., Regele, J.D.: A finite-volume HLLC-based scheme for compressible interfacial flows with surface tension. J. Comput. Phys. 339, 46–67 (2017)
Harlow, F., Amsden, A.: Fluid Dynamics. Monograph LA-4700, Los Alamos National Laboratory (1971)
Harlow, F.H., Amsden, A.A.: A numerical fluid dynamics calculation method for all flow speeds. J. Comput. Phys. 8(2), 197–213 (1971)
Hauke, G., Hughes, T.J.: A comparative study of different sets of variables for solving compressible and incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 153(1–2), 1–44 (1998)
Hirt, C., Nichols, B.: Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 39(1), 201–225 (1981)
Hou, T.Y., Floch, P.G.L.: Why nonconservative schemes converge to wrong solutions: error analysis. Math. Comput. 62(206), 497–530 (1994)
Issa, R.: Solution of the implicitly discretised fluid flow equations by operator-splitting. J. Comput. Phys. 62, 40–65 (1985)
Karimian, S.M.H., Schneider, G.E.: Pressure-based computational method for compressible and incompressible flows. J. Thermophys. Heat Trans. 8(2), 267–274 (1994)
Karki, K.C., Patankar, S.V.: Pressure based calculation procedure for viscous flows at all speeds in arbitrary configurations. AIAA J. 27(9), 1167–1174 (1989)
Kunz, R., Cope, W., Venkateswaran, S.: Development of an implicit method for multi-fluid flow simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 152(1), 78–101 (1999)
Lauterborn, W., Lechner, C., Koch, M., Mettin, R.: Bubble models and real bubbles: Rayleigh and energy-deposit cases in a Tait-compressible liquid. IMA J. Appl. Math. 83(4), 556–589 (2018)
Le Métayer, O., Massoni, J., Saurel, R.: Élaboration des lois d’état d’un liquide et de sa vapeur pour les modèles d’écoulements diphasiques. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 43(3), 265–276 (2004)
Liu, C., Hu, C.: Adaptive THINC-GFM for compressible multi-medium flows. J. Comput. Phys. 342, 43–65 (2017)
Liu, T., Khoo, B., Yeo, K.: Ghost fluid method for strong shock impacting on material interface. J. Comput. Phys. 190(2), 651–681 (2003)
Meng, J.C., Colonius, T.: Numerical simulations of the early stages of high-speed droplet breakup. Shock Waves 25(4), 399–414 (2015)
Moukalled, F., Mangani, L., Darwish, M.: The Finite Volume Method in Computational Fluid Dynamics: An Advanced Introduction with OpenFOAM and Matlab. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Murrone, A., Guillard, H.: A five equation reduced model for compressible two phase flow problems. J. Comput. Phys. 202(2), 664–698 (2005)
Park, J.H., Munz, C.D.: Multiple pressure variables methods for fluid flow at all Mach numbers. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 49(8), 905–931 (2005)
Patankar, S.: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. Hemisphere Publishing Company (1980)
Plesset, M.S.: The dynamics of cavitation bubbles. J. App. Mech. 16, 277–282 (1949)
Popinet, S.: An accurate adaptive solver for surface-tension-driven interfacial flows. J. Comput. Phys. 228(16), 5838–5866 (2009)
Popinet, S.: Numerical models of surface tension. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 50, 49–75 (2018)
Prosperetti, A.: Motion of two superposed viscous fluids. Phys. Fluids 24(7), 1217–1223 (1981)
Rhie, C.M., Chow, W.L.: Numerical study of the turbulent flow past an airfoil with trailing edge separation. AIAA J. 21(11), 1525–1532 (1983)
Rohde, C., Zeiler, C.: A relaxation Riemann solver for compressible two-phase flow with phase transition and surface tension. Appl. Numer. Math. 95, 267–279 (2015)
Scardovelli, R., Zaleski, S.: Analytical relations connecting linear interfaces and volume fractions in rectangular grids. J. Comput. Phys. 164(1), 228–237 (2000)
Shyue, K.M.: A volume-fraction based algorithm for hybrid barotropic and non-barotropic two-fluid flow problems. Shock Waves 15(6), 407–423 (2006)
Toro, E.F.: Riemann Solvers and Numerical Fluid Dynamics: A Practical Introduction, 3rd edn. Springer (2009)
Toutant, A.: General and exact pressure evolution equation. Phys. Lett. A 381(44), 3739–3742 (2017)
Turkel, E., Fiterman, A., van Leer, B.: Preconditioning and the Limit to the Incompressible Flow Equations. Tech. rep., NASA CR-191500 (1993)
Ubbink, O., Issa, R.: A method for capturing sharp fluid interfaces on arbitrary meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 153, 26–50 (1999)
van der Heul, D., Vuik, C., Wesseling, P.: A conservative pressure-correction method for flow at all speeds. Comp. Fluids 32(8), 1113–1132 (2003)
Van Doormaal, J., Raithby, G., McDonald, B.: The segregated approach to predicting viscous compressible fluid flows. J. Turbomach. 109(April 1987), 268–277 (1987)
van Wachem, B., Schouten, J.: Experimental validation of 3-D Lagrangian VOF model: Bubble shape and rise velocity. AIChE J. 48(12), 2744–2753 (2002)
Wadhwa, A.R., Abraham, J., Magi, V.: Hybrid compressible-incompressible numerical method for transient drop-gas flows. AIAA J. 43(9), 1974–1983 (2005)
Wesseling, P.: Principles of Computational Fluid Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Xiao, C.N., Denner, F., van Wachem, B.: Fully-coupled pressure-based finite-volume framework for the simulation of fluid flows at all speeds in complex geometries. J. Comput. Phys. 346, 91–130 (2017)
Yamamoto, T., Takatani, K.: Pressure-based unified solver for gas-liquid two-phase flows where compressible and incompressible flows coexist. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids (2018)
Zhou, Z.W., Lin, S.P.: Effects of compressibility on the atomization of liquid jets. J. Propuls. Power 8(4), 736–740 (1992)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation), grant numbers 420239128 and 447633787.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Denner, F., van Wachem, B. (2022). A Unified Algorithm for Interfacial Flows with Incompressible and Compressible Fluids. In: Zeidan, D., Zhang, L.T., Da Silva, E.G., Merker, J. (eds) Advances in Fluid Mechanics. Forum for Interdisciplinary Mathematics. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1438-6_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1438-6_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-1437-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-1438-6
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)