Abstract
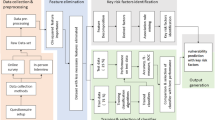
Substance consumption has been a global public health epidemic causing numerous disorders and fatalities. In order to curb at the initial onset of consumption, it is required to understand the patterns of consumption and substance-specific features so that targeted intervention strategies can be implemented. This article focuses on understanding substance use patterns and identifies key predictors in substance-specific classes. The University of California, Irvine (UCI) repository dataset and classifications performed by K-Nearest Neighbors (K-NN), Random Forest (RF), and Decision Tree (DT) classifier algorithms are used to gain insight into the consumption pattern of user and non-user groups. The result revealed the impulsivity factor of personality traits as a key predictor, and there are inherent substances that are influencing the consumption pattern. RF scored the highest accuracy of 80%. The result suggests substance consumption isn’t a unitary event, but early tests of personality traits and prediction of the consumption pattern could minimize the risks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pomeroy, E.C., Anderson, K.: The DSM-5 has arrived (2013)
Finn, K.: Why marijuana will not fix the opioid epidemic. Mo. Med. 115, 191–193 (2018)
Zou, Z., Wang, H., Uquillas, F.D.O., Wang, X., Ding, J., Chen, H.: Definition of substance and non-substance addiction. Substance and Non-substance Addiction 21–41
Poria S., Gelbukh A., Agarwal B., Cambria E., Howard N.: Common sense knowledge based personality recognition from text. In: Castro F., Gelbukh A., González M. (eds) Advances in Soft Computing and Its Applications, MICAI 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 8266. Springer, Berlin (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-45111-9_42
Peacock, A., Leung, J., Larney, S., Colledge, S., Hickman, M., Rehm, J., Ali, R.: Global statistics on alcohol, tobacco and illicit drug use: 2017 status report. Addiction 113(10), 1905–1926 (2017)
Ambekar, A., Agrawal, A., Rao, R., Mishra, A.K., Khandelwal, S.K., Chadda, R.K.: Magnitude of substance use in India. New Delhi: Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India (2019)
Abuse, S.: Mental health services administration. In: Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results From the 2016 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. SMA 17–5044, NSDUH Series H-52). Rockville, MD: Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (2017)
Drug misuse and dependence. www.assets.publishing.service.gov.uk (2017)
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). World drug report 2017. Vienna: UNODC (2017)
Badiani, A., Belin, D., Epstein, D., Calu, D., Shaham, Y.: Opiate versus psychostimulant addiction: the differences do matter. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12(11), 685–700 (2011)
George, O., Koob, G.F.: Individual differences in prefrontal cortex function and the transition from drug use to drug dependence. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 35 (2010)
Vassileva, J., Paxton, J., Moeller, F.G., Wilson, M.J., Bozgunov, K., Martin, E.M., Gonzalez, R., Vasilev, G.: Heroin and amphetamine users display opposite relationships between trait and neurobehavioral dimensions of impulsivity. Addict. Behav. 39, 652–659 (2014)
Ahn, W.Y., Vassileva, J.: Machine-learning identifies substance-specific behavioral markers for opiate and stimulant dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 161, 247–257 (2016)
Clark, S.L., Gillespie, N.A., Adkins, D.E., Kendler, K.S., Neale, M.C.: Psychometric modeling of abuse and dependence symptoms across six illicit substances indicates novel dimensions of misuse. Addict. Behav. 53, 132–140 (2016)
Peters, J., Pattij, T., De Vries, T.J.: Targeting cocaine versus heroin memories: divergent roles within ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 34(12), 689–695 (2013)
Wadekar, A.S.: Understanding opioid use disorder (OUD) using tree-based classifiers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 208, 107839 (2020)
Afzali, M.H., Sunderland, M., Stewart, S., Masse, B., Seguin, J., Newton, N., Conrod, P.: Machine-learning prediction of adolescent alcohol use: a cross-study, cross-cultural validation. Addiction 114(4), 662–671 (2019)
Ahn, W.Y., Ramesh, D., Moeller, F.G., Vassileva, J.: Utility of machine-learning approaches to identify behavioral markers for substance use disorders: impulsivity dimensions as predictors of current cocaine dependence. Front. Psych. 7, 34 (2016)
Coughlin, L.N., Tegge, A.N., Sheffer, C.E., Bickel, W.K.: A machine-learning approach to predicting smoking cessation treatment outcomes. Nicotine Tob. Res. 22(3), 415–422 (2020)
Liu, J., Weitzman, E.R., Chunara, R.: Assessing behavior stage progression from social media data. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing. IEEE, pp. 1320–1333 (2017)
Wang, J.M., Zhu, L., Brown, V.M., De La Garza II, R., Newton, T., King-Casas, B., Chiu, P.H.: In cocaine dependence, neural prediction errors during loss avoidance are increased with cocaine deprivation and predict drug use. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 4(3), 291–299 (2019).
Kumari, D., Kilam, S., Nath, P., Swetapadma, A.: Prediction of alcohol abused individuals using artificial neural network. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 10(2), 233–237 (2018)
Machine learning repository. https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Drug+consumption
Drug wheel: https://adf.org.au/
Fehrman, E., Egan, V., Gorban, A. N., Levesley, J., Mirkes, E.M., Muhammad, A.K.: Personality traits and drug consumption. Springer International Publishing (2019)
Fehrman, E., Muhammad, A.K., Mirkes, E.M., Egan, V., Gorban, A.N.: The five factor model of personality and evaluation of drug consumption risk. In: Data Science. Springer, Cham, pp. 231–242 (2017)
Argyriou, E., Um, M., Carron, C., Cyders, M.A.: Age and impulsive behavior in drug addiction: a review of past research and future directions. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 164, 106–117 (2018)
Zhang, X., Huang, R., Li, P., Ren, Y., Gao, J., Mueller, J.F., Thai, P.K.: Temporal profile of illicit drug consumption in Guangzhou, China monitored by wastewater-based epidemiology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26(23), 23593–23602 (2019)
Chhetri, B., Goyal, L.M., Mittal, M., Gurung, S.: Consumption of licit and illicit substances leading to mental illness: a prevalence study. EAI Endorsed Trans. Pervasive Health Technol. 6, 21 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chhetri, B., Goyal, L.M., Mittal, M. (2022). Identifying Predictors for Substance Consumption Pattern Using Machine Learning Techniques. In: Agarwal, B., Rahman, A., Patnaik, S., Poonia, R.C. (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems. Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7136-4_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7136-4_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-7135-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-7136-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)