Abstract
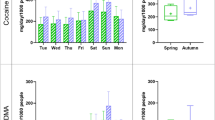
Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) has been widely used as a complementary method for estimating consumption of illicit drugs in the population. Temporal drug consumption estimates derived from WBE can provide important information for law enforcement and public health authorities in understanding changes in supply and demand of illicit drugs, but currently lacking in China. In this study, influent wastewater samples from a municipal sewage treatment plant in Guangzhou, China were collected for 8 weeks to investigate the temporal change in consumption of six illicit drugs in the catchment. The results indicated that methamphetamine and ketamine were the dominant illicit drugs in Guangzhou with the per capita use of 14.7–470.7 mg/day/1000 people and 64.9–673.7 mg/day/1000 people, respectively. No distinct weekly patterns were observed for illicit drug consumption in Guangzhou, indicating that drug users are likely to be regular ones. Further assessment about the impact of public holidays on the consumption behavior of drugs showed little impact for ketamine (p = 0.689), but higher consumptions of methamphetamine (p = 0.003) and cocaine (p = 0.027) were observed during public holidays than the control period. The considerable decrease in drug consumption observed in October 2017 compared with January and May 2017 was possibly the consequence of law enforcement action.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archer E, Castrignanò E, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Wolfaardt GM (2018) Wastewater-based epidemiology and enantiomeric profiling for drugs of abuse in South African wastewaters. Sci Total Environ 625:792–800
Baker DR, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2013) Spatial and temporal occurrence of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in the aqueous environment and during wastewater treatment: new developments. Sci Total Environ 454:442–456
Baker DR, Barron L, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2014) Illicit and pharmaceutical drug consumption estimated via wastewater analysis. Part a: chemical analysis and drug use estimates. Sci Total Environ 487:629–641
Been F, Rossi L, Ort C, Rudaz S, Delémont O, Esseiva P (2014) Population normalization with ammonium in wastewater-based epidemiology: application to illicit drug monitoring. Environ Sci Technol 48(14):8162–8169
Been F, Lai FY, Kinyua J, Covaci A, van Nuijs ALN (2016) Profiles and changes in stimulant use in Belgium in the period of 2011–2015. Sci Total Environ 565:1011–1019
Castiglioni S, Bijlsma L, Covaci A, Emke E, Hernández F, Reid M, Ort C, Thomas KV, van Nuijs ALN, de Voogt P, Zuccato E (2013) Evaluation of uncertainties associated with the determination of community drug use through the measurement of sewage drug biomarkers. Environ Sci Technol 47(3):1452–1460
Causanilles A, Emke E, De Voogt P (2016) Determination of phosphodiesterase type V inhibitors in wastewater by direct injection followed by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Sci Total Environ 565:140–147
Chiaia AC, Banta-Green C, Field J (2008) Eliminating solid phase extraction with large-volume injection LC/MS/MS: analysis of illicit and legal drugs and human urine indicators in US wastewaters. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8841–8848
China Anti-Drug Network (2017) China Drug Situation Report (2016). http://www.nncc626.com/2017-03/27/c_129519255.htm. 2017.3.27. (in Chinese)
China Food And Drug Administration (2017) National Drug Abuse Monitoring Annual Report (2016). http://samr.cfda.gov.cn/WS01/CL0844/175994.html. 2017.8.11. (in Chinese)
Daughton CG (2012) Real-time estimation of small-area populations with human biomarkers in sewage. Sci Total Environ 414(1):6–21
Du P, Li K, Li J, Xu Z, Fu X, Yang J, Zhang H, Li X (2015) Methamphetamine and ketamine use in major Chinese cities, a nationwide reconnaissance through sewage-based epidemiology. Water Res 84:76–84
Du P, Zhou Z, Bai Y, Xu Z, Gao T, Fu X, Li X (2017) Estimating heroin abuse in major Chinese cities through wastewater-based epidemiology. Sci Total Environ 605:158–165
Feng L, Yu W, Chang W, Han E, Chung H, Li J (2016) Comparison of illegal drug use pattern in Taiwan and Korea from 2006 to 2014. ASHRAE J 11(1):1–13
Foppe KS, Hammond-Weinberger DR, Subedi B (2018) Estimation of the consumption of illicit drugs during special events in two communities in Western Kentucky, USA using sewage epidemiology. Sci Total Environ 633:249–256
Gao J, O'Brien J, Lai FY, van Nuijs ALN, He J, Mueller JF, Xu J, Thai PK (2015) Could wastewater analysis be a useful tool for China? - a review. J Environ Sci-China 27(C):70–79
Gonzalez-Marino I, Quintana JB, Rodriguez I, Cela R (2010) Determination of drugs of abuse in water by solid-phase extraction, derivatisation and gaschromatography–ion trap-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1217(11):1748–1760
Guangzhou Municipal Public Security Bureau (2018) Guangzhou cracked the problem of drug addicts “someone manages, how to manage, and manages well”. http://www.gzjd.gov.cn/gzjdw/gaxw/ztbd/payx/20180508/detail-370793.shtml. 2018-5-8. (in Chinese)
Guangzhou Statistics Bureau (2016) The main data bulletin 1 of sample survey in national 1% population in Guangzhou, 2015. http://www.gzstats.gov.cn/gzstats/tjgb_glpcgb/201607/5e233ef85e3a441f83b186cf51a54d0b.shtml. 2016.7.2. (in Chinese)
Han E, Kwon NJ, Feng L, Li J, Chung H (2016) Illegal use patterns, side effects, and analytical methods of ketamine. Forensic Sci Int 268:25–34
INCB (2017) Narcotic substances: estimated world requirements for 2017 — statistics for 2015. INCB (International Narcotics Control Board), New York http://www.incb.org/documents/Narcotic-Drugs/Technical-Publications/2016/Narcotic_Drugs_Publication_2016.pdf
Irvine RJ, Kostakis C, Felgate PD, Jaehne EJ, Chen C, White JM (2011) Population drug use in Australia: a wastewater analysis. Forensic Sci Int 210(1–3):69–73
Jiang J, Lee C, Fang M, Tu B, Liang Y (2015) Impacts of emerging contaminants on surrounding aquatic environment from a youth festival. Environ Sci Technol 49:792–799
Karolak S, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Lindberg RH, Lopez de Alda M, Meierjohann A, Ort C, Pico Y, Quintana JB, Reid M, Rieckermann J, Terzic S, van Nuijs AL, de Voogt P (2012) Comparing illicit drug use in 19 European cities through sewage analysis. Sci Total Environ 432:432–439
Khan U, van Nuijs ALN, Li J, Maho W, Du P, Li K, Hou L, Zhang J, Meng X, Li X, Covaci A (2014) Application of a sewage-based approach to assess the use of ten illicit drugs in four Chinese megacities. Sci Total Environ 487:710–721
Kim KY, Lai FY, Kim H, Thai PK, Mueller JF, Oh J (2015) The first application of wastewater-based drug epidemiology in five South Korean cities. Sci Total Environ 524-525:440–446
Lai FY, Ort C, Gartner C, Carter S, Prichard J, Kirkbride P, Bruno R, Hall W, Eaglesham G, Mueller JF (2011) Refining the estimation of illicit drug consumptions from wastewater analysis: co-analysis of prescription pharmaceuticals and uncertainty assessment. Water Res 45(15):4437–4448
Lai FY, Bruno R, Hall W, Gartner C, Ort C, Kirkbride P, Prichard J, Thai PK, Carter S, Mueller JF (2013a) Profiles of illicit drug use during annual key holiday and control periods in Australia: wastewater analysis in an urban, a semi-rural and a vacation area. Addiction 108(3):556–565
Lai FY, Bruno R, Leung HW, Thai PK, Ort C, Carter S, Thompson K, Lam PKS, Mueller JF (2013b) Estimating daily and diurnal variations of illicit drug use in Hong Kong: a pilot study of using wastewater analysis in an Asian metropolitan city. Forensic Sci Int 233(1–3):126–132
Lai FY, Anuj S, Bruno R, Carter S, Gartner C, Hall W, Kirkbride KP, Mueller JF, O'Brien JW, Prichard J (2014) Systematic and day-to-day effects of chemical-derived population estimates on wastewater-based drug epidemiology. Environ Sci Technol 49(2):999–1008
Lai FY, O'Brien J, Bruno R, Hall W, Prichard J, Kirkbride P, Gartner C, Thai P, Carter S, Lloyd B, Burns L, Mueller J (2016a) Spatial variations in the consumption of illicit stimulant drugs across Australia: a nationwide application of wastewater-based epidemiology. Sci Total Environ 568:810–818
Lai FY, O'Brien JW, Thai PK, Hall W, Chan G, Bruno R, Ort C, Prichard J, Carter S, Anuj S, Kirkbride KP, Gartner C, Humphries M, Mueller JF (2016b) Cocaine, MDMA and methamphetamine residues in wastewater: consumption trends (2009–2015) in South East Queensland, Australia. Sci Total Environ 568:803–809
Leimanis E, Best BM, Atayee RS, Pesce AJ (2012) Evaluating the relationship of methadone concentrations and EDDP formation in chronic pain patients. J Anal Toxicol 36(4):239–249
Li J, Hou L, Du P, Yang J, Li K, Xu Z, Wang C, Zhang H, Li X (2014) Estimation of amphetamine and methamphetamine uses in Beijing through sewage-based analysis. Sci Total Environ 490:724–732
Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H (2012) A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380:2224–2260
Lin W, Zhang X, Tan Y, Li P, Ren Y (2019) Can water quality indicators and biomarkers be used to estimate real-time population? Sci Total Environ 660:603–610
McCall AK, Bade R, Kinyua J, Lai FY, Thai PK, Covaci A, Bijlsma L, van Nuijs ALN, Ort C (2016) Critical review on the stability of illicit drugs in sewers and wastewater samples. Water Res 88(1):933–947
Metcalfe C, Tindale K, Li H, Rodayan A, Yargeau V (2010) Illicit drugs in Canadian municipal wastewater and estimates of community drug use. Environ Pollut 158(10):3179–3185
Nefau T, Karolak S, Castillo L, Boireau V, Levi Y (2013) Presence of illicit drugs and metabolites in influents and effluents of 25 sewage water treatment plants and map of drug consumption in France. Sci Total Environ 461-462:712–722
O'Brien JW, Thai PK, Eaglesham G, Ort C, Scheidegger A, Carter S, Lai FY, Mueller JF (2014) A model to estimate the population contributing to the wastewater using samples collected on census day. Environ Sci Technol 48(1):517–525
Skees AJ, Foppe KS, Loganathan B, Subedi B (2018) Contamination profiles, mass loadings, and sewage epidemiology of neuropsychiatric and illicit drugs in wastewater and river waters from a community in the Midwestern United States. Sci Total Environ 631-632:1457–1464
Sun H, Li X, Chow EPF, Li T, Xian Y, Lu Y, Tian T, Zhuang X, Zhang L (2015) Methadone maintenance treatment programme reduces criminal activity and improves social well-being of drug users in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 5(1):e5997
Terzic S, Senta I, Ahel M (2010) Illicit drugs in wastewater of the city of Zagreb (Croatia)--estimation of drug abuse in a transition country. Environ Pollut 158(8):2686–2693
Thai PK, Lai FY, Bruno R, Dyken EV, Hall W, O'Brien J, Prichard J, Mueller JF (2016) Refining the excretion factors of methadone and codeine for wastewater analysis — combining data from pharmacokinetic and wastewater studies. Environ Int 94:307–314
The Compilation Committee of First National Census of Pollution Sources (2011) Manual for pollutant discharge coefficient of pollution source census. China Environmental Science Press (in Chinese)
Thomas KV, Bijlsma L, Castiglioni S, Covaci A, Emke E, Grabic R, Hernández F, Karolak S, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Lindberg RH, Lopez De Alda M, Meierjohann A, Ort C, Pico Y, Quintana JB, Reid M, Rieckermann J, Terzic S, van Nuijs ALN, de Voogt P (2012) Comparing illicit drug use in 19 European cities through sewage analysis. Sci Total Environ 432:432–439
Tscharke BJ, Chen C, Gerber JP, White JM (2015) Trends in stimulant use in Australia: a comparison of wastewater analysis and population surveys. Sci Total Environ 536:331–337
Tscharke BJ, Chen C, Gerber JP, White JM (2016) Temporal trends in drug use in Adelaide, South Australia by wastewater analysis. Sci Total Environ 565:384–391
UNDOC (2016) World drug report (2016). UNDOC, New York
UNDOC (2018) World drug report (2018). UNDOC, New York
van Nuijs AL, Mougel JF, Tarcomnicu I, Bervoets L, Blust R, Jorens PG, Neels H, Covaci A (2011a) Sewage epidemiology--a real-time approach to estimate the consumption of illicit drugs in Brussels, Belgium. Environ Int 37(3):612–621
van Nuijs ALN, Mougel JF, Tarcomnicu I, Bervoets L, Blust R, Jorens PG, Neels H, Covaci A (2011b) A one year investigation of the occurrence of illicit drugs in wastewater from Brussels, Belgium. J Environ Monit 13(4):1008–1016
van Nuijs ALN, Abdellati K, Bervoets L, Blust R, Jorens PG, Neels H, Covaci A (2012) The stability of illicit drugs and metabolites in wastewater, an important issue for sewage epidemiology. J Hazard Mater 239(240):19–23
Wang Z, Shao XT, Tan DQ, Yan JH, Xiao Y, Zheng QD, Pei W, Wang Z, Wang DG (2019) Reduction in methamphetamine consumption trends from 2015 to 2018 detected by wastewater-based epidemiology in Dalian, China. Drug Alcohol Depend 194:302–309
Wieber J, Gugler R, Hengstmann JH, Dengler HJ (1975) Pharmacokinetics of ketamine in man. Anaesthesist 24:260–263
Xu Z, Du P, Li K, Gao T, Wang Z, Fu X (2017) Tracing methamphetamine and amphetamine sources in wastewater and receiving waters via concentration and enantiomeric profiling. Sci Total Environ 601-602:159–166
Yargeau V, Taylor B, Li H, Rodayan A, Metcalfe CD (2014) Analysis of drugs of abuse in wastewater from two Canadian cities. Sci Total Environ 487:722–730
Zheng QD, Lin JG, Pei W, Guo MX, Wang Z, Wang DG (2017) Estimating nicotine consumption in eight cities using sewage epidemiology based on ammonia nitrogen equivalent population. Sci Total Environ 590:226–232
Zheng Q, Wang Z, Liu C, Yan J, Pei W, Wang Z (2019) Applying a population model based on hydrochemical parameters in wastewater-based epidemiology. Sci Total Environ 657:466–475
Zuccato E, Chiabrando C, Castiglioni S, Calamari D, Bagnati R, Schiarea S, Fanelli R (2005) Cocaine in surface waters: a new evidence-based tool to monitor community drug abuse. Environ Health 4(1):14
Zuccato E, Chiabrando C, Castiglioni S, Bagnati R, Fanelli R (2008) Estimating community drug abuse by wastewater analysis. Environ Health Perspect 116(8):1027–1032
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41877466) and Research Fund of SIT of Guangzhou (Grant No. 201707010158). Some of the data reported in this paper was obtained at the Central Analytical Research Facility operated by the Institute for Future Environments (QUT). Access to CARF is supported by generous funding from the Science and Engineering Faculty (QUT). Yuan Ren was funded by the State Scholarship Fund as a Senior Visiting Fellow by CSC. Jianfa Gao received an ARC scholarship (DP150100645). Phong K. Thai was funded by the QUT VC Fellowship in part of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics statement
This paper is our original work.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 517 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Huang, R., Li, P. et al. Temporal profile of illicit drug consumption in Guangzhou, China monitored by wastewater-based epidemiology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 23593–23602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05575-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05575-3