Abstract
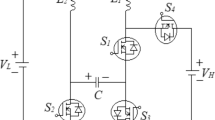
In this paper, comparison of transformer less bi-directional dc–dc converter with conventional buck-boost converter topology is done. BDC has many advantages such as power flow in both directions, high gain, high efficiency, simple circuit structure, reduced switching components, with wide voltage range, reduced switching loss due to zero voltage switching, reduce voltage stress and reduced size. Bi-directional converters are of different topologies and are used for different applications based on their features. Isolated converters are bulky and are of large size due to high frequency transformer, therefore they are useful for static energy storage applications, whereas transformer less BDC are lightweight and convenient for dynamic applications like Electric Vehicle. BDC with energy storage devices is used for frequent start–stop of motors and electric vehicles. BDC is also helpful in energy transfer between two dc buses of different voltage level. Transformer less converter topology is compared with traditional converter topology which is simulated in MATLAB/SIMULINK.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tytelmaier, K.: A review of non-isolated bidirectional DC-DC converters for energy storage systems. In: 2016 II International Young Scientists Forum on Applied Physics and Engineering (YSF), pp. 22–28 (2016)
Yahyazadeh, S., Khaleghi M.: A new structure of bidirectional DC-DC converter for electric vehicle applications. In: 2020, 11th power electronics, drive systems, and technologies conference, pp. 1–6 (2020)
Han, J.: Dynamic improvement with a feedforward control strategy of bidirectional DC-DC converter for battery charging and discharging. Electronics 9, 1738 (2020)
Keshavarzi, M.D.: A novel bidirectional DC-DC converter for dynamic performance enhancement of hybrid AC/DC Microgrid. Electronics 9, 1653 (2020)
Farhani, S., Barhoumi, E. M., Bacha, F.: Design and hardware investigation of a new configuration of an isolated DC-DC converter for fuel cell vehicle. Ain Shams Eng. J. 12(1), 591–598 (2021)
Rodriguez, A.O.: A survey on bidirectional DC/DC power converter topologies for the future hybrid and all electric aircrafts. Energies 13, 4883 (2020)
Chandrasekar, B.: Non-isolated high-gain triple port DC–DC buck-boost converter with positive output voltage for photovoltaic applications. IEEE Access 8, 113,649–113,666 (2020)
Shin, S.U.: An analysis of non-isolated DC-DC converter topologies with energy transfer media. Energies, 12, 1468 (2019)
Elsayad, N.: Design and implementation of a new transformerless bidirectional DC–DC converter with wide conversion ratios. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66, 7067–7077 (2018)
Kaye, R., Kalam, A.: Non-isolated DC/DC buck/boost converters for off-grid hybrid renewable system. In: 2019, 29th Australasian universities power engineering conference (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Swarnkar, R., HariKrishnan, R. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Transformer Less Bi-directional DC–DC Converter and Conventional Converter for Battery Charging-Discharging Applications. In: Natarajan, S.K., Prakash, R., Sankaranarayanasamy, K. (eds) Recent Advances in Manufacturing, Automation, Design and Energy Technologies. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4222-7_102
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4222-7_102
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-4221-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-4222-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)