Abstract
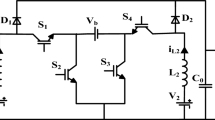
A modified topology to obtain a high efficiency bidirectional type DC–DC converter without magnetic coupling is proposed in this paper. The modified circuit contains four switches with their body diodes, two inductors and a capacitor, and the topology arrangement uses two boost converters to develop the gain. The input current of the modified topology is divided between two different values of inductors, which results in high efficiency. In the buck mode, an obvious reduction in the voltage gain and an improved efficiency can be seen using synchronous rectification. The modified topology improves performance, allows for easy control structures and can be used in low output voltage high current battery charging applications. Simulations of the proposed system have been carried out through MATLAB/SIMULINK software. In addition, it has been validated through a 12 V/120 V, 40 W prototype circuit.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seyezhai, R., Anitha, R., Mahalakshmi, S., Bhavani, M.: High gain interleaved boost converter for fuel cell applications. BEEI 2(4), 265–271 (2013)
Lee, J.-Y., Hwang, S.-N.: Non-isolated high-gain boost converter using voltage-stacking cell. Electron. Lett. 44(10), 644–645 (2008)
Barreto, L.H.S.C., Praca, P.P., Oliveira, D.S., Silva, R.N.A.L.: High-voltage gain boost converter based on three-state commutation cell for battery charging using PV panels in a single conversion stage. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 29(1), 150–158 (2014)
Duan, R.-Y., Lee, J.-D.: High-efficiency bidirectional DC–DC converter with coupled inductor. IET Power Electron. 5(1), 115–123 (2012)
Tao, H., Duarte, J.L., Hendrix, M.A.M.: Line-interactive UPS using a fuel cell as the primary source. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55(8), 3012–3021 (2008)
Hsieh, Y.-P., Chen, J.-F., Liang, T.-J., Yang, L.-S.: Novel high step-up DC–DC converter for distributed generation system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 60(4), 1473–1482 (2013)
Chen, G., Lee, Y.-S., Hui, S.Y.R., Xu, D., Wang, Y.: Actively clamped bidirectional flyback converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 47(4), 770–779 (2000)
Zhang, F., Yan, Y.: Novel forward-flyback hybrid bidirectional DC–DC converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56(5), 1578–1584 (2009)
Lin, B.-R., Huang, C.-L., Lee, Y.-E.: Asymmetrical pulse-width modulation bidirectional DC–DC converter. IET Power Electron. 1(3), 336–347 (2008)
Mi, C., Bai, H., Wang, C., Gargies, S.: Operation, design and control of dual H-bridge-based isolated bidirectional DC–DC converter. IET Power Electron. 1(4), 507–517 (2008)
Khan, F.H., Tolbert, L.M., Webb, W.E.: Hybrid electric vehicle power management solutions based on isolated and nonisolated configurations of multilevel modular capacitor-clamped converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56(8), 3079–3095 (2009)
Sergio, B.-M., Alepuz, S., Bordonau, J.: A bidirectional multilevel boost-buck DC–DC converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26(8), 2172–2183 (2011)
Peng, F.-Z., Zhang, F., Qian, Z.: A magnetic-less DC–DC converter for dual voltage automotive systems. In: Conference Record of the 2002 IEEE Industry Application 37th IAS Annual Meeting, pp 1303–1310 (2002)
Lee, Y.-S., Chiu, Y.-Y.: Zero-current-switching switched-capacitor bidirectional DC–DC converter. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 152(6), 1525–1530 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-epa:20050138
Saravanan, S., Ramesh Babu, N.: Design and development of single switch high step-up DC–DC converter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 6(2), 855–863 (2018)
Yang, L.-S., Liang, T.-J., Chen, J.-F.: Transformerless DC–DC converters with high step-up voltage gain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56(8), 3144–3152 (2009)
Yang, L.-S., Liang, T.-J.: Analysis and implementation of a novel bidirectional DC–DC converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(1), 422–434 (2012)
Hussain, A., Akhtar, R., Ali, B., Awan, S.E., Iqbal, S.: A novel bidirectional DC–DC converter with low stress and low magnitude ripples for stand-alone photovoltaic power systems. Energies 12(15), 1–29 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/en12152884
Zhang, Y., Gao, Y., Li, J., Wang, M.S.P., Zhou, L.: High ratio bidirectional DC–DC converter with a synchronous rectification H-bridge for hybrid energy sources electric vehicles. J. Power Electron. 16(6), 2035–2044 (2016)
Zhang, Y., Gao, Y., Li, J., Sumner, M.: A wide voltage-gain range asymmetric H-bridge bidirectional DC–DC converter with a common ground for energy storage systems. J. Power Electron. 18(2), 343–355 (2018)
Lai, C.-M.: Development of a novel bidirectional DC/DC converter topology with high voltage conversion ratio for electric vehicles and DC-microgrids. Energies 9(6), 1–25 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3390/en9060410
Ma, C.-T.: Design and implementation of a bidirectional DC/DC converter for BESS operations. In: Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, vol. II (2017)
Narasimharaju, B.L., Reddy, U.R., Dogga, R.: Design and analysis of voltage clamped bidirectional DC–DC converter for energy storage applications. J. Eng. 2018(7), 367–374 (2018)
Razzaghzadeh, B., Salimi, M.: Analysis of a bidirectional DC–DC converter with high voltage gain. BEEI 4(4), 280–288 (2015)
Babaei, E., Saadatizadeh, Z., Cecati, C.: High step-up high step-down bidirectional DC/DC converter. IET Power Electron. 10(12), 1556–1571 (2017)
Babes, B., Boutaghane, A., Hamouda, N., Mezaache, M., Kahla, S.: A robust adaptive fuzzy fast terminal synergetic voltage control scheme for DC/DC buck converter. In: 2019 International Conference on Advanced Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), pp. 1–5 (2019)
Babes, B., Boutaghane, A., Hamouda, N., Mezaache, M.: Design of a robust voltage controller for a DC–DC buck converter using fractional-order terminal sliding mode control strategy. In: 2019 International Conference on Advanced Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), pp 1–6 (2019)
Erickson, R.W., Maksimovic, D.: Fundamentals of Power Electronics, Chap. 4, 2nd edn. Kluwer, Norwell (2001)
Kazimierczuk, M.K.: Pulse-Width Modulated DC–DC Power Converters, 1st edn. Wiley, Chichester (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somalinga, S.S., Santha, K. Modified high-efficiency bidirectional DC–DC converter topology. J. Power Electron. 21, 257–268 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-020-00160-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-020-00160-1