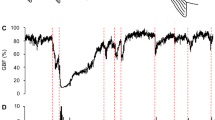
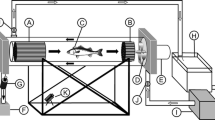
Abstract
Heart rate (HR) has been proven to be an informative indicator of metabolism in mollusks. Extensive studies showed that the HR determination of mollusks under different environmental conditions can help to investigate the mechanisms how these species physiologically respond to the environmental stresses and to understand the ecological impacts of environment stresses. Recently, infrared radiation sensors have been widely used for heart rate measurement. Along with the development of related techniques, the applications of HR measurement of mollusks have been introduced in many fields, including ecology, aquaculture, and ecotoxicology. In this chapter, we briefly introduce the method of HR measurement in mollusks using infrared radiation sensors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chelazzi G, Williams GA, Gray DR (1999) Field and laboratory measurement of heart rate in a tropical limpet, Cellana grata. J Mar Biol Assoc U K 79:749–751
Chen N, Luo X, Gu Y, Han GD, Dong YW, You WW, Ke CH (2016) Assessment of the thermal tolerance of abalone based on cardiac performance in Haliotis discus hannai, H. gigantea and their interspecific hybrid. Aquaculture 465:258–264
Curtis TM, Williamson R, Depledge MH (2000) Simultaneous, long-term monitoring of valve and cardiac activity in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis exposed to copper. Mar Biol 136:837–846
Depledge MH, Andersen BB (1990) A computer-aided physiological monitoring system for continuous, long-term recording of cardiac activity in selected invertebrates. Comp Biochem Physiol 96:473–477
Deutsch CA, Tewksbury JJ, Huey RB, Sheldon KS, Ghalambor CK, Haak DC, Martin PR (2008) Impacts of climate warming on terrestrial ectotherms across latitude. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:6668–6672
Dong YW, Williams GA (2011) Variations in cardiac performance and heat shock protein expression to thermal stress in two differently zoned limpets on a tropical rocky shore. Mar Biol 158:1223–1231
Dong YW, Han GD, Ganmanee M, Wang J (2015) Latitudinal variability of physiological responses to heat stress of the intertidal limpet Cellana toreuma along the Asian coast. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 529:107–119
Dong YW, Li XX, Choi F, Williams GA, Somero GN, Helmuth B (2017) Untangling the roles of microclimate, behavior and physiological polymorphism in governing vulnerability of intertidal snails to heat stress. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 284:20162367
Han GD, Zhang S, Marshall DJ, Ke CH, Dong YW (2013) Metabolic energy sensors (AMPK and SIRT1), protein carbonylation and cardiac failure as biomarkers of thermal stress in an intertidal limpet: linking energetic allocation with environmental temperature during aerial emersion. J Exp Biol 216:3273–3282
Helm MM, Trueman ER (1967) The effect of exposure on the heart rate of the mussel, Mytilus edulis L. Comp Biochem Physiol 21:171–177
Marshall DJ, Dong YW, McQuaid CD, Williams GA (2011) Thermal adaptation in the intertidal snail Echinolittorina malaccana contradicts current theory by revealing the crucial roles of resting metabolism. J Exp Biol 214:3649–3657
Seo E, Sazi T, Togawa M, Nagata O, Murakami M, Kojima S, Seo Y (2016) A portable infrared photoplethysmograph: heartbeat of Mytilus galloprovincialis analyzed by MRI and application to Bathymodiolus septemdierum. Biol Open 5:1752–1757
Sinclair BJ, Marshall KE, Sewell MA, Levesque DL, Willett CS, Slotsbo S, Dong YW, Harley CDG, Marshall DJ, Helmuth BS, Huey RB (2016) Can we predict ectotherm responses to climate change using thermal performance curves and body temperatures? Ecol Lett 19:1372–1385
Stenseng E, Braby CE, Somero GN (2005) Evolutionary and acclimation-induced variation in the thermal limits of heart function in congeneric marine snails (genus Tegula): implications for vertical zonation. Biol Bull 208:138–144
Stillman J, Somero G (1996) Adaptation to temperature stress and aerial exposure in congeneric species of intertidal porcelain crabs (genus Petrolisthes): correlation of physiology, biochemistry and morphology with vertical distribution. J Exp Biol 199:1845–1855
Sunday JM, Bates AE, Kearney MR, Colwell RK, Dulvy NK, Longino JT, Huey RB (2014) Thermal-safety margins and the necessity of thermoregulatory behavior across latitude and elevation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:5610–5615
Xing Q, Li YP, Guo HB, Yu Q, Huang XT, Wang S, Hu XL, Zhang LL, Bao ZM (2016) Cardiac performance: a thermal tolerance indicator in scallops. Mar Biol 163:244
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Science Press and Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Dong, Y., Han, G., Li, X. (2021). Heart Rate Measurement in Mollusks. In: Gao, K., Hutchins, D.A., Beardall, J. (eds) Research Methods of Environmental Physiology in Aquatic Sciences. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5354-7_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5354-7_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-5353-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-5354-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)