Abstract
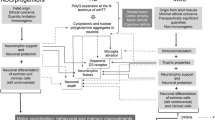
Huntington’s disease (HD) is an inherited neurodegenerative disorder which is characterised by a triad of highly debilitating motor, cognitive, and psychiatric symptoms. While cell death occurs in many brain regions, GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs) in the striatum experience preferential and extensive degeneration. Unlike most neurodegenerative disorders, HD is caused by a single genetic mutation resulting in a CAG repeat expansion and the production of a mutant Huntingtin protein (mHTT). Despite identifying the mutation causative of HD in 1993, there are currently no disease-modifying treatments for HD. One potential strategy for the treatment of HD is the development of cell-based therapies. Cell-based therapies aim to restore neuronal circuitry and function by replacing lost neurons, as well as providing neurotropic support to prevent further degeneration. In order to successfully restore basal ganglia functioning in HD, cell-based therapies would need to reconstitute the complex signalling network disrupted by extensive MSN degeneration. This chapter will discuss the potential use of foetal tissue grafts, pluripotent stem cells, neural stem cells, and somatic cell reprogramming to develop cell-based therapies for treating HD.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. An, N. Zhang, G. Scott, D. Montoro, T. Wittkop, S. Mooney, S. Melov, L.M. Ellerby, Genetic correction of Huntington’s disease phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 11, 253–263 (2012)
M.C. An, R.N. O’Brien, N. Zhang, B.N. Patra, M. De La Cruz, A. Ray, L.M. Ellerby, Polyglutamine disease modeling: epitope based screen for homologous recombination using CRISPR/Cas9 system. PLoS Curr, 1 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/currents.hd.0242d2e7ad72225efa72f6964589369a
C. Arber, S.V. Precious, S. Cambray, J.R. Risner-Janiczek, C. Kelly, Z. Noakes, M. Fjodorova, A. Heuer, M.A. Ungless, T.A. Rodriguez, A.E. Rosser, S.B. Dunnett, M. Li, Activin A directs striatal projection neuron differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Development 142, 1375–1386 (2015)
L. Aubry, A. Bugi, N. Lefort, F. Rousseau, M. Peschanski, A.L. Perrier, Striatal progenitors derived from human ES cells mature into DARPP32 neurons in vitro and in quinolinic acid-lesioned rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 16707–16712 (2008)
A.C. Bachoud-Levi, P. Remy, J.P. Nguyen, P. Brugieres, J.P. Lefaucheur, C. Bourdet, S. Baudic, V. Gaura, P. Maison, B. Haddad, M.F. Boisse, T. Grandmougin, R. Jeny, P. Bartolomeo, G. Dalla Barba, J.D. Degos, F. Lisovoski, A.M. Ergis, E. Pailhous, P. Cesaro, P. Hantraye, M. Peschanski, Motor and cognitive improvements in patients with Huntington’s disease after neural transplantation. Lancet 356, 1975–1979 (2000)
A.-C. Bachoud-Lévi, V. Gaura, P. Brugières, J.-P. Lefaucheur, M.-F. Boissé, P. Maison, S. Baudic, M.-J. Ribeiro, C. Bourdet, P. Remy, Effect of fetal neural transplants in patients with Huntington’s disease 6 years after surgery: a long-term follow-up study. Lancet Neurol 5, 303–309 (2006)
R.A. Barker, S.L. Mason, T.P. Harrower, R.A. Swain, A.K. Ho, B.J. Sahakian, R. Mathur, S. Elneil, S. Thornton, C. Hurrelbrink, The long-term safety and efficacy of bilateral transplantation of human fetal striatal tissue in patients with mild to moderate Huntington’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 84, 657–665 (2013)
A. Benraiss, S.A. Goldman, Cellular therapy and induced neuronal replacement for Huntington’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 8, 577–590 (2011)
A. Brederlau, A.S. Correia, S.V. Anisimov, M. Elmi, G. Paul, L. Roybon, A. Morizane, F. Bergquist, I. Riebe, U. Nannmark, Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cells to a rat model of Parkinson’s disease: effect of in vitro differentiation on graft survival and teratoma formation. Stem Cells 24, 1433–1440 (2006)
C. Cepeda, N. Wu, V.M. André, D.M. Cummings, M.S. Levine, The corticostriatal pathway in Huntington’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 81, 253–271 (2007)
C. Cepeda, V.M. Andre, I. Yamazaki, N. Wu, M. Kleiman-Weiner, M.S. Levine, Differential electrophysiological properties of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-containing striatal medium-sized spiny neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 27, 671–682 (2008)
K. Chen, S.M. Hughes, B. Connor, Neural progenitor cells derived from the adult rat subventricular zone: characterization and transplantation. Cell Transplant. 16, 799–810 (2007)
Y. Chen, R.L. Carter, I.K. Cho, A.W. Chan, Cell-based therapies for Huntington’s disease. Drug Discov. Today 19, 980–984 (2014)
G. Cisbani, M. Saint-Pierre, F. Cicchetti, Single-cell suspension methodology favors survival and vascularization of fetal striatal grafts in the YAC128 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Cell Transplant. 23, 1267–1278 (2014)
D.J. Clarke, S.B. Dunnett, O. Isacson, A. Björklund, Striatal grafts in the ibotenic acid-lesioned neostriatum: ultrastructural and immunocytochemical studies. Prog. Brain Res. 78, 47–53 (1988a)
D.J. Clarke, S.B. Dunnett, O. Isacson, D.J.S. Sirinathsinghji, A. Björklund, Striatal grafts in rats with unilateral neostriatal lesions—I. Ultrastructural evidence of afferent synaptic inputs from the host nigrostriatal pathway. Neuroscience 24, 791–801 (1988b)
P. Dayalu, R.L. Albin, Huntington disease: pathogenesis and treatment. Neurol. Clin. 33, 101–114 (2015)
A.W. Deckel, T.H. Moran, J.T. Coyle, P.R. Sanberg, R.G. Robinson, Anatomical predictors of behavioral recovery following fetal striatal transplants. Brain Res. 365, 249–258 (1986)
A. Delli Carri, M. Onorati, M.J. Lelos, V. Castiglioni, A. Faedo, R. Menon, S. Camnasio, R. Vuono, P. Spaiardi, F. Talpo, M. Toselli, G. Martino, R.A. Barker, S.B. Dunnett, G. Biella, E. Cattaneo, Developmentally coordinated extrinsic signals drive human pluripotent stem cell differentiation toward authentic DARPP-32+ medium-sized spiny neurons. Development 140, 301–312 (2013)
S.B. Dunnett, O. Isacson, D.J.S. Sirinathsinghji, D.J. Clarke, A. Björklund, Striatal grafts in rats with unilateral neostriatal lesions—III. Recovery from dopamine-dependent motor asymmetry and deficits in skilled paw reaching. Neuroscience 24, 813–820 (1988a)
S.B. Dunnett, O. Isacson, D.J.S. Sirinathsinghji, D.J. Clarke, A. Björklund, Striatal grafts in the ibotenic acid-lesioned neostriatum: functional studies. Prog. Brain Res. 78, 39–45 (1988b)
S.B. Dunnett, F. Nathwani, A. Björklund, The integration and function of striatal grafts. Prog. Brain Res. 127, 345–380 (2000)
M. Farrington, T.G. Wreghitt, A.M.L. Lever, S.B. Dunnett, A.E. Rosser, R.A. Barker, Neural transplantation in Huntington’s disease: the NEST-UK donor tissue microbiological screening program and review of the literature. Cell Transplant. 15, 279–294 (2006)
T.B. Freeman, R.A. Hauser, A.E. Willing, T. Zigova, P.R. Sanberg, S. Saporta, Transplantation of human fetal striatal tissue in Huntington’s disease: rationale for clinical studies, in Neural Transplantation in Neurodegenerative Disease: Current Status and New Directions, Novartis Foundation Symposium 231, (Wiley, Chichester, 2000a), pp. 129–144
T.B. Freeman, F. Cicchetti, R.A. Hauser, T.W. Deacon, X.J. Li, S.M. Hersch, G.M. Nauert, P.R. Sanberg, J.H. Kordower, S. Saporta, O. Isacson, Transplanted fetal striatum in Huntington’s disease: phenotypic development and lack of pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 13877–13882 (2000b)
S. Furtado, V. Sossi, R.A. Hauser, A. Samii, M. Schulzer, C.B. Murphy, T.B. Freeman, A.J. Stoessl, Positron emission tomography after fetal transplantation in Huntington’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 58, 331–337 (2005)
P. Gallina, M. Paganini, A. Di Rita, L. Lombardini, M. Moretti, G.B. Vannelli, N. Di Lorenzo, Human fetal striatal transplantation in Huntington’s disease: a refinement of the stereotactic procedure. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 86, 308–313 (2008)
V. Gaura, A.C. Bachoud-Lévi, M.J. Ribeiro, J.P. Nguyen, V. Frouin, S. Baudic, P. Brugières, J.F. Mangin, M.F. Boissé, S. Palfi, Striatal neural grafting improves cortical metabolism in Huntington’s disease patients. Brain 127, 65–72 (2004)
L.R. Gauthier, B.C. Charrin, M. Borrell-Pagès, J.P. Dompierre, H. Rangone, F.P. Cordelières, J. De Mey, M.E. MacDonald, V. Leßmann, S. Humbert, Huntingtin controls neurotrophic support and survival of neurons by enhancing BDNF vesicular transport along microtubules. Cell 118, 127–138 (2004)
R.J. Gordon, A.S. Tattersfield, E.M. Vazey, A.P. Kells, A.L. McGregor, S.M. Hughes, B. Connor, Temporal profile of subventricular zone progenitor cell migration following quinolinic acid–induced striatal cell loss. Neuroscience 146, 1704–1718 (2007)
R.J. Gordon, A.L. McGregor, B. Connor, Chemokines direct neural progenitor cell migration following striatal cell loss. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 41, 219–232 (2009)
X. Guo, M.-H. Disatnik, M. Monbureau, M. Shamloo, D. Mochly-Rosen, X. Qi, Inhibition of mitochondrial fragmentation diminishes Huntington’s disease–associated neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 5371 (2013)
A.D. Ha, J. Jankovic, Exploring the correlates of intermediate CAG repeats in Huntington disease. Postgrad. Med. 123, 116–121 (2011)
R.A. Hauser, S. Furtado, C.R. Cimino, H. Delgado, S. Eichler, S. Schwartz, D. Scott, G.M. Nauert, E. Soety, V. Sossi, Bilateral human fetal striatal transplantation in Huntington’s disease. Neurology 58, 687–695 (2002)
O. Isacson, X.O. Breakefield, Benefits and risks of hosting animal cells in the human brain. Nat. Med. 3, 964–969 (1997)
O. Isacson, S.B. Dunnett, A. Björklund, Graft-induced behavioral recovery in an animal model of Huntington disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 83, 2728–2732 (1986)
I. Jeon, N. Lee, J.-Y. Li, I.-H. Park, K.S. Park, J. Moon, S.H. Shim, C. Choi, D.-J. Chang, J. Kwon, S.-H. Oh, D.A. Shin, H.S. Kim, J.T. Do, D.R. Lee, M. Kim, K.-S. Kang, G.Q. Daley, P. Brundin, J. Song, Neuronal properties, in vivo effects, and pathology of a Huntington’s disease patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 30, 2054–2062 (2012)
A.J. Joannides, D.J. Webber, O. Raineteau, C. Kelly, K.A. Irvine, C. Watts, A.E. Rosser, P.J. Kemp, W.F. Blakemore, A. Compston, M.A. Caldwell, N.D. Allen, S. Chandran, Environmental signals regulate lineage choice and temporal maturation of neural stem cells from human embryonic stem cells. Brain 130, 1263–1275 (2007)
V. Johann, J. Schiefer, C. Sass, J. Mey, G. Brook, A. Krüttgen, C. Schlangen, C. Bernreuther, M. Schachner, M. Dihné, Time of transplantation and cell preparation determine neural stem cell survival in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Exp. Brain Res. 177, 458–470 (2007)
K.S. Jones, B. Connor, Proneural transcription factors Dlx2 and Pax6 are altered in adult SVZ neural precursor cells following striatal cell loss. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 47, 53–60 (2011)
K.S. Jones, B.J. Connor, The effect of pro-neurogenic gene expression on adult subventricular zone precursor cell recruitment and fate determination after excitotoxic brain injury. J. Stem Cells Regen. Med 12, 25 (2016)
T.A. Juopperi, W.R. Kim, C.-H. Chiang, H. Yu, R.L. Margolis, C.A. Ross, G. Ming, H. Song, Astrocytes generated from patient induced pluripotent stem cells recapitulate features of Huntington’s disease patient cells. Mol. Brain 5, 17 (2012)
A.L. Kendall, F.D. Rayment, E.M. Torres, H.F. Baker, R.M. Ridley, S.B. Dunnet, Functional integration of striatal allografts in a primate model of Huntington’s disease. Nat. Med. 4, 727–729 (1998)
A. Klein, E.L. Lane, S.B. Dunnett, Brain repair in a unilateral rat model of Huntington’s disease: new insights into impairment and restoration of forelimb movement patterns. Cell Transplant. 22, 1735–1751 (2013)
P. Krystkowiak, V. Gaura, M. Labalette, A. Rialland, P. Remy, M. Peschanski, A.-C. Bachoud-Lévi, Alloimmunisation to donor antigens and immune rejection following foetal neural grafts to the brain in patients with Huntington’s disease. PLoS One 2, e166 (2007)
I. Kulbatski, Stem/precursor cell-based CNS therapy: the importance of circumventing immune suppression by transplanting autologous cells. Stem Cell Rev. 6, 405–410 (2010)
C. Landles, G.P. Bates, Huntingtin and the molecular pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease. EMBO Rep. 5, 958–963 (2004)
S.-T. Lee, K. Chu, J.-E. Park, K. Lee, L. Kang, S.U. Kim, M. Kim, Intravenous administration of human neural stem cells induces functional recovery in Huntington’s disease rat model. Neurosci. Res. 52, 243–249 (2005)
S.-T. Lee, J.-E. Park, K. Lee, L. Kang, K. Chu, S.U. Kim, M. Kim, J.-K. Roh, Noninvasive method of immortalized neural stem-like cell transplantation in an experimental model of Huntington’s disease. J. Neurosci. Methods 152, 250–254 (2006)
L. Ma, B. Hu, Y. Liu, S.C. Vermilyea, H. Liu, L. Gao, Y. Sun, X. Zhang, S.-C. Zhang, Human embryonic stem cell-derived GABA neurons correct locomotion deficits in quinolinic acid-lesioned mice. Cell Stem Cell 10, 455–464 (2012)
V.B. Mattis, C.N. Svendsen, Modeling Huntingtons disease with patient-derived neurons. Brain Res. 1656, 76 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.10.001
J.L. McBride, S.P. Behrstock, E.Y. Chen, R.J. Jakel, I. Siegel, C.N. Svendsen, J.H. Kordower, Human neural stem cell transplants improve motor function in a rat model of Huntington’s disease. J. Comp. Neurol. 475, 211–219 (2004)
R.R. Mitchell, E. Szabo, Y.D. Benoit, D.T. Case, R. Mechael, J. Alamilla, J.H. Lee, A. Fiebig-Comyn, D.C. Gillespie, M. Bhatia, Activation of neural cell fate programs toward direct conversion of adult human fibroblasts into tri-potent neural progenitors using OCT-4. Stem Cells Dev. 23, 1937–1946 (2014)
N. Nakao, T. Itakura, Fetal tissue transplants in animal models of Huntington’s disease: the effects on damaged neuronal circuitry and behavioral deficits. Prog. Neurobiol. 61, 313–338 (2000)
I. Nasonkin, V. Mahairaki, L. Xu, G. Hatfield, B.J. Cummings, C. Eberhart, D.K. Ryugo, D. Maric, E. Bar, V.E. Koliatsos, Long-term, stable differentiation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors grafted into the adult mammalian neostriatum. Stem Cells 27, 2414–2426 (2009)
C. Nicoleau, C. Varela, C. Bonnefond, Y. Maury, A. Bugi, L. Aubry, P. Viegas, F. Bourgois-Rocha, M. Peschanski, A.L. Perrier, Embryonic stem cells neural differentiation qualifies the role of Wnt/beta-catenin signals in human telencephalic specification and regionalization. Stem Cells 31, 1763–1774 (2013)
S. Palfi, F. Condé, D. Riche, E. Brouillet, C. Dautry, V. Mittoux, A. Chibois, M. Peschanski, P. Hantraye, Fetal striatal allografts reverse cognitive deficits in a primate model of Huntington disease. Nat. Med. 4, 963–966 (1998)
M. Pritzel, O. Isacson, P. Brundin, L. Wiklund, A. Björklund, Afferent and efferent connections of striatal grafts implanted into the ibotenic acid lesioned neostriatum in adult rats. Exp. Brain Res. 65, 112–126 (1986)
I. Reuter, Y.F. Tai, N. Pavese, K.R. Chaudhuri, S. Mason, C.E. Polkey, C. Clough, D.J. Brooks, R.A. Barker, P. Piccini, Long-term clinical and positron emission tomography outcome of fetal striatal transplantation in Huntington’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 948–951 (2008)
K.L. Ring, L.M. Tong, M.E. Balestra, R. Javier, Y. Andrews-Zwilling, G. Li, D. Walker, W.R. Zhang, A.C. Kreitzer, Y. Huang, Direct reprogramming of mouse and human fibroblasts into multipotent neural stem cells with a single factor. Cell Stem Cell 11, 100–109 (2012)
C.A. Ross, S.J. Tabrizi, Huntington’s disease: from molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. Lancet Neurol 10, 83–98 (2011)
A.L. Ross, D.E. Leder, J. Weiss, J. Izakovic, J.M. Grichnik, Genomic instability in cultured stem cells: associated risks and underlying mechanisms. Regen. Med. 6, 653–662 (2011)
A.E. Rosser, R.A. Barker, T. Harrower, C. Watts, M. Farrington, A.K. Ho, R.M. Burnstein, D.K. Menon, J.H. Gillard, J. Pickard, Unilateral transplantation of human primary fetal tissue in four patients with Huntington’s disease: NEST-UK safety report ISRCTN no 36485475. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 73, 678–685 (2002)
J.K. Ryu, J. Kim, S.J. Cho, K. Hatori, A. Nagai, H.B. Choi, M.C. Lee, J.G. McLarnon, S.U. Kim, Proactive transplantation of human neural stem cells prevents degeneration of striatal neurons in a rat model of Huntington disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 16, 68–77 (2004)
H. Sakahira, P. Breuer, M.K. Hayer-Hartl, F.U. Hartl, Molecular chaperones as modulators of polyglutamine protein aggregation and toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 16412–16418 (2002)
D.J. Sirinathsinghji, S.B. Dunnett, O. Isacson, D.J. Clarke, K. Kendrick, A. Bjorklund, Striatal grafts in rats with unilateral neostriatal lesions—II. In vivo monitoring of GABA release in globus pallidus and substantia nigra. Neuroscience 24, 803–811 (1988)
J. Song, S.T. Lee, W. Kang, J.E. Park, K. Chu, S.E. Lee, T. Hwang, H. Chung, M. Kim, Human embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursor transplants attenuate apomorphine-induced rotational behavior in rats with unilateral quinolinic acid lesions. Neurosci. Lett. 423, 58–61 (2007)
Y. Sun, A. Savanenin, P.H. Reddy, Y.F. Liu, Polyglutamine-expanded huntingtin promotes sensitization of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors via post-synaptic density 95. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 24713–24718 (2001)
K. Takahashi, S. Yamanaka, Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676 (2006)
K. Takahashi, K. Tanabe, M. Ohnuki, M. Narita, T. Ichisaka, K. Tomoda, S. Yamanaka, Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131, 861–872 (2007)
T.S. Tang, E. Slow, V. Lupu, I.G. Stavrovskaya, M. Sugimori, R. Llinas, B.S. Kristal, M.R. Hayden, I. Bezprozvanny, Disturbed Ca2+ signaling and apoptosis of medium spiny neurons in Huntington’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 2602–2607 (2005)
The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group, A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. Cell 72, 971–983 (1993)
E.M. Vazey, B. Connor, Differential fate and functional outcome of lithium chloride primed adult neural progenitor cell transplants in a rat model of Huntington disease. Stem Cell Res Ther 1, 41 (2010)
E.M. Vazey, K. Chen, S.M. Hughes, B. Connor, Transplanted adult neural progenitor cells survive, differentiate and reduce motor function impairment in a rodent model of Huntington’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 199, 384–396 (2006)
E.M. Vazey, M. Dottori, P. Jamshidi, D. Tomas, M.F. Pera, M. Horne, B. Connor, Comparison of transplant efficiency between spontaneously derived and noggin-primed human embryonic stem cell neural precursors in the quinolinic acid rat model of Huntington’s disease. Cell Transplant. 19, 1055–1062 (2010)
M.B. Victor, M. Richner, T.O. Hermanstyne, J.L. Ransdell, C. Sobieski, P.-Y. Deng, V.A. Klyachko, J.M. Nerbonne, A.S. Yoo, Generation of human striatal neurons by microRNA-dependent direct conversion of fibroblasts. Neuron 84, 311–323 (2014)
P. Weydt, S.M. Soyal, C. Gellera, S. DiDonato, C. Weidinger, H. Oberkofler, G.B. Landwehrmeyer, W. Patsch, The gene coding for PGC-1α modifies age at onset in Huntington’s. Mol. Neurodegener. 4, 3 (2009)
C. Zuccato, M. Tartari, A. Crotti, D. Goffredo, M. Valenza, L. Conti, T. Cataudella, B.R. Leavitt, M.R. Hayden, T. Timmusk, D. Rigamonti, E. Cattaneo, Huntingtin interacts with REST/NRSF to modulate the transcription of NRSE-controlled neuronal genes. Nat. Genet. 35, 76–83 (2003)
C. Zuccato, M. Marullo, P. Conforti, M.E. MacDonald, M. Tartari, E. Cattaneo, Systematic assessment of BDNF and its receptor levels in human cortices affected by Huntington’s disease. Brain Pathol. 18, 225–238 (2008)
C. Zuccato, M. Valenza, E. Cattaneo, Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutical targets in Huntington’s disease. Physiol. Rev. 90, 905–981 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Monk, R., Connor, B. (2020). Cell Replacement Therapy for Huntington’s Disease. In: Han, F., Lu, P.(. (eds) Stem Cell-based Therapy for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1266. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4370-8_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4370-8_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-4369-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-4370-8
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)