Summary
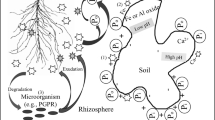
This chapter discusses the processes in the rhizosphere that are determined by exudates from roots and that in turn affect the availability of phosphorus to plants. These include control of rhizosphere pH, exudation of organic acids and root phosphatases. Possibilities for manipulating these processes in order to improve phosphorus acquisition in agricultural plants are discussed in the context of the phosphorus cycle in agriculture.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts JMMJG, Hontelez JGJ, Fischer P,Verkerk R, van Kammen A, Zabel P (1991) Acid phosphatase1, a tightly linked molecular maker for root-knot nematode resistance in tomato: from protein to gene, using PCR and degenerate primers containing deoxyinosine. Plant Mol Biol 16: 647–661
Adams MA, Pate JS (1992) Availability of organic and inorganic forms of phosphorus to lupins (Lupinus spp.). Plant Soil 145: 107–113
Ae N,Arihara J, Okada K (1991) Phosphorus uptake mechanisms of Pigeon pea grown in Alfisols and Vertisols. In: Johansen C, Lee KK, Sahrawat KL (Eds) Phosphorus nutrition of grain legumes in the semi-arid Tropics. ICRISAT, Patancheru, AP India, pp 91–98
Ae N,Arihara J, Okada K,Yoshihara T, Otani T, Johansen C (1993) The role of piscidic acid secreted by pigeon pea roots grown on an Alfisol with low-P fertility. In: Randall PJ, Delhaize E, Richards RA, Munns R (Eds) Genetic aspects of plant mineral nutrition. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 279–288
Anderson G (1980) Assessing organic phosphorus in soils. In: Khasawneh FE, Sample EC, Kamprath EJ (Eds) The role of phosphorus in agriculture. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 411–431
Armstrong RD, Helyar KR, Prangnell R (1993) Direct assessment of mineral phosphorus availability to tropical crops using 32P labeled compounds. Plant Soil 150: 279–287
Ascencio J (1996) Growth strategies and utilization of phosphorus in Cajanus cajan L. Millsp. and Desmodium tortuosum (Sw.) DC under phosphorus deficiency. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 27: 1971–1993
Ascencio 1 (1997) Root secreted acid phosphatase kinetics as a physiological marker for phosphorus deficiency. J Plant Nut 20: 9–26
Asmar F (1997) Variation in activity of root extracellular phytase between genotypes of barley. Plant Soil 195: 61–64
Barber SA (1984) Soil nutrient bioavailability. Wiley, New York.
Barrett DJ, Richardson AE, Gifford RM (1998) Elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations increase wheat root phosphatase activity when growth is limited by phosphorus. Aust J Plant Physiol 25: 87–93
Barrett-Lennard EG,Dracup M, Greenway H (1993) Role of extracellular phosphatases in the phosphorus nutrition of clover. J Exp Bot 44: 1595–1600
Barrow NJ (1982) Soil fertility changes. In: Costin AB, Williams CH (Eds) Phosphorus in Australia. Centre for Resource and Environment Studies, Australian National University, Canberra, pp 197–220
Bar-Yosef B (1991) Root excretions and their environmental effects. Influence on availability of phosphorus. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Kafkafi U (Eds) Plant roots. The hidden half. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 529–557
Bekele T, Cino BJ, Ehlert PAI, van der Maas AA, van Diest A (1983) An evaluation of plant-borne factors promoting the solubilization of alkaline rock phosphates. Plant Soil 75: 361–378
Bieleski RL (1973) Phosphate pools, phosphate transport and phosphate availability.Ann Rev Plant Physiol 24: 225–252
Blair G (1993) Nutrient efficiency–what do we really mean? In: Randall PJ, Delhaize E, Richards RA, Munns R (Eds) Genetic aspects of plant mineral nutrition. KluwerAcademic,Dordrecht,pp 205–214
Blair GJ, Mamaril CP, Miller MH (1971) Influence of nitrogen source on phosphorus uptake by corn from soils differing in pH. Agron J 63: 235–238
Bolan NS, Naidu R, Mahimairaja S, Baskaran S (1994) Influence of low molecular-weight organic acids on solubilization of phosphates. Biol Fertil Soils 18: 311–319
Bosse D, Kock M (1998) Influence of phosphate starvation on phosphohydrolases during development of tomato seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 21: 325–332
Bowen GD (1980) Misconceptions, concepts and approaches in rhizosphere biology. In: Elwood DG, (Ed) Contemporary microbial ecology. Academic, London, pp 283–304
Braum SM, Helmke PA (1995) White lupin utilizes soil phosphorus that is unavailable to soybean. Plant Soil 176: 95–100
Bromfield SM (1958) The solution of y-MnO, by substances released from soil and roots of oats and vetch in relation to manganese availability. Plant Soil 10: 147–160
Caradus JR (1995) Genetic control of phosphorus uptake and phosphorus status in plants. In: Johansen C, Lee KK, Sharma KK, Subbarao GV, Kueneman AE (Eds) Genetic manipulation of crop plants to enhance integrated nutrient management in cropping systems. 1. Phosphorus. ICRISAT, Patancheru, AP India, pp 55–74
Clark RB (1983) Plant genotype differences to uptake, translocation, accumulation, and use of mineral elements. In: Saric MR (Ed) Genetic specificity of mineral nutrition of plants. Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Belgrade, pp 41–55
Cosgrove DJ, Irving GCJ, Bromfield SM (1970) Inositol phosphate phosphatases of microbiological origin. The isolation of soil bacteria having inositol phosphate phosphatase activity. Aust J Biol Sci 23: 339–343
Curl EA, Trueglove B (1986) The rhizosphere. Springer, Berlin
Dalal RC (1977) Soil organic phosphorus.AdvAgron 29: 85–117
Darrah PR (1993) The rhizosphere and plant nutrition: a quantitative approach. In: Barrow NJ (Ed) Plant nutrition–from genetic engineering to field practice. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 3–22
de la Fuente JM, Ramirez-Rodriguez V, Cabrera-Ponce JL, Herrera-Estrella L (1997) Aluminumtolerance in transgenic plants by alteration of citrate synthesis. Science 276: 1566–1588
Delhaize E, and Ryan PR (1995) Aluminum toxicity and tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol 107: 315–321
Delhaize E, Randall PJ, Wallace PA, Pinkerton A (1993a) Screening Arabidopsis for mutants in mineral nutrition. Plant Soil 155 /156: 131–134
Delhaize E, Ryan PR, Randall PJ (1993b) Aluminum tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). II. Aluminum-stimulated excretion of malic acid from root apices. Plant Physiol 103: 695–702
Dinkelaker B, Romheld V, Marschner H (1989) Citric acid excretion and precipitation of calcium citrate in the rhizosphere of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Cell Environ 12: 285–292
Dinkelaker B, Hengeler C, Marschner H (1995) Distribution and function of proteoid roots and other root clusters. Bot Acta 108: 183–200
Dracup MNH, Barrett-Lennard EG,Greenway H, Robson AD (1984) Effect of phosphorus deficiency on phosphatase activity of cell walls from roots of subterranean clover. J Exp Bot 35: 466–480
Duff SMG, Plaxton WC, Lefebvre DD (1991) Phosphate-starvation response in plant cells: De novo synthesis and degradation of acid phosphatases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9538–9542
Duff SMG, Sarath G, Plaxton WC (1994) The role of acid phosphatases in plant phosphorus me-tabolism. Physiol Plant 90: 791–800
Findenegg GR,Nelemans JA (1993) The effect of phytase on the availability of P from myo-inositol hexaphosphate (phytate) for maize roots. Plant Soil 154: 189–196
Gahoonia TS, Claassen N, Junk A (1992) Mobilization of phosphate in different soils by ryegrass supplied with ammonium or nitrate. Plant Soil 140: 241–248
Gardner WK, Barber DA, Parbery DG (1982a) The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albus L. I. Some characteristics of the soil/root interface. Plant Soil 68: 19–32
Gardner WK, Parbery DG, Barber DA (1982b) The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albus L. II. The effect of varying phosphorus supply and soil type on some characteristics of the soil-root interface. Plant Soil 68: 33–41
Gardner WK, Barber DD, Parbery DG (1983) The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albus L. III. The probable mechanisms by which phosphorus movement in the soil/root interface is enhanced. Plant Soil 70: 107–124
Gerke J, Romer W, Jungk A (1994) The excretion of citric and malic acid by proteoid roots of Lupinus albus L.: effects on soil solution concentrations of phosphate, iron, and aluminum in the proteoid rhizosphere in samples of an oxisol and a luvisol. Z Pflanzenernahr Bodenkd 157: 289–294
Gerke J, Meyer U, Romer W (1995) Phosphate, Fe and Mn uptake of N2 fixing red clover and ryegrass from an Oxisol as affected by P and model humic substances application. 1. Plant parameters and soil solution composition. Z Pflanzenernahr Bodenkd 158: 261–268
Gibson DM, Ullah AHJ (1988) Purification and characterization of phytase from cotyledons of germinating soybean seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys 260: 503–513
Godo GH, Reisenauer HM (1980) Plant effects on soil manganese availability. Soil Sci Soc Am J 34: 993–995
Goldstein AH, Baertlein DA, McDaniel RG (1988) Phosphate starvation inducible metabolism in Lycopersicon esculentum. I. Excretion of acid phosphatase by tomato plants and suspension-cultured cells. Plant Physiol 87: 711–715
Graham RD (1984) Breeding for nutritional characteristics. In: Tinker PB, Lauchli A (Eds) Advances in plant nutrition. Praeger, New York, Vol 1, pp 57–102
Grierson PF (1992) Organic acids in the rhizosphere of Banksia integrifolia L.f. Plant Soil 144: 259265
Handreck KA (1996) Phosphorus requirements of Australian native plants. Aust J Soil Res 35: 241–289
Harrison AF (1987) Soil organic phosphorus: A world review. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau, International, Wallingford, UK
Hayes JE, Richardson AE, Simpson RJ (1999) Phytase and acid phosphatase activities in extracts
from roots of temperate pasture grass and legume seedlings. Aust J Plant Physiol 26:801–809 Haynes RJ (1990) Active ion uptake and maintenance of cation-anion balance: A critical examina-tion of their role in regulating rhizosphere pH. Plant Soil 126: 247–264
Hedley MJ, Nye PH, White RE (1983) Plant induced changes in the rhizosphere of rape (Brassica napus var. Emerald) seedlings. IV. The effect of rhizosphere phosphorus status on the pH, phosphatase activity and depletion of soil phosphorus fractions in the rhizosphere and on cation-anion balance in the plants. New Phytol 95: 69–82
Heinrich PA, Mulligan DR, Patrick JW (1988) The effect of ectomycorrhizas on the phosphorus and dry weight acquisition of Eucalyptus seedlings. Plant Soil 109: 147–149
Helal HM (1990) Varietal differences in root phosphatase activity as related to the utilization of organic phosphates. In: El Bassam N, Dambroth M, Loughman BC (Eds) Genetic aspects of plant mineral nutrition. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 103–105
Helal HM, Sauerbeck D (1991) Soil and root phosphatase activity and the utilization of inositol phosphates as dependent on phosphorus supply. In: McMichael BL, Persson H (Eds) Plant roots and their environment. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 93–97
Hendriks L, Claassen N, Jungk A (1981) Phosphatverarmung des wurzelnahen Bodens and Phosphataufnahme von Mais and Raps. Z Pflanzenernahr Bodenkd 144: 486–499
Hilger AB, Krause HH (1989) Growth characteristics of Laccaria laccata and Paxillus involutus in liquid culture media with inorganic and organic phosphorus sources. Can J Bot 67: 1782–1789
Hinsinger P, Gilkes RJ (19%) Mobilization of phosphate from phosphate rock and alumina-sorbedphosphate by the roots of ryegrass and clover as related to rhizosphere pH. Eur J Soil Sci 47: 533–544
Hinsinger P, Gilkes RJ (1997) Dissolution of phosphate rock in the rhizosphere of five plant spe-cies grown in an acid, P-fixing mineral substrate. Geoderma 75: 231–249
Hocking PJ, Keerthisinghe G, Smith FW, Randall PJ (1997) Comparison of the ability of different crop species to access poorly-available soil phosphorus. In: Ando T, Fujita K, Mae T, Matsumoto H, Mori S, Sekiya J (Eds) Proceedings XIII International plant nutrition colloquium. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 305–308
Hoffland E (1992) Quantitative evaluation of the role of organic acid exudation in the mobilization of rock phosphate by rape. Plant Soil 140: 279–289
Hoffland E, Findenegg GR, Nelemans JA (1989) Solubilization of rock phosphate by rape. II. Local root exudation of organic acids as a response to P-starvation. Plant Soil 113: 161–165
Hoffland E,Van den Boogaard R, Nelemans J, Findenegg G (1992) Biosynthesis and root exudation of citric and malic acids in phosphate-starved rape plants. New Phytol 122: 675–680
Hübel F, Beck E (1993) In-situ determination of the P-relations around the primary root of maize with respect to inorganic and phytate-P. Plant Soil 157: 1–9
Hübel F, Beck E (1996) Maize root phytase. Purification, characterization, and localization of enzyme activity and its putative substrate. Plant Physiol 112: 1429–1436
Hue NV, Craddock GR, Adams F (1986) Effect of organic acids on aluminum toxicity in subsoils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50: 28–34
Hunter DA, Watson LM, McManus MT (1999) Cell wall proteins in white clover: influence of plant phosphate status. Plant Physiol Biochem 37: 25–32
Imas P, Bar-Yosef B, Kafkafi U, Ganmore-Neumann R (1997) Phosphate induced carboxylate and proton release by tomato roots. Plant Soil 191: 35–39
Jarvis SC, Robson AD (1983a) A comparison of cation/anion balance of ten cultivars of Trifolium subterraneum L. and their effects on soil acidity. Plant Soil 75: 235–243
Jarvis SC, Robson AD (1983b) The effects of nitrogen nutrition of plants on the development of acidity in Western Australian soils. I. Effects with subterranean clover grown under leaching conditions. Aust J Agric Res 34: 341–353
Jarvis SC, Robson AD (1983c) The effects of nitrogen nutrition of plants on the development of acidity in Western Australian soils. II. Effects of differences in cation-anion balance between plant species grown under non-leaching conditions. Aust J Agric Res 34: 354–365
Jauregui MA, Reisenauer HM (1982) Dissolution of oxides of manganese by root exudate components. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46: 314–317
Jayachandran K, Schwab AP, Hetrick BAD (1992) Mineralization of organic phosphorus by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Biol Biochem 24: 897–903
Jescke WD, Pate JS (1995) Mineral nutrition and transport in xylem and phloem of Banksia prionotes ( Proteaceae), a tree with dimorphic root morphology. J Exp Bot 46: 895–905
Johnson JF, Allan DL, Vance CP (1994) Phosphorus stress-induced proteoid roots show altered metabolism in Lupinus albus. Plant Physiol 104: 657–665
Johnson JF, Allan DL, Vance CP, Weiblen G (1996) Root carbon dioxide fixation by phosphorus-deficient Lupinus albus. Plant Physiol 112: 19–30
Jones DL (1998) Organic acids in the rhizosphere–a critical review. Plant Soil 205: 25–44
Jones DL, Darrah PR (1995) Influx and efflux of organic acids across the soil-root interface of Zea mays L. and its implications in rhizosphere C flow. Plant Soil 173: 103–109
Jones LJ, Darrah PR (1994) Role of root derived organic acids in the mobilization of nutrients from the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 166: 247–2570
Jungk AO (1991) Dynamics of nutrient movement at the soil-root interface. In: Waisel Y, Eshel A, Kafkafi U (Eds) Plant roots: the hidden half. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 455–481
Keerthisinghe G, Hocking PJ, Ryan PR, Delhaize E (1998) Effect of phosphorus supply on the formation and function of proteoid roots of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Cell Environ 21: 467–478
Kirk GJD, Santos EE, Santos MB (1999) Phosphate solubilization by organic anion excretion from rice growing in aerobic soil: rates of excretion and decomposition, effects on rhizosphere pH and effects on phosphate solubility and uptake. New Phytol 142: 185–200
Klabunde T, Stahl B, Suerbaum H, Hahner S, Karas M, Hillenkamp F, Krebs B, Witzel H (1994) The amino acid sequence of the red kidney bean Fe(III)-Zn(II) purple acid phosphatase. Determination of the amino acid sequence by a combination of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and automated Edman sequencing. Eur J Biochem 226: 369–375
Konietzny U, Greiner R, Jany K-D (1995) Purification and characterization of a phytase from spelt. J Food Biochem 18: 165–183
Kroehler CJ, Linkins AE (1991) The absorption of inorganic phosphate from 32P-labeled inositol hexaphosphate by Eriophorum vaginatum. Oecologia 85: 424–428
Kucey RMN, Janzen HH, Leggett ME (1989) Microbially mediated increase in plant available phosphorus. Adv Agron 42: 199–228
Laboure A-M, Gagnon J, Lescure A-M (1993) Purification and characterization of a phytase (myoinositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolase) accumulated in maize (Zea mays) seedlings during germination. Biochem J 295: 413–419
Lefebvre DD, Duff SMG, Fife CA, Julien-Inalsingh C, Plaxton WC (1990) Response to phosphate deprivation in Brassica nigra suspension cells. Enhancement of intracellular, cell surface, and secreted phosphatase activities compared to increases in Pi-absorption rate. Plant Physiol 93: 504–511
Li M, Osaki M, Honma M, Tadano T (1997a) Purification and characterization of phytase induced in tomato roots under phosphorus-deficient conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 43: 179–190
Li M, Osaki M, Rao IM, Tadano T (1997b) Secretion of phytase from the roots of several plant species under phosphorus-deficient conditions. Plant Soil 195: 161–169
Li M, Shinano T, Tadano T (1997c) Distribution of exudates of lupin roots in the rhizosphere under phosphorus deficient conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 43: 237–245
Lipton DS, Blanchar RW, Blevins DG (1987) Citrate, malate, and succinate concentration in exu- dates from P-sufficient and P-stressed Medicago sativa L. seedlings. Plant Physiol 85: 315–317
Loss SP, Robson AD, Ritchie GSP (1993) IT/OH- excretion and nutrient uptake in upper and lower parts of lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) root systems. Ann Bot 72: 315–320
Loss SP, Robson AD, Ritchie GSP (1994) Nutrient uptake and organic acid anion metabolism in lupins and peas supplied with nitrate. Ann Bot 74: 69–74
Marschner H (1986) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic, London
Marschner H, Romheld V, Horst WJ, Martin P (1986) Root induced changes in the rhizosphere: Importance for the mineral nutrition of plants. Z Pflanzenernahr Bodenkd 149: 441–456
Marschner H, Romheld V, Cakmak I (1987) Root-induced changes of nutrient availability in the rhizosphere. J Plant Nut 10: 1175–1184
Martin JK (1970) Preparation of 32P-labeled inositol hexaphosphate. Anal Biochem 36: 233–237
Martin JK (1973) The influence of rhizosphere microflora on the availability of 32P-myo-inositol hexaphosphate phosphorus to wheat. Soil Biol Biochem 5: 473–483
Martin JK, Cartwright B (1971) The comparative plant availability of 32P myo-inositol hexaphosphate and KH232P0, added to soils. Soil Sci Plant Anal 2: 375–381
Maugenest S, Martinez I, Lescure A-M (1997) Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding a maize seedling phytase. Biochem. J. 322: 511–517
Maugenest S, Martinez I, Godin B, Perez P, Lescure A-M (1999) Structure of two maize phytase genes and their spatio-temporal expression during seedling development. Plant Mol Biol 39: 503–514
McLachlan KD (1976) Comparative phosphorus response in plants to a range of available phos-phorus situations. Aust J Agric Res 27: 323–341
McLachlan KD (1980) Acid phosphatase activity of intact roots and phosphorus nutrition in plants. I. Assay conditions and phosphatase activity. Aust J Agric Res 31: 429–440
McLachlan KD, De Marco DG (1982) Acid phosphatase activity of intact roots and phosphorus nutrition of plants. 3. Its relation to phosphorus garnering by wheat and a comparison with leaf activity as a measure of phosphorus status. Aust J Agric Res 33: 1–12
McLaughlin MJ, Alston AM, Martin JK (1988) Phosphorus cycling in wheat-pasture rotations. 1. The source of phosphorus taken up by wheat. Aust J Soil Res 26: 323–331
McLaughlin MJ, Baker TG, James TR, Rundle JA (1990) Distribution and forms of phosphorus and aluminium in acidic topsoils under pastures in south-eastern Australia.Aust J Soil Res 28: 371–385
McLaughlin MJ, Fillery IR, Till AR (1992) Operations of the phosphorus, sulphur and nitrogen cycles. In: Gifford RM, Barson MM (Eds) Australia’s renewable resources: sustainability and global change. Bureau of Rural Resources Proceedings No. 14, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra
Mimura T, Sakano K, Shimmen T (1996) Studies on the distribution, re-translocation and homeostasis of inorganic phosphate in barley leaves. Plant Cell Environ 19: 311–320
Moghimi A, Lewis DG, Oades JM (1978) Release of phosphate from calcium phosphates by rhizosphere products. Soil Biol Biochem 10: 277–281
Moorby H, White RE, Nye PH (1988) The influence of phosphate nutrition on H ion efflux from the roots of young rape plants. Plant Soil 105: 247–256
Neumann G, Massonneau A, Martinoia E, Romheld V (1999) Physiological adaptations to phos-phorus deficiency during proteoid root development in white lupin. Planta 208: 373–382
Newman RH, Tate KR (1980) Soil phosphorus characterisation by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 11: 835–842
Noble AD, Zenneck I, Randall PJ (1996) Leaf litter ash alkalinity and neutralisation of soil acidity. Plant Soil 179: 293–302
Ohwaki Y, Sugahara K (1997) Active extrusion of protons and exudation of carboxylic acids in response to iron deficiency by roots of chickpea (Cicer arietinium L). Plant Soil 189: 49–55
Otani T, Ae N (1997) The exudation of organic acids by pigeonpea roots for solubilizing iron-and aluminum-bound phosphorus. In: Ando T, Fujita K, Mae T, Matsumoto H, Mori S, Sekiya J (Eds) Proceedings XIII International plant nutrition colloquium. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 325–326
Otani T, Ae N, Tanaka H (1996) Phosphorus ( P) uptake mechanisms of crops grown in soils with low P status II Significance of organic acids in root exudates of pigeon pea. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 42: 553–560
Ozawa K, Osaki M, Matsui H, Honma M, Tadano T (1995) Purification and properties of acid phosphatase secreted from lupin roots under phosphorus-deficiency conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 41: 461–469
Panara F, Pasqualini S,Antonielli M (1990) Multiple forms of barley root acid phosphatase: purification and some characteristics of the major cytoplasmic isoenzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta 1037: 73–80
Pellet DM, Grunes DL, Kochian LV (1995) Organic acid exudation as an aluminum-tolerance mechanism in maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 164: 788–795
Pierre WH, Banwart WL (1973) Excess-base and excess-base/ nitrogen ratio of various crop species and parts of plants. Agron J 65: 91–96
Reuter DG, Robinson JB (1997) Plant analysis: an interpretation manual. CSIRO, Melbourne Richardson AE ( 1994 ) Soil microorganisms and phosphorus availability. In: Pankhurst CE, Doube
BM, Gupta VVSR Grace PR (Eds) Management of the soil biota in sustainable farming systems. CSIRO Publishing, Melbourne, pp 50–62
Richardson AE, Hadobas PA (1997) Soil isolates of Pseudomonas spp. that utilize inositol phosphates. Can J Microbiol 43: 509–516
Ridge EH, Rovira AD (1971) Phosphatase activity of intact young wheat roots under sterile and non-sterile conditions. New Phytol 70: 1017–1026
Rogers HT, Pearson RW, Pierre WH (1940) Absorption of organic phosphorus by corn and tomato plants and the mineralizing action of exo-enzyme systems of growing roots. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 285–291
Romheld V, Marschner H (1981) Rhythmic iron stress reactions in sunflower at suboptimal iron supply. Physiol Plant 53: 347–353
Ron Vaz MD, Edwards AC, Shand CA, Cresser MS (1993) Phosphorus fractions in soil solution: Influence of soil acidity and fertilizer additions. Plant Soil 148: 175–183
Rovira AD (1962) Plant-root exudates in relation to the rhizosphere microflora. Soils Fert 25:167–172 Rovira AD (1969) Plant root exudates. Bot Rev 35: 35–57
Rovira AD, Davey CB (1974) Biology of the rhizosphere. In: Carson EW (Ed) The plant root and its environment. University of Virginia Press, Charlottesville, pp 153–204
Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Randall PJ (1995) Characterisation of Al-stimulated efflux of malate from the apices of Al-tolerant wheat roots. Planta 196: 103–110
Sample EC, Soper RJ, Racz GJ (1980) Reactions of phosphate fertilizers in soils. In: Khasawneh EC, Sample CE, Kamprath EJ (Eds) The role of phosphorus in agriculture. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wis, pp 263–310
Schwab SM, Menge JA, Leonard RT (1983) Quantitative and qualitative effects of phosphorus on extracts and exudates of sudan grass roots in relation to vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza formation. Plant Physiol 73: 761–765
Seeling B, Jungk A (1996) Utilization of organic phosphorus in calcium chloride extracts of soil by barley plants and hydrolysis by acid and alkaline phosphatases. Plant Soil 178: 179–184
Seeling B, Zasoski RJ (1993) Microbial effects in maintaining organic and inorganic solution phos-phorus concentrations in a grassland topsoil. Plant Soil 148: 277–284
Sharpley AN (1986) Disposition of fertilizer phosphorus applied to winter wheat. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50: 953–958
Shaykh MM, Roberts LW (1974) A histochemical study of phosphatases in root apical meristems. Ann Bot 38: 165–174
Smith FW (1981) Availability of soil phosphate to tropical pasture species. In: Proceedings of XIV International Grassland Congress, Lexington, USA, pp 282–285
Smith KF, Rebetzke GJ, Eagles HA, Anderson MW, Easton HS (1999) Genetic control of mineral concentration and yield in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.), with special emphasis on minerals related to grass tetany. Aust J Agric Res 50: 79–86
Specht RL, Groves RH (1966) A comparison of the phosphorus nutrition of Australian heath plants and introduced economic plants. Aust J Bot 14: 201–221
Stephens CG, Donald CM (1958) Australian soils and their responses to fertilizer. Adv Agron 10: 167256
Subbarao GV, Ae N, Otani T (1997a) Genetic variation in acquisition, and utilisation of phosphorus from iron-bound phosphorus in pigeonpea. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 43: 511–519
Subbarao GV, Ae N, Otani T (1997b) Genotypic variation in iron-and aluminum-phosphate solubilizing activity of pigeonpea root exudates under P deficient conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 43: 295–305
Tadano T, Ozawa K, Sakai H, Osaki M, Matsui H (1993) Secretion of acid phosphatase by the roots of crop plants under phosphorus-deficient conditions and some properties of the enzyme secreted by lupin roots. Plant Soil 155 /156: 95–98
Tagaki S (1976) Naturally occurring iron-chelating compound in oat-and rice-root washings. 1. Activity measurements and preliminary characterisation. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 22: 423–433
Takagi S, Nomoto K, Takemoto T (1984) Physiological aspects of mugeneic acid, a possible phytosiderophore of graminaceous plants. J Plant Nut 7: 469–477
Tarafdar JC, Jungk A (1987) Phosphatase activity in the rhizosphere and its relation to the depletion of soil organic phosphorus. Biol Fertil Soils 3: 199–204
Tarafdar JC, Marschner H (1994) Efficiency of VAM hyphae in utilisation of organic phosphorus by wheat plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 40: 593–600
Tarafdar JC,Marschner H (1995) Dual inoculation with Aspergillus fumigatus and Glomus mossae enhances biomass production and nutrient uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) supplied with organic phosphorus as Na-phytate. Plant Soil 173: 97–102
Trainia SJ, Sposito G, Hesterberg D, Kafkafi U (1986) Effects of organic acids on orthosphosphate solubility in an acidic, montmorillonitic soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50: 45–52
Uren NC (1982) Chemical reduction at the root surface. J Plant Nut 5: 515–520
Uren NC, Reisenauer HM (1988) The role of root exudates in nutrient acquisition. In: Tinker B, Lauchli A (Eds) Advances in plant nutrition. Praeger, New York, Vol 3, pp 79–114
Wasaki J, Omura M, Osaki M, Ito H, Matsui H, Shinano T, Tadano T (1999) Structure of a cDNA for an acid phosphatase from phosphate-deficient lupin (Lupinus albus L.) roots. Soil Sci Plant Nutr (Tokyo) 45: 439–449
Watt M, Evans JR (1999) Linking development and determinacy with organic acid efflux from proteoid roots of white lupin grown with low phosphorus and ambient or elevated atmospheric CO, concentration. Plant Physiol 120: 705–716
White RE (1980) Retention and release of phosphate by soil and soil constituents. In: Tinker PB (Ed) Soils and agriculture. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, Vol 2, pp 71–114
Whitelaw MA, Harden TJ, Helyar KR (1999) Phosphate solubilization in solution culture by the soil fungus Penicillium radicum. Soil Biol Biochem 31: 655–665
Wild A, Oke OL (1966) Organic phosphate compounds in calcium chloride extracts of soils: identification and availability to plants. J Soil Sci 17: 356–371
Williams CH, Anderson G (1968) Inositol phosphates in some Australian soils. Aust J Soil Res 6: 121–130
Williams CH,Andrew CS (1970) Mineral nutrition of pastures. In: Moore MR(Ed) Australian grasslands. ANU, Canberra, pp 321–338
Williamson VM, Colwell G (1991) Acid phosphatase-1 from nematode resistant tomato. Isolation and characterization of its gene. Plant Physiol 97: 139–146
Wodzinski RJ, Ullah AHJ (1996) Phytase. Adv Appl Microbiol 42: 263–302
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer Japan
About this paper
Cite this paper
Randall, P.J., Hayes, J.E., Hocking, P.J., Richardson, A.E. (2001). Root Exudates in Phosphorus Acquisition by Plants. In: Ae, N., Arihara, J., Okada, K., Srinivasan, A. (eds) Plant Nutrient Acquisition. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-66902-9_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-66902-9_3
Publisher Name: Springer, Tokyo
Print ISBN: 978-4-431-66904-3
Online ISBN: 978-4-431-66902-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive