Abstract
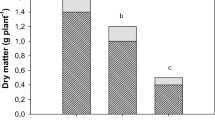
The effect of adding phytase to the root medium of maize plants on the P-availability of added myo-inositol hexaphosphate (phytin) has been studied in pot experiments. When 40 mM phytin-P in nutrient solution was incubated in quartz-sand for 15 days in the absence of plants, 80% of it could be recovered from the solution as soluble organic P. Maize plants growing on this mixture assimilated P from phytin at rates comparable to those from inorganic phosphate (Pi). At a lower addition rate (2 mM phytin-P) only 10% was recovered in the soil solution, and plant growth was severely limited by P. At this low phytin level, the addition of phytase (10 enzyme units per kg sand) increased the plants' dry weight yield by 32%. The relative increases of the Pi concentration in the solution and of the amount of P in the plants were even higher, indicating that the observed growth stimulation was due to an increased rate of phytin hydrolysis. The enzyme-induced growth stimulation was also observed with plants growing in pots filled with soil low in P, when phytin was added. However, on three different soils the addition rates of phytin and phytase necessary for obtaining a significant phytase effect were both about 10 times higher than those required in quartzsand. It is concluded that the P-availability from organic sources can be limited by the rate of their hydrolytic cleavage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Pi:
-
inorganic phosphate
References
Adams M A and Pate J S 1992 Availability of organic and inorganic forms of phosphorus to lupins (Lupinus spp.). Plant and Soil 145, 107–113.
Anderson G 1980 Assessing organic phosphorus in soils. In The Role of Phosphorus in Agriculture. Eds. F E Khasawneh, E C Sample and E J Kamprath. pp 411–431. Amer. Soc. Agron., Madison, Wis.
Dalal R C 1978 Organic phosphorus. Adv. Agron. 29, 83–117.
Flaig W, Schmid W G, Wagner E and Keppel H 1960 Die Aufnahme von Phosphor aus Inositol hexaphosphat. Landwirtsch. Forsch. Sonderh. 14, 43–48.
Greaves M P and Webley D M 1969 The hydrolysis of myo-inositol hexaphosphate by soil microorganisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1, 37–43.
Helal H M and Sauerbeck D R 1984 Influence of plant roots on C and P metabolism in soil. Plant and Soil 76, 175–182.
Jackman R H and Black C A 1951 Solubility of iron, aluminium, calcium, and magnesium inositol phosphates at different pH values. Soil Sci. 72, 179–186.
Jackman R H and Black C A 1952a Phytase activity of soils. Soil Sci. 73, 117–125.
Jackman R H and Black C A 1952b Hydrolysis of phytate phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci. 73, 167–171.
Martin J K and Cartwright B 1971 The comparative plant availability of 32P myo-inositol hexaphosphate and KH2 32PO4 added to soils. Commun. Soil Sci Plant Analysis. 2, 375–381.
Rogers H T, Pearson R W and Pierre W H 1940 Adsorption of organic phosphorus by corn and tomato plants and the mineralization action of exo-enzyme systems of growing roots. Soil Sci. Am. Proc. 5, 285–291.
Speir T W and Ross D J 1978 Soil phosphatase and sulphatase. In Soil Enzymes. Ed. R G Burns. pp 197–250. Acad. Press, London.
Tarafdar J C and Claassen N 1988 Organic phosphorus compounds as a phosphorus source for higher plants through the activity of phosphatases produced by plant roots and microorganisms. Biol. Fertil. Soils 5, 308–312.
Tarafdar J C and Jungk A 1987 Phosphatase activity in the rhizosphere and its relation to the depletion of soil organic phosphorus. Biol. Fertil. Soils 3, 199–204.
Thompson E J and Black C A 1970 Changes in extractable phosphorus in soil in the presence and absence of plants. III. Phosphatase effect. Plant and Soil 32, 335–348.
Wild A Oke O L 1966 Organic phosphorus compounds in calcium chloride extracts of soils. Identification and availability to plants. J. Soil Sci. 17, 357–371.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Findenegg, G.R., Nelemans, J.A. The effect of phytase on the availability of P from myo-inositol hexaphosphate (phytate) for maize roots. Plant Soil 154, 189–196 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012524
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012524