Summary
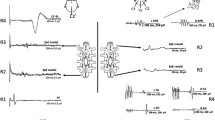
Conducted spinal cord evoked potentials (SEPs) were elicited preoperatively from the thoracic epidural space following spinal cord stimulation in 22 patients with thoracic myelopathy. The waveform changes in SEPs, namely, decrease of amplitude or positive-going potentials were observed and proved to be a successful method for determining the main lesions in all cases. In 20 patients with compressive myelopathy, waveform changes were recorded at the most compressed site in each case. A decrease in amplitude of more than 70% was demonstrated frequently in the moderately involved patients, whereas positive-going potentials were elicited predominantly in the patients with severe myelopathy. The waveform changes reflected to some extent the severity of the neurological symptoms; however, it was not possible to estimate the prognosis of the postoperative neurological symptoms by studying the preoperative SEP waveform. Conducted SEPs provide important information regarding determination of the surgical procedure and range of surgical decompression.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba H, Shima I, Tomita K et al. (1985) Clinical usefulness of spinal cord evoked potentials. In: Schramm J, Jones SJ (eds) Spinal cord monitoring. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp. 245–249
Baba H, Shima I, Tomita K et al. (1985) Somatosensory evoked potentials in cervical myelopathy. In: Schramm J, Jones SJ (eds) Spinal cord monitoring. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 284–289
Baba H, Tomita K, Umeda S et al. (1988) Clinical study of spinal cord evoked potentials. In: Ducker TB, Brown RH (eds) Neurophysiology and standards of spinal cord monitoring. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 216–221
Baba H, Tomita K, Umeda S et al. (1988) Somatosensory evoked potentials in the cervical OPLL myelopathy. Clin Orthop Surg 23: 1409–1416
Baba H, Tomita K, Umeda S et al. (1987) Somatosensory evoked potentials in the upper cervical spine disorder. Orthop Surg Traumatol 30: 1075–1082
Okuma T (1987) Level diagnosis of cervical myelopathy using evoked spinal action potentials. J Jpn Orthop Ass 61: 477–489
Kurokawa T (1979) Clinical application of the evoked electrospinogram. Adv Neurol Sci 23: 409–420
Nagata S (1988) Experimental studies on the spinal cord evoked potentials in compression injury of the cervical spinal cord. J Juzen Med Soc 97: 688–703
Schramm J, Shigeno T, Brock M (1983) Clinical signs and evoked response alternations associated with chronic experimental cord compression. J Neurosurg 58: 734–741
Shimomiya K (1985) Clinical study of cervical spondylotic myelopathy using evoked spinal cord potentials. In: Schramm J, Jones SJ (eds) Spinal cord monitoring. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 290–301
Tomita K, Baba H, Takahashi K (1989) Total (anterior and posterior) decompression of the spinal cord. J Jpn Orthop Ass 63: 501–506
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kikuchi, Y. et al. (1991). Experience of Diagnosis of Thoracic Myelopathy Using Spinal Cord Evoked Potentials. In: Shimoji, K., Kurokawa, T., Tamaki, T., Willis, W.D. (eds) Spinal Cord Monitoring and Electrodiagnosis. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-75744-0_56
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-75744-0_56
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-75746-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-75744-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive