Abstract
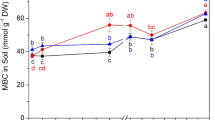
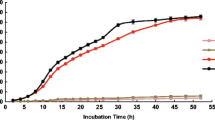
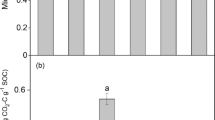
The short and long term influence of depleted uranium (DU) on soil microbial populations remains largely understudied. To understand short term effect of DU on soil microbial activity, an incubation study was conducted using 14C-labeled glucose. Two soils of contrasting texture (Eurtic cambisol and Haplic podzol) were amended with increasing concentrations (0.5 mmol·L−1 to 10 mmol·L−1) of either potassium nitrate (KNO3) or DU as uranyl nitrate UO2(NO3)2. Following addition, 14C-labeled glucose was then added to the soil and 14CO2 production from the mineralization of glucose measured at different time intervals (1 h to 14 d) to assess microbial activity. Glucose mineralization by the microbial community showed non-significant effect by different concentrations of DU on both soils. Fitting a double first order kinetic equation revealed that 87%∼92% of the added glucose was retained in the microbial biomass prior to mineralization. However, comparison of the kinetic values for different concentrations of KNO3 and DU also showed non-significant difference in both soils. The results imply that there is no significant deleterious effect of DU on soil microbial activity in the short (<24 h) or longer term (<30 d).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Francis AJ (2008) Microbial transformations of uranium in wastes and implication on its mobility. Int. Conf. U Min. Hydr. Germany
Neves O, Abreu MM, Vicente EM (2008) Uptake of uranium by lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in natural uranium contaminated soils in order to assess chemical risk for consumers. Water Air Soil Pollut. 195: 73–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Zhejiang University Press, Hangzhou and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ahmad, R., Jones, D.L. (2010). Effects of Depleted Uranium on Soil Microbial Activity: A Bioassay Approach Using 14C-labeled Glucose. In: Xu, J., Huang, P.M. (eds) Molecular Environmental Soil Science at the Interfaces in the Earth’s Critical Zone. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-05297-2_90
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-05297-2_90
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-05296-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-05297-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)