Abstract
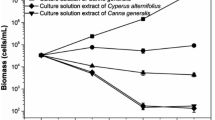
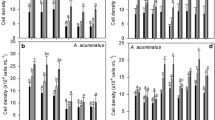
Organic compounds not directly involved in the normal growth, development and reproduction of organism are called secondary metabolites. The growth and development of biological and agricultural systems could be affected by secondary metabolites with biological activity. This phenomenon is known as allelopathy. Allelochemicals could have influence on different physiological processes of target organism cells, which could lead to growth inhibition or even death. The goal of this work was to investigate allelopathic influence of cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa on green algae Chlorella vulgaris. Both species occur in Baltic Sea; furthermore, M. aeruginosa could locally form toxic blooms (HABs) in coastal zone. Axenic cyanobacterial monocultures were cultivated in the flasks on liquid medium. After 30 days of growth cell-free solutions from cyanobacterial cultures were collected by filtering through the glass-fiber filters in sterile conditions and added to Chlorella vulgaris cultures. The influence of obtained extracellular secretion on growth of green microalgae was investigated after 3 and 7 days. In other experiment the influence of living cyanobacterial cells on growth of green algae was investigated (cocultures). In both experiments M. aeruginosa demonstrated allelopathic effects towards green algae.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babica P, Hilscherová K, Bártová K, Bláha L, Maršálek B (2007) Effects of dissolved microcystins on growth of planktonic photoautotrophs. Phycologia 46:137–142
Bhagavathy S, Sumathi P, Jancy Sherene Bell I (2011) Green algae Chlorococcum humicola-a new source of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial activity. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed S1–S7
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Phycological studies IV. Some soil algae from enchanted rock and related algal species, vol 6318. University of Texas Publishing, pp 1–95
Cembella A (2003) Chemical ecology of eukaryotic microalgae in marine ecosystems. Phycologia 42:420–447
Fergola P, Cerasuolo M, Pollio A, Pinto G, DellaGreca M (2007) Allelopathy and competition between Chlorella vulgaris and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata: experiments and mathematical model. Ecol Model 208:205–214
Fistarol GO, Legrand C, Selander E, Hummert C, Stolte W, Graneli E (2004) Allelopathy in Alexandrium spp.: effect on a natural plankton community and algal monocultures. Aquat Microb Ecol 35:45–56
Gantar M, Berry JP, Thomas S, Wang M, Perez R, Rein KS, King G (2008) Allelopathic activity among Cyanobacteria and microalgae isolated from Florida freshwater habitats. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64(1):55–64
Graneli E, Weberg M, Salomon PS (2008) Harmful algal blooms of allelopathic microalgal species: the role of Eutrophication. Harmful Algae 8:94–102
Gross EM (2003) Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:313–339
Hu Z, Liu Y, Li D (2004) Physiological and biochemical analyses of microcystin-RR toxicity to the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus. Environ Toxicol 19:571–577
Hu Z, Liu Y, Li D, Dauta A (2005) Growth and antioxidant system of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus in response to microcystin-RR. Hydrobiologia 534:23–29
Kaebernick M, Neilan BA (2001) Ecological and molecular investigations of cyanotoxin production. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:1–9
Legrand C, Reigefors K, Fistarol GO, Graneli E (2003) Allelopathy in phytoplankton—biochemical, ecological and evolutionary aspects. Phycologia 42:406–419
Maso M, Garces E (2006) Harmful microalgae blooms (HAB); problematic and conditions that induce them. Mar Pollut Biull 53:620–630
Mulderij G, Mooij WM, Smolders AJP, Van Donk E (2005) Allelopathic inhibition of phytoplankton by exudates from Stratiotes aloides. Aquat Bot 82:284–296
Ou D, Song L, Gan N, Chen W (2005) Effects of microcystins on and toxin degradation by Poteriomonas sp. Environ Toxicol 20:373–380
Qian H, Xu X, Chen W, Jiang H, Jin Y, Liu W, Fu Z (2009) Allelochemical stress causes oxidative damage and inhibition of photosynthesis in Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.12.040
Singh DP, Tyagi MB, Kumar A, Thakur JK, Kumar A (2001) Antialgal activity of a hepatotoxin-producing cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:15–22
Sukenik A, Eskhol R, Livne A, Hadas O, Rom M, Tchernov D, Vardi A, Kaplan A (2002) Inhibition of growth and photosynthesis of the dinoflagellate Peridinium gatunense by Microcystis sp. (cyanobacteria): a novel Allelopathic mechanism. Limnol Oceanogr 47(6):1656–1663
Svircev Z, Cetojevic-Simin D, Simeunovic J, Karaman M, Stojanovic D (2008) Antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic activity of terrestrial cyanobacterial strains from Serbia. Sci China Ser C Life Sci 51(10):941–947
Tillmann U, Alpermann T, John U, Cembella A (2008) Allelochemical interactions and short-term effects of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium on selected photoautotrophic and heterotrophic protists. Harmful Algae 7:52–64
Tuney U, Cadirci HB, Unal D, Sukatar A (2006) Antimicrobial activities of the extracts of marine algae from the coast of Urla (Üzmir, Turkey) Turk. J Biol 30:171–175
Weir TL, Park SW, Vivanco JM (2004) Biochemical and physiological mechanisms mediated by allelochemicals. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:472–479
Żak A, Musiewicz K, Kosakowska A (2012) Allelopathic activity of the Baltic cyanobacteria against microalgae. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2011.10.007
Acknowledgments
The study was partially supported by the Polish State Committee for Scientific Research (grant No. N N306 214137) and by the statutory programme of the Institute of Oceanology, PAS (grant No. II.3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Żak, A., Kosakowska, A. (2014). Allelopathic Influence of Cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa on Green Algae Chlorella vulgaris . In: Zielinski, T., Pazdro, K., Dragan-Górska, A., Weydmann, A. (eds) Insights on Environmental Changes. GeoPlanet: Earth and Planetary Sciences. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03683-0_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-03683-0_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-03682-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-03683-0
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)