Abstract
It is said that KANO model is one of the key findings in analyzing and categorizing various product qualities. The model says qualities are not only one dimensional in terms of the relations between quality fulfilment and customer satisfaction. If a designer could find a delighter which can increase customer satisfaction greatly without enhancing specification too much may contribute to increase product eco-efficiency, since higher specifications usually lead to larger environmental burden. The study extracts some design specifications of smartphones and carries out an online survey to smartphone users in order to identify the relations between the specification levels and customer satisfaction levels. As the result of the survey, a true exciter could not be found in the case study products. However, regression coefficients estimated by applying conjoint analysis to the selected specifications showed there were specifications which can effectively increase customer satisfaction such as battery capacity or display size, and also there was a specification having little effect in increasing it. The survey results suggested that there are optimum values of product specifications. Identifying the optimum values and avoiding over-specification is significant in finding appropriate design solutions which may decouple the customer satisfaction and the environmental burden increase. The study concluded that the approach is helpful in enhancing product sustainability by Ecodesign.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
In designing industrial products, designers are trying to enhance the performance of the product as much as they can, under some balance with production cost. And of course, the reason to build-in high functionalities in the products is to fulfill customer requirements and enhance product attractiveness. For smartphones, it seems that the overall product performance has increased steadily over the years [1]. It means that the designers have focused and the consumers have required such increase of the specifications.
KANO model [2] made an important suggestion on this tendency. The model said product qualities are not always linear to customer satisfaction. The model explains that there are 3 major types of quality attributes and by focusing on the so-called “delighters,” customer satisfaction levels can be increased efficiently. But even for low-cost products, so-called “must-bes” qualities should not be eliminated. Some previous studies [3,4,5,6] have focused in applying the concept to environmentally benign design. By focusing on delighters, it might be possible to increase product attractiveness without enhancing product performance greatly that requires extra environmental burden.
However, it is not always possible to find delighters in real products, especially for matured products/markets, since people soon start to think they are must-bes, once it is build-in commercial products. The author surveyed weights of design specifications and estimated eco-efficiencies of the design specifications in a previous study [7], and explained that it is possible to enhance product eco-efficiency by focusing some specifications. The author notified customer’s voice such as “this specification is important, but I am satisfied at the current level.” This was an important suggestion to think that must-bes can be found and the bending points of the curves can be specified. Since the enhancement of product performances require certain amounts of environmental burdens, it is not eco-efficient to increase the performance beyond these points. Thus, the objective of this study is to clarify the design specifications of the case study product are delighters, one-dimensional or must-bes, and whether there is a bending point in each specification, by a customer survey. Through this effort, the study can clarify the optimum levels of design specifications, in the context of eco-design.
2 Why KANO Model
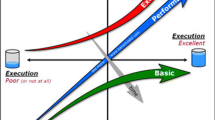
The simplified KANO model in three different quality attributes can be expressed as Fig. 1 [8]. The figure clearly shows that if we can find the bending point of the mut-be curve, it will greatly contribute in eco-efficient design. If there is no drastic change of manufacturing technologies and the environmental burden to increase the design specification level is proportional to the increase amount like memory capacity, eco-efficiencies of design specifications defined by Eq. (1) will peak at the bending point of the must-be. At the same time, it will be the same for one-dimensional and will continuously increase for delighters. But even for a one-dimensional, a bending point can be found. Finding the bending points will be helpful to extract suggestions in designing eco-efficient products. That was the motivation of the study and the reason to carry out a customer survey to know customer’s preference on design specifications.
Simplified KANO model [7]
3 Internet Survey of Customer Satisfaction
3.1 Target Product Specifications
In choosing the case study example as a smartphone, some design specifications to investigate customer preference were selected as below. Four different specification levels were set for each specification.
-
Battery capacity
-
Storage capacity
-
Display size
-
Variations of smartphone case
-
Price
The first three specifications are the top three functions listed to be important functions for smartphones in the preliminary survey. “Variations of smartphone case” was found to be relatively important among the three features related to outlook of the product, those were color, texture and variations of smartphone case, investigated in the previous study. The last one, price, was designated because it is helpful to know the willingness to pay of other specification by comparing to the preference to price. It is also possible to check the accuracy of survey by calculating the customer preference for the different levels of price, since the reactions to different prices are thought to be linear to the price itself. This is the background of the pricing system which can be seen in the reverse linear relationship between price and demand in basic economics theory.
3.2 Outline of the Customer Survey
Table 1 shows the four different specification levels of five design specifications of smartphones. The four specification levels were determined based on the actual values in the current smartphone market. The customer survey was designed based on conjoint analysis method [9]. Assuming that there are no interactions between the five specifications, L16 orthogonal array which can be used for five attributes and four levels was used to design the conjoint cards. Each card was evaluated with full score of 10. The survey was made to 230 respondents via internet.
3.3 Results of the Survey
The result of the customer survey shown in the previous section for five design specifications are indicated in Fig. 2 to Fig. 6 below.
4 Estimation of Eco-efficiencies
4.1 Estimation of Environmental Burden
Since the customer satisfaction levels corresponding to the different specification levels were estimated through the customer survey, the numerator of eco-efficiency equation has been identified. In order to identify the denominator, environmental burden to increase design specifications were investigated and extrapolated through previous studies [10, 11]. Table 2 shows the environmental burden increase quantified by CO2 emission corresponding to the increase of three design specifications except for variations of case and price.
As for the increase of variations of smartphone case, since there are molding types and one-by-one manufacturing types, increase of CO2 emission per unit is not linear to the increase to the variations, since some of the variations of smartphone cases are made by molding and some are one by one manufactured. Table 3 shows the calculated values considering this. The value was calculated referring plastic parts fabrication of automobile [12]. As it was shown in Fig. 6 in the previous section, customer satisfaction increase corresponding to the price decrease is almost linear. So, it seems that the approach is reasonable. Eco-efficiencies of four design specifications were calculated.
4.2 Eco-efficiency Calculation
By using the data used in Figs. 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 and the data shown in Table 2 and 3, it is possible to calculate eco-efficiency of performance enhancement as Tables 4, 5, 6 and 7. Figure 7 is the visual expression of these results. The figure shows that storage capacity has smaller eco-efficiency than others and some specifications have smaller speak value at the second level performances.
5 Discussion
Considering the survey results shown in Figs. 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6, no delighter was found in the target design specifications of a smartphone. Among the four specifications except price, storage capacity seems like one-dimensional, while battery capacity and display size look like must-bes. Unlike the motivation of the study in the beginning, significance of finding bending points of the must-be curves was clarified through the study. By finding the points, it will be possible to designate the proper design specifications that are the critical points to stop the performance enhancement beyond there.
For the design specifications in the case study, it is not eco-efficient to focus on increase of storage capacity anymore, since the eco-efficiency is relatively low at all the levels. As it is shown in Fig. 7, contrarily for battery capacity and display size, since the eco-efficiency of performance enhancement is not that low, it is helpful to focus on these specifications. However, there are critical points where the performance should be stopped to increase at the point. For battery capacity, eco-efficiency is rather high till 4,000mAh. Thus, the suitable value of battery capacity can be 4,000mAh. As for the display size, since the eco-efficiency drastically decreases and is almost 0 for the increase from 5.8 inches to 6.8 inches, the optimum display size can be 5.8 inches.
This strategy to limit the product performance at a certain level is a paradigm shift for modern product design that has been aiming to enhance performance as much as possible. Although the actual values might change due to technological levels and market situations, there can be critical points of product performances that the designers should avoid to enhance them beyond the points. For a competitive and matured product, it is likely to have must-bes. Because, if someone find a delighter, it would be caught up by the competitor. Therefore, it is likely to have bending points in the performance-customer satisfaction curves.
6 Summary
The paper proposed a procedure to know the practical behaviors of product design specifications based on KANO model and carried out a customer survey to know that. Throughout the study, although no delighter has been found for the matured product like smartphones, the significance of must-bes, especially, finding bending points of the curves was explained in the context of eco-efficient design. Then, the paper showed a method to estimate the eco-efficiencies of specific designs, by dividing the increase of customer satisfaction levels by the increase of environmental burden to enhance product performance. Using this procedure, the paper indicated some design specifications should be focused for ecodesign of the case study. Future work is to increase the reliability of the customer survey and gather more design specifications and product examples to clarify whether such optimum design specifications can be found always.
References
https://www.androidauthority.com/smartphone-performance-improvements-timeline-626109/
Kano, N., Seraku, N., Takahashi, F., Tsuji, S.: Attractive quality and must-be quality. J. Japanese Soc. Qual. Control 14, 39–48 (1984)
Sakao, T.: Quality engineering for early stage of environmentally conscious design. In: Proceedings of 11th QMOD Conference, pp.50–59. Helsingborg; Sweden (2008)
Rasamoelina, F., Bouchard, C., Aoussat, A.: Towards a Kansei-based user modeling methodology for eco-design. Int. J. Affect. Eng. 12(2), 337–348 (2013)
Horani, L.: Optimizing customer satisfaction by using kano’s model for eco-efficiency and green design. J. Investment Manage. 4(5), 285–290 (2013)
Dace, E., Stibe, A., Timma, L.: A holistic approach to manage environmental quality by using the Kano model and social cognitive theory. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 27, 430–443 (2020)
Mishima, N., Kudo, T., Naito, T.: Eco-Efficiency Evaluation of Design Features Based on Value Engineering Methodology, Transdisciplinary Engineering Methods for Social Innovation of Industry 4.0, p.873 (2018)
Rotar, L., Kozar, M.: The use of the kano model to enhance customer satisfaction. Organizacija 50(4), 339–351 (2017)
Green, P. E., Srinivasan, V.: Conjoint analysis in consumer research. Stanford University Research Paper, vol. 435 (1978)
Güvendik, M., From Smartphone to Futurephone: assessing the environmental impacts of different circular economy scenarios of a smartphone using LCA, Master thesis of Technical University of Delft (2014). https://repository.tudelft.nl/islandora/object/uuid%3A13c85c95-cf75-43d2-bb61-ee8cf0acf4ff
Boyd, S.B.: Life Cycle Assessment of Semiconductors, Ph.D. thesis in UC Berkeley. http://digitalassets.lib.berkeley.edu/etd/ucb/text/Boyd_berkeley_0028E_10192.pdf
Sano, S., Tomioka, K., Ooi, Y.; LCA study of automobile recycling. Trans. Autom. Technol. Assoc. 49(4), 845–848 (2018). (in Japanese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s)
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mishimar, N. (2023). Identification of Product Specifications Based on KANO Model and Application to Ecodesign. In: Kohl, H., Seliger, G., Dietrich, F. (eds) Manufacturing Driving Circular Economy. GCSM 2022. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-28839-5_87
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-28839-5_87
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-28838-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-28839-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)