Abstract
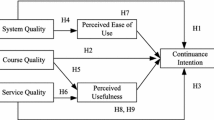
OMO (Online Merge Offline), the combination of online and offline services, has attracted increasing attention in the education industry. This study aims to investigate the predictors of learners’ continuance participation in OMO learning. Based on Expectation-Confirmation Theory, IS Success Model and Satisfaction-Loyalty Theory, we develop a research model to explore how online teaching quality (online content quality, online service quality and system quality) and offline teaching quality (offline content quality and offline service quality) jointly affect students’ satisfaction and loyalty, and ultimately determine their continuance usage intention. 301 valid samples were collected via an online survey. SmartPLS 3 was used to verify the research model and hypotheses. Findings show that: (1) online content quality, online service quality, system quality, offline content quality and offline service quality positively affect satisfaction; (2) satisfaction positively influence loyalty and continuance intention; (3) continuance intention has positive impact on loyalty. Implications for theory and practice are discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNICEF. Keeping the World’s Children Learning through COVID-19. https://www.unicef.org/coronavirus/keeping-worlds-children-learning-through-covid-19. Accessed 20 Apr 2020
UNICEF. UNICEF calls for averting a lost generation as COVID-19 threatens to cause irreversible harm to children’s education, nutrition and well-being. https://www.unicef.org/press-releases/unicef-calls-averting-lost-generation-covid-19-threatens-cause-irreversible-harm. Accessed 18 Nov 2020
Li, K.F.: Rush to the OMO Era. Manager 2, 4 (2018)
Xiao, J., Sun-Lin, H.Z., Cheng, H.C.: A framework of online-merge-offline (OMO) classroom for open education: a preliminary study. Asian Assoc. Open Univ. J. 14(2), 134–146 (2019)
Ministry of Education of P.R. China. Guiding opinions of six departments including the Ministry of education on promoting the construction of new educational infrastructure and building a high-quality education support system. http://www.moe.gov.cn/srcsite/A16/s3342/202107/t20210720_545783.html. Accessed 14 Oct 2021
Ministry of Education of P.R. China. Reply to proposal No. 4271 (Education No. 437) of the fourth session of the 13th National Committee of the Chinese people's Political Consultative Conference. http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_xxgk/xxgk_jyta/jyta_kjs/202111/t20211104_577687.html. Accessed 21 July 2021
Oliver, R.L.: A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. J. Mark. Res. 17(4), 460–469 (1980)
Bhattacherjee, A.: An empirical analysis of the antecedents of electronic commerce service continuance. Decis. Support Syst. 32(2), 201–214 (2001)
Zhang, Z., Wang, Y.N., Chen, X.H., Gao, Y.: An empirical research on the factors affecting learners' continuous learning intention in MOOC: a modified expectation-confirmation model. e-Edu. Res. 22(01), 100–111 (2016)
Yang, G.F.: Factors affecting the continued use of MOOC user behavior. Open Edu. Res. 22(01), 100–111 (2016)
Yan, A., Yan, Y.L.: An empirical study of influential factors of the intention of continually using electronic resources in university library. Libr. Tribune 33(03), 43–50+30 (2013)
Chen, C.P., Lai, H.M., Ho, C.Y.: Why do teachers continue to use teaching blogs? the roles of perceived voluntariness and habit. Comput. Educ. 82, 236–249 (2015)
Shannon, C.E., Weaver, W.: The Mathematical Theory of Communication, pp. 1–54. University of Illinois Press, Urbana IL (1949)
Mason, R.O.: Measuring information output: a communication systems approach. Inf. Manage. 5(1), 219–234 (1978)
Delone, W.H., Mclean, E.R.: Information systems success: the quest for the dependent variable. Inf. Syst. Res. 3(1), 60–95 (1992)
Delone, W.H., Mclean, E.R.:. The Delone and Mclean model of information systems success: a ten-year update. J. Manage. Inf. Syst. 19(4), 9–30 (2003)
Oliver, T.A., Oliver, R.L., Macmillan, I.C.: A Catastrophe model for developing service satisfaction strategies. J. Mark. 251–257 (1992)
Lee, J., Lee, J., Feick, L.: The impact of switching costs on the customer satisfaction-loyalty link: mobile phone service in France. J. Serv. Mark. 15(1), 35–48 (2001)
Anderson, R.E., Srinivasan, S.S.: E-satisfaction and e-loyalty: a contingency framework. Psychol. Mark. 20(2), 123–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.10063
Jen, W., Tu, R., Lu, T.: Managing passenger behavioral intention: an integrated framework for service quality, satisfaction, perceived value, and switching barriers. Transportation 38, 321–342 (2011)
Tian, C.Y., Pei, Z.B.: Study on the relationship between perceived value, satisfaction and loyalty of tourists in cultural heritage sites. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 35(02), 203–208 (2021)
Yin, X.J., Xie, T.: Researching transformation path from consumer satisfaction to consumer loyalty of cross-border import e-commerce platform. J. Commercial Econo. 01, 90–93 (2021)
Shi, M.: Investigating students' satisfaction and loyalty in Higher Vocational Colleges. Qingdao University (2020)
Huang, L., Pei, X.N., Zhu, Y.X.: A new study on the evaluation index system for content quality of online course: a perspective from learner experience and knowledge payment. J. Dist. Educ. 38(01), 104–112 (2020)
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V.A., Berry, L.L.: A conceptual model of service quality and its implication for future research (SERVQUAL). J. Mark. 49(4), 41–50 (1985)
Cardozo, R.N.: An experimental study of customer effort, expectation, and satisfaction. J. Mark. Res. 2(8) (1965)
Lee, M.C.: Explaining and predicting users’ continuance intention toward e-learning: an extension of the expectation confirmation model. Comput. Educ. 54(2), 506–516 (2010)
Inseong, L., Jaesoo, K., Jinwoo, K.: Use contexts for the mobile Internet: alongitudinal study monitoring actual use of mobile Internet services. Int. J. Human-Comput. Interact. 18(3), 269–292 (2007)
Yang, G.F.: An empirical study on continuance intention of mobile reading service——to content aggregation APP as an example. J. Mod. Inf. 35(03), 57–63 (2015)
Brown, G.: Brand loyalty-fact or fiction? Advert. Age 23(1), 53–55 (1952)
Cunningham, R.M.: Brand loyalty-what, where, how much? Harv. Bus. Rev. 34(1), 116–128 (1956)
Wang, C.X., Han, X.Y., Wen, B.Y.: An empirical study of the relationship between customer satisfaction and loyalty. Nankai Bus. Rev. 04, 70–74 (2003)
Hair, J., Black, B., Babin, B., et al.: Multivariate Data Analysis (6ª ed.) (2006)
Chin, W.W., Marcoulides, G.: The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Adv. Hospitality Lsure 8(2), 295–336 (1998)
Fornell, C., Larcker, D.F.: Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: algebra and statistics. J. Mark. Res. 18(3), 382–388 (1981)
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities No. NR2021003 awarded to the second author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jiang, J., Liu, L., Ren, S., Yang, S., Zong, P., Lai, H. (2022). Continuance Usage of Online-Merge-Offline (OMO) Educational Services: An Empirical Study. In: Meiselwitz, G., et al. HCI International 2022 - Late Breaking Papers. Interaction in New Media, Learning and Games. HCII 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13517. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22131-6_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-22131-6_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-22130-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-22131-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)