Abstract
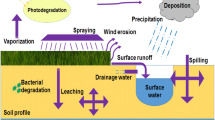
Although pesticides protect crops against pests and stimulate crop productivity, due to their persistence and their toxic effects on the environment and human health, a significant number of pesticides have been banned from being used and even produced. Most organic banned pesticides belong to the insecticides based on chlorinated hydrocarbons, organophosphorus, carbamate, triazine, organotin, and pyrazole(phenyl-) insecticide classes. Notwithstanding the harmful effects of numerous pesticides, their application in agriculture is still practiced in many regions of the world. In this framework, this chapter is a literature review focused on highlighting (i) the role in agriculture and the actually annual production of 15 banned pesticides with high persistence (lindane, dieldrin, aldrin, endosulfan, parathion and parathion-metil, tributyltin oxide, DDT, pentachlorophenol, chlordane, heptachlor, paraquat, carbofuran, fenbutatin oxide, fipronil, and atrazine), (ii) its spreading in soil, water, air, and products, (iii) its toxicity on animals and humans and its fate in the environment compartments, and (iv) the ability of microorganisms to remove these compounds from the environment. Following the analysis of databases on the production, marketing and use have been found that pesticides such as lindane, dieldrin, aldrin, endosulfan, pentachlorophenol, chlordane, and heptachlor are still produced and marketed, even if the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants impose measures to eliminate their production and use. Furthermore, these pesticides are detected in fruits, vegetables, cereals, dairy products, meat products, chicken eggs, and aquatic organisms, thus increasing the risks to human health. For further remediation of the contaminated environments, the potential of microorganisms to biodegrade these substances was analyzed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Salam, J., Lakshmi, V., Das, D., & Das, N. (2013). Biodegradation of lindane using a novel yeast strain, Rhodotorula sp. VITJzN03 isolated from agricultural soil. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 29, 475–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1201-4
Adeyi, A. A., Babalola, B., & Akpotu, S. O. (2021). Occurrence, distribution, and risk of organochlorine pesticides in food and greenness assessment of method. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 33433–33444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13047-w
Adeyinka, A., Muco, E., & Pierre, L. (2021). Organophosphates. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
Aktar, W., Sengupta, D., & Chowdhury, A. (2009). Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 2, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10102-009-0001-7
Alexander, M. (1999). Biodegradation and bioremediation (2nd ed.). Academic Press.
Amaeze, N. H., Komolafe, B. O., Salako, A. F., Akagha, K. K., Briggs, T.-M. D., Olatinwo, O. O., & Femi, M. A. (2020). Comparative assessment of the acute toxicity, haematological and genotoxic effects of ten commonly used pesticides on the African Catfish, Clarias gariepinus Burchell 1822. Heliyon, 6, e04768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04768
Amizadeh, M., & Amizadeh, M. (2011). Effects of endosulfan on human health. WebmedCentral Toxicology, 2(12), 9. https://doi.org/10.9754/journal.wmc.2011.002617
APMVA. (2012). Fipronil – Review scope document part 2: Environmental considerations summary.
APVMA. (2010). Atrazine toxicity: Analysis of potential modes of action. Australian Pesticides & Veterinary Medicines Authority.
Ashraf, M. A. (2015). Persistent organic pollutants (POPs): a global issue, a global challenge. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 4223–4227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5225-9
ATSDR. (2021). Toxic substances portal. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/substances/SubstanceAZ.aspx. Accessed 10 November 2021.
Badroo, I. A., Nandurkar, H. P., & Khanday, A. H. (2020). Toxicological impacts of herbicide paraquat dichloride on histological profile (gills, liver, and kidney) of freshwater fish Channa punctatus (Bloch). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 39054–39067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09931-6
Battaglino, B., Grinzato, A., & Pagliano, C. (2021). Binding properties of photosynthetic herbicides with the QB site of the D1 protein in plant photosystem II: A combined functional and molecular docking study. Plants, 10, 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10081501
Benimeli, C. S., Fuentes, M. S., Abate, C. M., & Amoroso, M. J. (2008). Bioremediation of lindane-contaminated soil by Streptomyces sp. M7 and its effects on Zea mays growth. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 61, 233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2007.09.001
Berntssen, M. H. G., Maage, A., & Lundebye, A.-K. (2017). Chemical contamination of finfish with organic pollutants and metals. In D. Schrenk (Ed.), Chemical contaminants and residues in food (pp. 517–551). Elsevier.
Berntssen, M. H. G., Maage, A., & Lundebye, A.-K. (2012). Contamination of finfish with persistent organic pollutants and metals. In D. Schrenk (Ed.), Chemical contaminants and residues in food (pp. 498–534). Elsevier.
Bethsass, J., & Colangelo, A. (2006). European union bans atrazine, while the United States negotiates continued use. International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Health, 12, 260–267. https://doi.org/10.1179/oeh.2006.12.3.260
Bhalerao, T. S., & Puranik, P. R. (2007). Biodegradation of organochlorine pesticide, endosulfan, by a fungal soil isolate, Aspergillus niger. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 59, 315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2006.09.002
Bhadouria, B. S., Mathur, V. B., & Kaul, R. (2012). Monitoring of organochlorine pesticides in and around Keoladeo National Park, Bharatpur, Rajasthan, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 5295–5300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2340-z
Bidleman, T. F., Alegria, H., Ngabe, B., & Green, C. (1998). Trends of chlordane and toxaphene in ambient air of Columbia, South Carolina. Atmospheric Environment, 32, 1849–1856. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(97)00401-9
Birolli, W. G., Yamamoto, K. Y., de Oliveira, J. R., Nitschke, M., Seleghim, M. H. R., & Porto, A. L. M. (2015). Biotransformation of dieldrin by the marine fungus Penicillium miczynskii CBMAI 930. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 4, 39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2014.06.002
Boedeker, W., Watts, M., Clausing, P., & Marquez, E. (2020). The global distribution of acute unintentional pesticide poisoning: Estimations based on a systematic review. BMC Public Health, 20, 1875. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09939-0
Bokade, P., Purohit, H. J., & Bajaj, A. (2021). Myco-remediation of chlorinated pesticides: Insights into fungal metabolic system. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 61, 237–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-021-00940-8
Bose, S., Kumar, P. S., Vo, D.-V. N., Rajamohan, N., & Saravanan, R. (2021). Microbial degradation of recalcitrant pesticides: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19, 3209–3228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01236-5
Boyer, I. J. (1989). Toxicity of dibutyltin, tributyltin and other organotin compounds to humans and to experimental animals. Toxicology, 55, 253–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483X(89)90018-8
Chakraborty, P., Zhang, G., Li, J., Xu, Y., Liu, X., Tanabe, S., & Jones, K. C. (2010). Selected organochlorine pesticides in the atmosphere of major Indian cities: Levels, regional versus local variations, and sources. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 8038–8043. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102029t
Chowdhury, I. F., Rohan, M., Stodart, B. J., Chen, C., Wu, H., & Doran, G. S. (2021). Persistence of atrazine and trifluralin in a clay loam soil undergoing different temperature and moisture conditions. Environmental Pollution, 276, 116687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116687
Cuozzo, S. A., Fuentes, M. S., Bourguignon, N., Benimeli, C. S., & Amoroso, M. J. (2012). Chlordane biodegradation under aerobic conditions by indigenous Streptomyces strains. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 66, 19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.09.011
De Gerónimo, E., Aparicio, V. C., Bárbaro, S., Portocarrero, R., Jaime, S., & Costa, J. L. (2014). Presence of pesticides in surface water from four sub-basins in Argentina. Chemosphere, 107, 423–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.01.039
Devi, N. L., Qi, S., Chakraborty, P., Zhang, G., & Yadav, I. C. (2011). Passive air sampling of organochlorine pesticides in a northeastern state of India, Manipur. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23, 808–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60453-6
Dobšíková, R. (2011). Acute toxicity of carbofuran to selected species of aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Plant Protection Science, 39, 103–108. https://doi.org/10.17221/3865-PPS
Doolotkeldieva, T., Bobusheva, S., & Konurbaeva, M. (2021). The improving conditions for the aerobic bacteria performing the degradation of obsolete pesticides in polluted soils. Air Soil Water Research, 14, 117862212098259. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178622120982590
Dowler, C. (2020). Thousands of tonnes of banned pesticides shipped to poorer countries from British and European factories. Greenpeace UK. https://unearthed.greenpeace.org/2020/09/10/banned-pesticides-eu-export-poor-countries/
Eddleston, M. (2016). Bipyridyl Herbicides. In J. Brent, K. Burkhart, P. Dargan, B. Hatten, B. Megarbane, & R. Palmer (Eds.), Critical care toxicology (pp. 1–20). Springer International Publishing.
EFSA, Medina-Pastor, P., & Triacchini, G. (2020). The 2018 European Union report on pesticide residues in food. EFSA Journal, 18, 6057. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2020.6057
Egorova, D. O., Farafonova, V. V., Shestakova, E. A., Andreyev, D. N., Maksimov, A. S., Vasyanin, A. N., Buzmakov, S. A., & Plotnikova, E. G. (2017). Bioremediation of soil contaminated by dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane with the use of aerobic strain Rhodococcus wratislaviensis Ch628. Eurasian Soil Science, 50, 1217–1224. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229317100015
European Commission. (2021). EU pesticides database. Food Safety. https://ec.europa.eu/food/plants/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database_en. Accessed 11 April 2021.
EUROSTAT. (2021). Pesticide sales. EUROSTAT. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/AEI_FM_SALPEST09__custom_1481312/default/table?lang=en
Fan, X., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Wang, H., Fan, W., & Dong, Z. (2021). Estimating the dietary exposure and risk of persistent organic pollutants in China: A national analysis. Environmental Pollution, 288, 117764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117764
FAO. (1997). Pesticide residues in food. 1997: Report.
FAO. (2021a). 2050: A third more mouths to feed. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. https://www.fao.org/news/story/en/item/35571/icode/
FAO. (2021b). Climate change fans spread of pests and threatens plants and crops, new FAO study. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. https://www.fao.org/news/story/en/item/1402920/icode/
FAOSTAT. (2021). Land, inputs and sustainability. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Fent, K. (1998). Effects of organotin compounds in fish: From the molecular to the population level. In T. Braunbeck, D. E. Hinton, & B. Streit (Eds.), Fish ecotoxicology (pp. 259–302). Birkhäuser Basel.
Filote, C., Roșca, M., Hlihor, R. M., Cozma, P., Simion, I. M., Apostol, M., & Gavrilescu, M. (2021). Sustainable application of biosorption and bioaccumulation of persistent pollutants in wastewater treatment: Current practice. PRO, 9, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101696
Fuentes, M. S., Colin, V. L., Amoroso, M. J., & Benimeli, C. S. (2016). Selection of an actinobacteria mixed culture for chlordane remediation. Pesticide effects on microbial morphology and bioemulsifier production: Actinobacteria mixed culture for chlordane remediation. Journal of Basic microbiology, 56, 127–137. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201500514
Gajendiran, A., & Abraham, J. (2017). Biomineralisation of fipronil and its major metabolite, fipronil sulfone, by Aspergillus glaucus strain AJAG1 with enzymes studies and bioformulation. 3Biotech, 7, 212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0820-8
Gao, L., Yuan, H., Xu, E., & Liu, J. (2020). Toxicology of paraquat and pharmacology of the protective effect of 5-hydroxy-1-methylhydantoin on lung injury caused by paraquat based on metabolomics. Scientific Reports, 10, 1790. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58599-y
Gavrilescu, M. (2005). Fate of pesticides in the environment and its bioremediation. Engineering in Life Sciences, 5, 497–526. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200520098
Gawarammana, I. B., & Buckley, N. A. (2011). Medical management of paraquat ingestion: Medical management of paraquat ingestion. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 72, 745–757. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04026.x
Guillén-Jiménez, F. d. M., Cristiani-Urbina, E., Cancino-Díaz, J. C., Flores-Moreno, J. L., & Barragán-Huerta, B. E. (2012). Lindane biodegradation by the Fusarium verticillioides AT-100 strain, isolated from Agave tequilana leaves: Kinetic study and identification of metabolites. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 74, 36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.04.020
Hamilton, D. J., Ambrus, Á., Dieterle, R. M., Felsot, A. S., Harris, C. A., Holland, P. T., Katayama, A., Kurihara, N., Linders, J., Unsworth, J., & Wong, S.-S. (2003). Regulatory limits for pesticide residues in water (IUPAC technical report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 75, 1123–1155. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200375081123
Hanson, W., Strid, A., Gervais, J., Cross, A., & Jenkins, J. (2020). Atrazine fact sheet. National Pesticide Information Center.
Hassaan, M. A., & El Nemr, A. (2020). Pesticides pollution: Classifications, human health impact, extraction and treatment techniques. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 46, 207–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2020.08.007
Herrero-Hernández, E., Andrades, M. S., Álvarez-Martín, A., Pose-Juan, E., Rodríguez-Cruz, M. S., & Sánchez-Martín, M. J. (2013). Occurrence of pesticides and some of their degradation products in waters in a Spanish wine region. Journal of Hydrology, 486, 234–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.01.025
Hertel, R. F., & International Programme on Chemical Safety (Eds.). (1993). Methyl parathion. World Health Organization.
Honeycutt, M., & Shirley, S. (2014). Dieldrin. In P. Wexler (Ed.), Encyclopedia of toxicology (pp. 107–110). Elsevier.
Huang, L., Wang, W., Shah, S. B., Hu, H., Xu, P., & Tang, H. (2019). The HBCDs biodegradation using a Pseudomonas strain and its application in soil phytoremediation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 380, 120833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120833
Hussain, S., Arshad, M., Saleem, M., & Khalid, A. (2007). Biodegradation of α- and β-endosulfan by soil bacteria. Biodegradation, 18, 731–740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-007-9102-1
Hussain, S., Zhang, J., Zhong, C., Zhu, L., Cao, X., Yu, S., Allen Bohr, J., Hu, J., & Jin, Q. (2017). Effects of salt stress on rice growth, development characteristics, and the regulating ways: A review. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 16, 2357–2374. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61608-8
IARC. (1991). Occupational exposures in insecticide application, and some pesticides. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans.
Isogai, N., Hogarh, J. N., Seike, N., Kobara, Y., Oyediran, F., Wirmvem, M. J., Ayonghe, S. N., Fobil, J., & Masunaga, S. (2018). Atmospheric monitoring of organochlorine pesticides across some West African countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 31828–31835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7284-y
Ito, K., Mahmood, A., Kataoka, R., & Takagi, K. (2021). Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) degradation by Streptomyces sp. isolated from DDT contaminated soil. Bioremediation Journal, 25, 148–158. https://doi.org/10.1080/10889868.2020.1867050
Jesitha, K., Nimisha, K. M., Manjusha, C. M., & Harikumar, P. S. (2015). Biodegradation of endosulfan by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Environmental Processes, 2, 225–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-015-0059-5
Kabasenche, W. P., & Skinner, M. K. (2014). DDT, epigenetic harm, and transgenerational environmental justice. Environmental Health, 13, 62. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-13-62
Kalipci, E., Özdemir, C., Öztas, F., & Sahinkaya, S. (2010). Ecotoxicological effects of Methyl parathion on living things and environment. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 5, 712–718. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR10.113
Kataoka, R., Takagi, K., Kamei, I., Kiyota, H., & Sato, Y. (2010). Biodegradation of Dieldrin by a soil fungus isolated from a soil with annual Endosulfan applications. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 6343–6349. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1000227
Kaur, R., Mavi, G. K., Raghav, S., & Khan, I. (2019). Pesticides classification and its impact on environment. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 8, 1889–1897. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2019.803.224
Kent, J. (1992). Pesticides in agriculture. Charles Sturt. http://www.regional.org.au/au/roc/1992/roc1992031.htm
Keswani, C., Dilnashin, H., Birla, H., Roy, P., Tyagi, R. K., Singh, D., Rajput, V. D., Minkina, T., & Singh, S. P. (2021). Global footprints of organochlorine pesticides: A pan-global survey. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 44, 149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00946-7
Kimutai, K. (2017). Is DDT Still Being Used?, Environment, WorldAtlas, https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/is-ddt-still-being-used.html
Kirchner, M., Jakobi, G., Körner, W., Levy, W., Moche, W., Niedermoser, B., Schaub, M., Ries, L., Weiss, P., Antritter, F., Fischer, N., Bernhard Henkelmann, B. H., & Schramm, K.-W. (2016). Ambient air levels of organochlorine pesticides at three high alpine monitoring stations: Trends and dependencies on geographical origin. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 16, 738–751. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2015.04.0213
Klementova, S., & Keltnerova, L. (2015). Triazine herbicides in the environment. In A. Price, J. Kelton, & L. Sarunaite (Eds.), Herbicides, physiology of action, and safety. INTECH.
Kucuksezgin, F., & Tolga Gonul, L. (2012). Distribution and ecological risk of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in surficial sediments from the Eastern Aegean. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64, 2549–2555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.07.032
Kumar B., Kumar S., Gaur R., Goel G., Mishra M., Singh S. K., Prakash D., Sharma C. S. (2011). Persistent organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in intensive agricultural soils from North India. Soil and Water Research, 6, 190–197. https://doi.org/10.17221/21/2011-SWR
Kumar, B., Verma, V. K., Mishra, M., Gaur, R., Kumar, S., & Sharma, C. S. (2014). DDT and HCH (Organochlorine Pesticides) in Residential Soils and Health Assessment for Human Populations in Korba, India. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 20, 1538–1549. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2013.858563
Leong, K. H., Benjamin Tan, L. L., & Mustafa, A. M. (2007). Contamination levels of selected organochlorine and organophosphate pesticides in the Selangor River, Malaysia between 2002 and 2003. Chemosphere, 66, 1153–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.06.009
León-Santiesteban, H. H., & Rodríguez-Vázquez, R. (2017). Fungal degradation of organochlorine pesticides. In S. N. Singh (Ed.), Microbe-induced degradation of pesticides (pp. 131–149). Springer International Publishing.
Li, Y. F., Zhulidov, A. V., Robarts, R. D., Korotova, L. G., Zhulidov, D. A., Gurtovaya, T. Y., & Ge, L. P. (2006). Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane usage in the former Soviet Union. Science of the Total Environment, 357, 138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.06.009
Malhotra, H., Kaur, S., & Phale, P. S. (2021). Conserved metabolic and evolutionary themes in microbial degradation of carbamate pesticides. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 648868. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.648868
Malusá, E., Tartanus, M., Danelski, W., Miszczak, A., Szustakowska, E., Kicińska, J., & Furmanczyk, E. M. (2020). Monitoring of DDT in agricultural soils under organic farming in Poland and the risk of crop contamination. Environmental Management, 66, 916–929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01347-9
Manz, M., Wenzel, K.-D., Dietze, U., & Schüürmann, G. (2001). Persistent organic pollutants in agricultural soils of central Germany. Science of the Total Environment, 277, 187–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00877-9
Miglioranza, K. S. B., Ondarza, P. M., Costa, P. G., de Azevedo, A., Gonzalez, M., Shimabukuro, V. M., Grondona, S. I., Mitton, F. M., Barra, R. O., Wania, F., & Fillmann, G. (2021). Spatial and temporal distribution of persistent organic pollutants and current use pesticides in the atmosphere of Argentinean Patagonia. Chemosphere, 266, 129015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129015
Mishra, S., Lin, Z., Pang, S., Zhang, W., Bhatt, P., & Chen, S. (2021). Recent advanced technologies for the characterization of xenobiotic-degrading microorganisms and microbial communities. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9, 632059. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.632059
Mitra, D., Díaz Rodríguez, A. M., Parra Cota, F. I., Khoshru, B., Panneerselvam, P., Moradi, S., Sagarika, M. S., Anđelković, S., Santos-Villalobos, S. d. l., & Das Mohapatra, P. K. (2021). Amelioration of thermal stress in crops by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 115, 101679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2021.101679
Mohammad Fakhrul Islam, S., & Karim, Z. (2020). World’s demand for food and water: The consequences of climate change. In M. Hossein Davood Abadi Farahani, V. Vatanpour, & A. Hooshang Taheri (Eds.), Desalination – challenges and opportunities. IntechOpen.
Narkhede, C. P., Patil, A. R., Koli, S., Suryawanshi, R., Wagh, N. D., Bipinchandra, K. S., & Patil, S. V. (2015). Studies on endosulfan degradation by local isolate Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 4, 259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2015.01.006
National Research Council. (1982). An assessment of the health risks of seven pesticides used for termite control. National Academies Press.
Neslen, A. (2018). Organophosphates: Ban entire pesticide class to protect children’s health say scientists. Environmental Health Sciences Center. https://environmentalhealth.ucdavis.edu/organophosphate-pesticide-ban-say-scientists
Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P., Maipas, S., Kotampasi, C., Stamatis, P., & Hens, L. (2016). Chemical Pesticides and Human Health: The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture. Frontiers in Public Health, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2016.00148
NRA. (1999). PARATHION-METHYL Interim Report Volume I. National Registration Authority for Agricultural and Veterinary Chemicals.
Oginawati, K., Susetyo, S. H., Rahmawati, S. I., Kurniawan, S. B., & Abdullah, S. R. S. (2021). Distribution of organochlorine pesticide pollution in water, sediment, mollusk, and fish at Saguling Dam, West Java, Indonesia. Toxicological Research, 38, 149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-021-00094-1
Okeke, B. C., Siddique, T., Arbestain, M. C., & Frankenberger, W. T. (2002). Biodegradation of γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane (Lindane) and α-Hexachlorocyclohexane in water and a soil slurry by a Pandoraea species. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50, 2548–2555. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf011422a
Okoro, H. K., Fatoki, O. S., Adekola, F. A., Ximba, B. J., & Snyman, R. G. (2014). Organotin compounds. In P. Wexler (Ed.), Encyclopedia of toxicology (pp. 720–725). Elsevier.
Ortiz, J. B., Gonzales de Canales, L. M., & Sarasquete, C. (2003). Histopathological changes induced by lindane (γ-HCH) in various organs of fishes. Scientia Marina, 67, 53–61.
Ostrakhovitch, E. A. (2015). Tin. In G. F. Nordberg, B. A. Fowler, & M. Nordberg (Eds.), Handbook on the toxicology of metals (pp. 1241–1285). Elsevier.
Özkara, A., Akyil, D., & Konuk, M. (2016). Pesticides, environmental pollution, and health. In M. Larramendy & S. Soloneski (Eds.), Environmental health risk – hazardous factors to living species. INTECH.
PAN Germany. (2011). Highly hazardous pesticides from BASF, Bayer, and Syngenta! Results of an international investigation.
Pant, G., Mistry, S. K., & Sibi, G. (2013). Isolation, identification and characterization of p, p′-DDT degrading bacteria from soil. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 6, 130–137. https://doi.org/10.3923/jest.2013.130.137
Parada, H., Wolff, M. S., Engel, L. S., White, A. J., Eng, S. M., Cleveland, R. J., Khankari, N. K., Teitelbaum, S. L., Neugut, A. I., & Gammon, M. D. (2016). Organochlorine insecticides DDT and chlordane in relation to survival following breast cancer: Organochlorine insecticides and breast cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 138, 565–575. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29806
Pathak, R. K., & Dikshit, A. K. (2012). Atrazine and human health. International Journal Ecosystem, 1, 14–23. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.ije.20110101.03
Plaza-Bolaños, P., Padilla-Sánchez, J. A., Garrido-Frenich, A., Romero-González, R., & Martínez-Vidal, J. L. (2012). Evaluation of soil contamination in intensive agricultural areas by pesticides and organic pollutants: South-eastern Spain as a case study. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 14, 1182. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2em10993j
Pope, C. (2014). Methyl parathion. In P. Wexler (Ed.), Encyclopedia of toxicology (pp. 324–326). Elsevier.
Popp, J., Pető, K., & Nagy, J. (2013). Pesticide productivity and food security. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 33, 243–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-012-0105-x
Pribylova, P., Kares, R., Boruvkova, J., Cupr, P., Prokes, R., Kohoutek, J., Holoubek, I., & Klanova, J. (2012). Levels of persistent organic pollutants and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air of Central and Eastern Europe. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 3, 494–505. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2012.057
PubChem. (2021). Tributyltin. National Library of Medicine National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Purnomo, A. S. (2017). Microbe-assisted degradation of aldrin and dieldrin. In S. N. Singh (Ed.), Microbe-induced degradation of pesticides (pp. 1–22). Springer International Publishing.
Purnomo, A. S., Mori, T., Kamei, I., & Kondo, R. (2011). Basic studies and applications on bioremediation of DDT: A review. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 65, 921–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.07.011
Rao, B. T., Thirupathi, T., & Venkaiah, Y. (2018). Effect of Methyl parathion (an organophosphate) on biochemical contents of fresh water cat fish heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 9, 2869–2874.
Reed, N. R., & Koshlukova, S. (2014). Heptachlor. In P. Wexler (Ed.), Encyclopedia of toxicology (pp. 840–844). Elsevier.
Roede, J. R., & Miller, G. W. (2014). Paraquat. In P. Wexler (Ed.), Encyclopedia of toxicology (pp. 756–758). Elsevier.
Romero-Aguilar, M., Tovar-Sánchez, E., Sánchez-Salinas, E., Mussali-Galante, P., Sánchez-Meza, J. C., Castrejón-Godínez, M. L., Dantán-González, E., Trujillo-Vera, M. Á., & Ortiz-Hernández, M. L. (2014). Penicillium sp. as an organism that degrades endosulfan and reduces its genotoxic effects. SpringerPlus, 3, 536. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-536
Rosales Landeros, C., Eduardo Barrera Díaz, C., & Bilyeu, B. (2019). Dissemination of endosulfan into the environment. In S. Kudom Donyinah (Ed.), Persistent Organic Pollutants. IntechOpen.
Roșca, M., Hlihor, R.-M., Cozma, P., & Gavrilescu, M. (2017). Tools for the characterization of pesticide risk in food products-an overview. International Proceedings of Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, 101, 9. https://doi.org/10.7763/IPCBEE
Rought, S. E., Yau, P. M., Guo, X. W., Chuang, L. F., Doi, R. H., & Chuang, R. Y. (2000). Modulation of CPP32 activity and induction of apoptosis in human CEM X 174 lymphocytes by heptachlor, a chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticide. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 14, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0461(2000)14:1<42::AID-JBT6>3.0.CO;2-X
Russo, F., Ceci, A., Pinzari, F., Siciliano, A., Guida, M., Malusà, E., Tartanus, M., Miszczak, A., Maggi, O., & Persiani, A. M. (2019). Bioremediation of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)-contaminated agricultural soils: Potential of two autochthonous saprotrophic fungal strains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 85, e01720-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01720-19
Sagar, V., & Singh, D. P. (2011). Biodegradation of lindane pesticide by non white- rots soil fungus fusarium sp. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 27, 1747–1754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0628-8
Sahoo, B., Ningthoujam, R., & Chaudhuri, S. (2019). Isolation and characterization of a lindane degrading bacteria Paracoccus sp. NITDBR1 and evaluation of its plant growth promoting traits. International Microbiology, 22, 155–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-00037-1
Salam, J. A., & Das, N. (2014). Lindane degradation by Candida VITJzN04, a newly isolated yeast strain from contaminated soil: Kinetic study, enzyme analysis and biodegradation pathway. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 1301–1313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1551-6
Sandu, M. A., & Virsta, A. (2015). Environmental toxicity of lindane and health effect. Journal of Environmental Protection and Ecology, 16, 933–944.
Sarkar, B., Mukhopadhyay, R., Mandal, A., Mandal, S., Vithanage, M., & Biswas, J. K. (2020). Sorption and desorption of agro-pesticides in soils. In M. N. V. Prasad (Ed.), Agrochemicals detection, treatment and remediation (pp. 189–205). Elsevier.
Sarker, S., Akbor, M. A., Nahar, A., Hasan, M., Islam, A. R. M. T., & Siddique, M. A. B. (2021). Level of pesticides contamination in the major river systems: A review on South Asian countries perspective. Heliyon, 7, e07270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07270
Shetty, P., Bhalerao, T., Mitra, J., Murthy, N., Namitha, K., Savitha, K., & Raghu, K. (2000). Biodegradation of cyclodiene insecticide endosulfan by Mucor thermohyalospora MTCC1384. Current Science, 79, 1381–1383.
Siddique, T., Okeke, B. C., Arshad, M., & Frankenberger, W. T. (2003). Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan-degrading microorganisms. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 47–54. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.4700
Silberman, J., & Taylor, A. (2021). Carbamate toxicity. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
Sim, S. F., Chung, L. Y., Jonip, J., & Chai, L. K. (2019). Uptake and dissipation of Carbofuran and its metabolite in Chinese kale and brinjal cultivated under humid tropic climate. Advances in Agriculture, 2019, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7937086
Simon-Delso, N., Amaral-Rogers, V., Belzunces, L. P., Bonmatin, J. M., Chagnon, M., Downs, C., Furlan, L., Gibbons, D. W., Giorio, C., Girolami, V., Goulson, D., Kreutzweiser, D. P., Krupke, C. H., Liess, M., Long, E., McField, M., Mineau, P., Mitchell, E. A. D., Morrissey, C. A., Noome, D. A., Pisa, L., Settele, J., Stark, J. D., Tapparo, A., Van Dyck, H., Van Praagh, J., Van der Sluijs, J. P., Whitehorn, P. R., & Wiemers, M. (2015). Systemic insecticides (neonicotinoids and fipronil): Trends, uses, mode of action and metabolites. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 5–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3470-y
Singh, A., Dwivedi, P., Kumar, V., & Kumar Pandey, D. (2021). Brassinosteroids and their analogs: Feedback in plants under in vitro condition. South African Journal of Botany, 143, 256–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2021.08.008
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., & Sinha, S. (2007). Persistent organochlorine pesticide residues in soil and surface water of northern indo-Gangetic alluvial plains. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 125, 147–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9247-0
Singh, S., & Chaube, R. (2019). Toxicological impact of pentachlorophenol on the hepatic and reproductive activity of the stinging catfish Heteropneustes fossilis. Aquaculture Studies, 19, 139–145. https://doi.org/10.4194/2618-6381-v19_2_07
Singh, T., & Singh, D. K. (2019). Rhizospheric microbacterium sp. P27 showing potential of Lindane degradation and plant growth promoting traits. Current Microbiology, 76, 888–895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01703-x
Solomon, K. R., Carr, J. A., Du Preez, L. H., Giesy, J. P., Kendall, R. J., Smith, E. E., & Van Der Kraak, G. J. (2008). Effects of atrazine on fish, amphibians, and aquatic reptiles: A critical review. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 38, 721–772. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408440802116496
Sreekumar, K. M., & Prathapan, K. D. (2021). An evidence-based inquiry into the endosulfan tragedy in Kasaragod, Kerala. Economic & Political Weekly, 56, 41–53.
Stoleru, V., Munteanu, N., Hura, C., Sellitto, V. M., & Gavrilescu, M. (2016). Organochlorine pesticide residues in soil and edible vegetable. Environmental Engineering & Management Journal, 15(3), 527–535. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2016.057
Stoleru, V., Munteanu, N., & Hura, C. (2015). Organophosphorus pesticide residues in soil and vegetable, through different growing systems. Environmental Engineering & Management Journal, 14(6), 1465–1473. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2015.158
Syafrudin, M., Kristanti, R. A., Yuniarto, A., Hadibarata, T., Rhee, J., Al-onazi Wedad A., Algarni T. S., Almarri A. H., Al-Mohaimeed, A. M. (2021). Pesticides in Drinking Water—A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020468
Tarcau, D., Cucu-Man, S., Boruvkova, J., Klanova, J., & Covaci, A. (2013). Organochlorine pesticides in soil, moss and tree-bark from North-Eastern Romania. Science of the Total Environment, 456–457, 317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.03.103
Thi Hue, N., Nguyen, T. P. M., Nam, H., & Hoang Tung, N. (2018). Paraquat in surface water of some streams in Mai Chau Province, the Northern Vietnam: Concentrations, profiles, and human risk assessments. Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8521012
Thiombane, M., Petrik, A., Di Bonito, M., Albanese, S., Zuzolo, D., Cicchella, D., Lima, A., Qu, C., Qi, S., & De Vivo, B. (2018). Status, sources and contamination levels of organochlorine pesticide residues in urban and agricultural areas: A preliminary review in central–southern Italian soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 26361–26382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2688-5
Tilman, D., Balzer, C., Hill, J., & Befort, B. L. (2011). Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108, 20260–20264. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116437108
Tsai, W.-T. (2013). A review on environmental exposure and health risks of herbicide paraquat. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 95, 197–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2012.761999
Tu, C. M., & Bollen, W. B. (2006). Interaction between paraquat and microbes in soils*. Weed Research, 8, 38–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.1968.tb01399.x
Tudi, M., Daniel Ruan, H., Wang, L., Lyu, J., Sadler, R., Connell, D., … Phung, D. T. (2021). Agriculture Development, Pesticide Application and Its Impact on the Environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031112
UNEP. (2013). Report of the persistent organic pollutants review committee on the work of its ninth meeting addendum risk profile on pentachlorophenol and its salts and esters. Rome.
Unyimadu, J. P., Osibanjo, O., & Babayemi, J. O. (2018). Selected persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in water of river Niger: Occurrence and distribution. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6378-4
USEPA. (1994). Fenbutatin-oxide.
USEPA. (2020). Atrazine interim registration review decision case number 0062. Environmental Protection Agency of United States of America.
van den Berg, H., Manuweera, G., & Konradsen, F. (2017). Global trends in the production and use of DDT for control of malaria and other vector-borne diseases. Malaria Journal, 16, 401. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-017-2050-2
Vasseghian, Y., Hosseinzadeh, S., Khataee, A., & Dragoi, E.-N. (2021). The concentration of persistent organic pollutants in water resources: A global systematic review, meta-analysis and probabilistic risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 796, 149000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149000
Victor-Costa, A. B., Bandeira, S. M. C., Oliveira, A. G., Mahecha, G. A. B., & Oliveira, C. A. (2010). Changes in testicular morphology and steroidogenesis in adult rats exposed to Atrazine. Reproductive Toxicology, 29, 323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2009.12.006
Vidau, C., Brunet, J.-L., Badiou, A., & Belzunces, L. P. (2009). Phenylpyrazole insecticides induce cytotoxicity by altering mechanisms involved in cellular energy supply in the human epithelial cell model Caco-2. Toxicology In Vitro, 23, 589–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2009.01.017
Villanneau, E. J., Saby, N. P. A., Marchant, B. P., Jolivet, C. C., Boulonne, L., Caria, G., Barriuso, E., Bispo, A., Briand, O., & Arrouays, D. (2011). Which persistent organic pollutants can we map in soil using a large spacing systematic soil monitoring design? A case study in Northern France. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 3719–3731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.048
Vogue, P. A., Kerle, E. A., & Jenkins, J. J. (1994). OSU extension pesticide properties database. National Pesticide Information Centre, Oregon State University.
WHO. (2004a). Lindane in drinking-water. World Health Organization.
WHO. (2004b). Methyl parathion in drinking-water. World Health Organization.
WHO. (2004c). Chlordane in drinking-water. World Health Organization.
WHO. (2006). Heptachlor. World Health Organization.
Wongputtisin, P., Supo, C., Suwannarach, N., Honda, Y., Nakazawa, T., Kumla, J., Lumyong, S., & Khanongnuch, C. (2021). Filamentous fungi with high paraquat-degrading activity isolated from contaminated agricultural soils in northern Thailand. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 72, 467–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13439
World Health Organization, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2021). Guidance on pesticide licensing schemes: International code of conduct on pesticide management. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Wu, C.-H., Lu, C.-W., Hsu, T.-H., Wu, W.-J., & Wang, S.-E. (2021). Neurotoxicity of fipronil affects sensory and motor systems in zebrafish. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 177, 104896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2021.104896
Xie, H., Zhu, L., Wang, J., Jiang, J., & Wang, J. (2017). Biodegradation of DDE and DDT by bacterial strain Stenotrophomonas sp. DXZ9. Journal of Environmental & Analytical Toxicology, 7, 5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0525.1000496
Yadav, I. C., Devi, N. L., Syed, J. H., Cheng, Z., Li, J., Zhang, G., & Jones, K. C. (2015). Current status of persistent organic pesticides residues in air, water, and soil, and their possible effect on neighboring countries: A comprehensive review of India. Science of The Total Environment, 511, 123–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.0
Yang, D., Qi, S.-H., Zhang, J.-Q., Tan, L.-Z., Zhang, J.-P., Zhang, Y., Xu F., Xing X.-L., Hu Y., Chen W., Yang J.-H., Xu, M.-H. (2012). Residues of Organochlorine Pesticides (OCPs) in Agricultural Soils of Zhangzhou City, China. Pedosphere, 22, 178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1002-0160(12)60004-6
Ye, X., Dong, F., & Lei, X. (2018). Microbial resources and ecology – Microbial degradation of pesticides. Natural Resources Conservation and Research, 1, 22–28. https://doi.org/10.24294/nrcr.v1i1.242
Zaranyika, M. F., Matimati, E., & Mushonga, P. (2020). Degradation kinetics of DDT in tropical soils: A proposed multi-phase zero order kinetic model that takes into account evaporation, hydrolysis, photolysis, microbial degradation and adsorption by soil particulates. Scientific African, 9, e00467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00467
Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., & Yang, M. (2021). Profiles and risk assessment of legacy and current use pesticides in urban rivers in Beijing, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 39423–39431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13140-0
Zheng, G., Selvam, A., & Wong, J. W. C. (2011). Rapid degradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) at low temperature by Sphingobium strains. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 65, 612–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.03.005
Zhu, G., Du, R., Du, D., Qian, J., & Ye, M. (2021). Keystone taxa shared between earthworm gut and soil indigenous microbial communities collaboratively resist chlordane stress. Environmental Pollution, 283, 117095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117095
Zou, E., & Matsumura, F. (2003). Long-term exposure to β-hexachlorocyclohexane (β-HCH) promotes transformation and invasiveness of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Biochemical Pharmacology, 66, 831–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00394-0
Acknowledgments
The authors contributed equally.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Roșca, M., Mihalache, G., Stoleru, V. (2023). Banned Pesticides with High Persistence: The Impact of Their Use in Agriculture and Their Removal by Microbial Biodegradation. In: Bhat, R.A., Butnariu, M., Dar, G.H., Hakeem, K.R. (eds) Microbial Bioremediation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18017-0_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18017-0_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-18016-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-18017-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)