Abstract
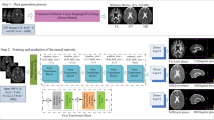
Deep learning has a great potential for estimating biomarkers in diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI). Atlases, on the other hand, are a unique tool for modeling the spatio-temporal variability of biomarkers. In this paper, we propose the first framework to exploit both deep learning and atlases for biomarker estimation in dMRI. Our framework relies on non-linear diffusion tensor registration to compute biomarker atlases and to estimate atlas reliability maps. We also use non-linear tensor registration to align the atlas to a subject and to estimate the error of this alignment. We use the biomarker atlas, atlas reliability map, and alignment error map, in addition to the dMRI signal, as inputs to a deep learning model for biomarker estimation. We use our framework to estimate fractional anisotropy and neurite orientation dispersion from down-sampled dMRI data on a test cohort of 70 newborn subjects. Results show that our method significantly outperforms standard estimation methods as well as recent deep learning techniques. Our method is also more robust to higher measurement down-sampling factors. Our study shows that the advantages of deep learning and atlases can be synergistically combined to achieve unprecedented biomarker estimation accuracy in dMRI.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, D.C., et al.: Imaging brain microstructure with diffusion MRI: practicality and applications. NMR Biomed. 32(4), e3841 (2019)
Andica, C., et al.: Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging reveals white matter microstructural alterations in adults with autism. Mol. Autism 12(1), 1–14 (2021)
Bastiani, M., et al.: Automated processing pipeline for neonatal diffusion MRI in the developing human connectome project. Neuroimage 185, 750–763 (2019)
Daducci, A., et al.: Accelerated microstructure imaging via convex optimization (AMICO) from diffusion MRI data. Neuroimage 105, 32–44 (2015)
Diniz, J.O.B., et al.: Esophagus segmentation from planning CT images using an atlas-based deep learning approach. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 197, 105685 (2020)
Dubois, J., et al.: The early development of brain white matter: a review of imaging studies in fetuses, newborns and infants. Neuroscience 276, 48–71 (2014)
Fick, R.H., et al.: The Dmipy toolbox: diffusion MRI multi-compartment modeling and microstructure recovery made easy. Front. Neuroinform. 13, 64 (2019)
Gibbons, E.K., et al.: Simultaneous NODDI and GFA parameter map generation from subsampled q-space imaging using deep learning. Magn. Reson. Med. 81(4), 2399–2411 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.27568
Golkov, V., et al.: q-space deep learning: twelve-fold shorter and model-free diffusion MRI scans. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1344–1351 (2016)
Hagler, D.J., Jr., et al.: Automated white-matter tractography using a probabilistic diffusion tensor atlas: application to temporal lobe epilepsy. Hum. Brain Mapp. 30(5), 1535–1547 (2009)
Harms, R.L., et al.: Robust and fast nonlinear optimization of diffusion MRI microstructure models. Neuroimage 155, 82–96 (2017)
Hasan, K.M., et al.: Serial atlas-based diffusion tensor imaging study of uncomplicated mild traumatic brain injury in adults. J. Neurotrauma 31(5), 466–475 (2014)
Jones, D.K., et al.: Optimal strategies for measuring diffusion in anisotropic systems by magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 42(3), 515–525 (1999)
Karimi, D., Gholipour, A.: Diffusion tensor estimation with transformer neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.05701 (2022)
Karimi, D., et al.: Deep learning-based parameter estimation in fetal diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroimage 243, 118482 (2021)
Karimi, D., et al.: Learning to estimate the fiber orientation distribution function from diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroimage 239, 118316 (2021)
Khan, S., et al.: Fetal brain growth portrayed by a spatiotemporal diffusion tensor MRI atlas computed from in utero images. Neuroimage 185, 593–608 (2019)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, (ICLR) (2014)
Koay, C.G., et al.: A unifying theoretical and algorithmic framework for least squares methods of estimation in diffusion tensor imaging. J. Magn. Reson. 182(1), 115–125 (2006)
Novikov, D.S., et al.: Quantifying brain microstructure with diffusion MRI: theory and parameter estimation. NMR Biomed. 32(4), e3998 (2019)
Palacios, E.M., et al.: The evolution of white matter microstructural changes after mild traumatic brain injury: a longitudinal DTI and NODDI study. Sci. Adv. 6(32), eaaz6892 (2020)
Pietsch, M., et al.: A framework for multi-component analysis of diffusion MRI data over the neonatal period. Neuroimage 186, 321–337 (2019)
Saghafi, B., et al.: Spatio-angular consistent construction of neonatal diffusion MRI atlases. Hum. Brain Mapp. 38(6), 3175–3189 (2017)
Skare, S., Hedehus, M., Moseley, M.E., Li, T.Q.: Condition number as a measure of noise performance of diffusion tensor data acquisition schemes with MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 147(2), 340–352 (2000)
Taquet, M., Scherrer, B., Boumal, N., Peters, J.M., Macq, B., Warfield, S.K.: Improved fidelity of brain microstructure mapping from single-shell diffusion MRI. Med. Image Anal. 26(1), 268–286 (2015)
Tian, Q., et al.: DeepDTI: high-fidelity six-direction diffusion tensor imaging using deep learning. Neuroimage 219, 117017 (2020)
Tournier, J.D., et al.: MRtrix3: a fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. Neuroimage 202, 116137 (2019)
Uus, A., et al.: Multi-channel 4D parametrized atlas of macro-and microstructural neonatal brain development. Front. Neurosci. 15, 661704 (2021)
Veraart, J., Rajan, J., Peeters, R.R., Leemans, A., Sunaert, S., Sijbers, J.: Comprehensive framework for accurate diffusion MRI parameter estimation. Magn. Reson. Med. 70(4), 972–984 (2013)
Ye, C.: Tissue microstructure estimation using a deep network inspired by a dictionary-based framework. Med. Image Anal. 42, 288–299 (2017)
Zhang, H., Schneider, T., Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A., Alexander, D.C.: NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 61(4), 1000–1016 (2012)
Zhang, H., Yushkevich, P.A., Alexander, D.C., Gee, J.C.: Deformable registration of diffusion tensor MR images with explicit orientation optimization. Med. Image Anal. 10(5), 764–785 (2006)
Zhang, H., Yushkevich, P.A., Rueckert, D., Gee, J.C.: Unbiased white matter atlas construction using diffusion tensor images. In: Ayache, N., Ourselin, S., Maeder, A. (eds.) MICCAI 2007. LNCS, vol. 4792, pp. 211–218. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75759-7_26
Acknowledgment
This study was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under grants R01EB031849, R01NS106030, and R01EB032366; and in part by the Office of the Director of the NIH under grant S10OD0250111.
The DHCP dataset is provided by the developing Human Connectome Project, KCL-Imperial-Oxford Consortium funded by the European Research Council under the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP/2007–2013)/ERC Grant Agreement no. [319456]. We thank the families who supported this trial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Karimi, D., Gholipour, A. (2022). Atlas-Powered Deep Learning (ADL) - Application to Diffusion Weighted MRI. In: Wang, L., Dou, Q., Fletcher, P.T., Speidel, S., Li, S. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13431. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16431-6_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16431-6_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16430-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16431-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)