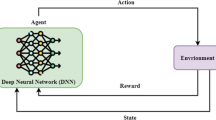
Abstract
The cybersecurity threat landscape has lately become overly complex. Threat actors leverage weaknesses in the network and endpoint security in a very coordinated manner to perpetuate sophisticated attacks that could bring down the entire network and many critical hosts in the network. Increasingly advanced deep and machine learning-based solutions have been used in threat detection and protection. The application of these techniques has been reviewed well in the scientific literature. Deep Reinforcement Learning has shown great promise in developing AI-based solutions for areas that had earlier required advanced human cognizance. Different techniques and algorithms under deep reinforcement learning have shown great promise in applications ranging from games to industrial processes where it is claimed to augment systems with general AI capabilities. These algorithms have recently also been used in cybersecurity, especially in threat detection and endpoint protection, where these are showing state-of-the-art results. Unlike supervised machine and deep learning, deep reinforcement learning is used in more diverse ways and are empowering many innovative applications in the threat defense landscape. However, there does not exist any comprehensive review of these unique applications and accomplishments. Therefore, in this paper, we intend to fill this gap and provide a comprehensive review of the different applications of deep reinforcement learning in cybersecurity threat detection and protection.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Rajab, M., Zarfoss, J., Monrose, F., Terzis, A.: A multifaceted approach to understanding the botnet phenomenon. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement, pp. 41–52 (2006)
Anderson, H.S., Kharkar, A., Filar, B., Roth, P.: Evading machine learning malware detection. Black Hat, pp. 1–6 (2017)
Apruzzese, G., Andreolini, M., Marchetti, M., Venturi, A., Colajanni, M.: Deep reinforcement adversarial learning against botnet evasion attacks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 17(4), 1975–1987 (2020)
Arulkumaran, K., Deisenroth, M.P., Brundage, M., Bharath, A.A.: Deep reinforcement learning: a brief survey. IEEE Sig. Process. Mag. 34(6), 26–38 (2017)
Athiwaratkun, B., Stokes, J.W.: Malware classification with LSTM and GRU language models and a character-level CNN. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2482–2486 (2017)
Behera, C.K., Bhaskari, D.L.: Different obfuscation techniques for code protection. Procedia Comput. Sci. 70, 757–763 (2015)
Bhuyan, M.H., Bhattacharyya, D.K., Kalita, J.K.: Network anomaly detection: methods, systems and tools. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 16(1), 303–336 (2014)
Birman, Y., Hindi, S., Katz, G., Shabtai, A.: Cost-effective malware detection as a service over serverless cloud using deep reinforcement learning. In: 2020 20th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing (CCGRID), pp. 420–429 (2020)
Bridges, R.A., Glass-Vanderlan, T.R., Iannacone, M.D., Vincent, M.S., Chen, Q.: A survey of intrusion detection systems leveraging host data. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 52(6), 1–35 (2019)
David, W.: NSL-KDD datasets (2019). https://www.kaggle.com/mrwellsdavid/unsw-nb15. Accessed 27 June 2021
Mohi-ud din, G.: NSL-KDD dataset (2017). https://www.unb.ca/cic/datasets/nsl.html. Accessed 27 June 2021
Fang, Z., Wang, J., Li, B., Wu, S., Zhou, Y., Huang, H.: Evading anti-malware engines with deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Access 7, 48867–48879 (2019)
Firstbrook, P., Hallawell, A., Girard, J., MacDonald, N.: Magic quadrant for endpoint protection platforms. Gartner RAS Core Research Note G 208912 (2009)
Gülmez, H.G., Angın, P.: A study on the efficacy of deep reinforcement learning for intrusion detection. Sakarya Univ. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 4, 11–25 (2021)
Heady, R., Luger, G., Maccabe, A., Servilla, M.: The architecture of a network level intrusion detection system. Office of Scientific and Technical Information, U.S. Department of Energy, August 1990
Hsu, Y.F., Matsuoka, M.: A deep reinforcement learning approach for anomaly network intrusion detection system. In: 2020 IEEE 9th International Conference on Cloud Networking (CloudNet), pp. 1–6 (2020)
Hu, W., Tan, Y.: Generating adversarial malware examples for black-box attacks based on GAN. ArXiv abs/1702.05983 (2017)
Kienzle, D.M., Elder, M.C.: Recent worms: a survey and trends. In: Proceedings of the 2003 ACM Workshop on Rapid Malcode, WORM 2003, pp. 1–10. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (2003)
Lakshmi, V.: Beginning Security with Microsoft Technologies. Springer, Berkeley (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-4853-9
Li, Y., Liu, J., Li, Q., Xiao, L.: Mobile cloud offloading for malware detections with learning. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), pp. 197–201 (2015)
Li, Y.: Deep reinforcement learning: an overview. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.07274 (2017)
Liao, H.J., Richard Lin, C.H., Lin, Y.C., Tung, K.Y.: Intrusion detection system: a comprehensive review. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 36(1), 16–24 (2013)
Lin, Z., Shi, Y., Xue, Z.: IDSGAN: generative adversarial networks for attack generation against intrusion detection. CoRR abs/1809.02077 (2018)
Liu, S.: Endpoint detection and response (EDR) and endpoint protection platform (EPP) market size worldwide from 2015 to 2020 (2020). https://www.statista.com/statistics/799060/worldwideedr-epp-market-size/. Accessed 27 June 2021
Liu, Y., Dong, M., Ota, K., Li, J., Wu, J.: Deep reinforcement learning based smart mitigation of DDoS flooding in software-defined networks. In: 2018 IEEE 23rd International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), pp. 1–6 (2018)
Lopez-Martin, M., Carro, B., Sanchez-Esguevillas, A.: Application of deep reinforcement learning to intrusion detection for supervised problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 141, 112963 (2020)
Mnih, V., et al.: Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518(7540), 529–533 (2015)
Nappa, A., Rafique, M.Z., Caballero, J.: The MALICIA dataset: identification and analysis of drive-by download operations. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 14(1), 15–33 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10207-014-0248-7
Nguyen, T.T., Reddi, V.J.: Deep reinforcement learning for cyber security. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.05799 (2019)
Pao, D., Lin, W., Liu, B.: A memory-efficient pipelined implementation of the aho-corasick string-matching algorithm. ACM Trans. Archit. Code Optim. (TACO) 7(2), 1–27 (2010)
Rathore, H., Agarwal, S., Sahay, S.K., Sewak, M.: Malware detection using machine learning and deep learning. In: Mondal, A., Gupta, H., Srivastava, J., Reddy, P.K., Somayajulu, D.V.L.N. (eds.) BDA 2018. LNCS, vol. 11297, pp. 402–411. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04780-1_28
Rathore, H., Sahay, S.K., Chaturvedi, P., Sewak, M.: Android malicious application classification using clustering. In: Abraham, A., Cherukuri, A.K., Melin, P., Gandhi, N. (eds.) ISDA 2018 2018. AISC, vol. 941, pp. 659–667. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16660-1_64
Rathore, H., Sahay, S.K., Nikam, P., Sewak, M.: Robust Android malware detection system against adversarial attacks using Q-learning. Inf. Syst. Front. 23, 867–882 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-020-10083-8
Rathore, H., Sahay, S.K., Rajvanshi, R., Sewak, M.: Identification of significant permissions for efficient Android malware detection. In: Gao, H., J. Durán Barroso, R., Shanchen, P., Li, R. (eds.) BROADNETS 2020. LNICST, vol. 355, pp. 33–52. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68737-3_3
Rathore, H., Sahay, S.K., Thukral, S., Sewak, M.: Detection of malicious Android applications: classical machine learning vs. deep neural network integrated with clustering. In: Gao, H., J. Durán Barroso, R., Shanchen, P., Li, R. (eds.) BROADNETS 2020. LNICST, vol. 355, pp. 109–128. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68737-3_7
Schulman, J., Levine, S., Abbeel, P., Jordan, M., Moritz, P.: Trust region policy optimization. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1889–1897. PMLR (2015)
Schulman, J., Moritz, P., Levine, S., Jordan, M., Abbeel, P.: High-dimensional continuous control using generalized advantage estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.02438 (2015)
Schulman, J., Wolski, F., Dhariwal, P., Radford, A., Klimov, O.: Proximal policy optimization algorithms. CoRR abs/1707.06347 (2017)
Sethi, K., Sai Rupesh, E., Kumar, R., Bera, P., Venu Madhav, Y.: A context-aware robust intrusion detection system: a reinforcement learning-based approach. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 19(6), 657–678 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10207-019-00482-7
Sewak, M.: Deep Reinforcement Learning - Frontiers of Artificial Intelligence. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8285-7
Sewak, M., Sahay, S., Rathore, H.: Value-approximation based deep reinforcement learning techniques: an overview. In: 2020 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computing Communication and Automation (ICCCA), pp. 379–384 (2020)
Sewak, M., Sahay, S., Rathore, H.: DRLDO a novel DRL based de obfuscation system for defense against metamorphic malware. Def. Sci. J. 71, 55–65 (2021)
Sewak, M., Sahay, S.K., Rathore, H.: DeepIntent: Implicitintent based Android IDS with E2E deep learning architecture. In: 2020 IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2020)
Sewak, M., Sahay, S.K., Rathore, H.: DOOM: a novel adversarial-DRL-based op-code level metamorphic malware obfuscator for the enhancement of IDS. In: UbiComp 2020 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 131–134. ACM (2020)
Sewak, M., Sahay, S.K., Rathore, H.: An overview of deep learning architecture of deep neural networks and autoencoders. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 17(1), 182–188 (2020)
Sewak, M., Sahay, S.K., Rathore, H.: Policy-approximation based deep reinforcement learning techniques: an overview. In: Joshi, A., Mahmud, M., Ragel, R.G., Thakur, N.V. (eds.) Information and Communication Technology for Competitive Strategies (ICTCS 2020). LNNS, vol. 191, pp. 493–507. Springer, Singapore (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0739-4_47
Suwannalai, E., Polprasert, C.: Network intrusion detection systems using adversarial reinforcement learning with deep Q-network. In: 2020 18th International Conference on ICT and Knowledge Engineering (ICT&KE), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2020)
Tehranipoor, M., Koushanfar, F.: A survey of hardware trojan taxonomy and detection. IEEE Des. Test Comput. 27(1), 10–25 (2010)
Van Hasselt, H., Guez, A., Silver, D.: Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning. CoRR abs/1509.06461 (2015)
Wan, X., Sheng, G., Li, Y., Xiao, L., Du, X.: Reinforcement learning based mobile offloading for cloud-based malware detection. In: GLOBECOM 2017–2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, pp. 1–6 (2017)
Wang, Y., Stokes, J.W., Marinescu, M.: Neural malware control with deep reinforcement learning. In: MILCOM 2019–2019 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), pp. 1–8 (2019)
Wang, Z., Schaul, T., Hessel, M., Van Hasselt, H., Lanctot, M., De Freitas, N.: Dueling network architectures for deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2016, vol. 48, pp. 1995–2003. JMLR.org (2016)
Wu, D., Fang, B., Wang, J., Liu, Q., Cui, X.: Evading machine learning botnet detection models via deep reinforcement learning. In: ICC 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 1–6 (2019)
You, I., Yim, K.: Malware obfuscation techniques: a brief survey. In: 2010 International Conference on Broadband, Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications, pp. 297–300 (2010)
Zahavy, T., Haroush, M., Merlis, N., Mankowitz, D.J., Mannor, S.: Learn what not to learn: action elimination with deep reinforcement learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 31, pp. 3562–3573 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sewak, M., Sahay, S.K., Rathore, H. (2022). Deep Reinforcement Learning for Cybersecurity Threat Detection and Protection: A Review. In: Krishnan, R., Rao, H.R., Sahay, S.K., Samtani, S., Zhao, Z. (eds) Secure Knowledge Management In The Artificial Intelligence Era. SKM 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1549. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97532-6_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-97532-6_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-97531-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-97532-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)