Abstract
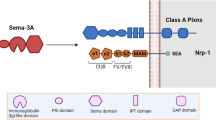
Semaphorin3E belongs to the large family of semaphorin proteins. Semaphorin3E was initially identified as axon guidance cues in the neural system. It is universally expressed beyond the nervous system and contributes to regulating essential cell functions such as cell migration, proliferation, and adhesion. Binding of semaphorin3E to its receptor, plexinD1, triggers diverse signaling pathways involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases from cancer to autoimmune and allergic disorders. Here, we highlight the novel findings on the role of semaphorin3E in airway biology. In particular, we highlight our recent findings on the function and potential mechanisms by which semaphorin3E and its receptor, plexinD1, impact airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, and remodeling in the context of asthma.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization: Global surveillance, prevention and control of chronic respiratory diseases: a comprehensive approach. 2007.
Khare A, Krishnamoorthy N, Oriss TB, Fei M, Ray P, Ray A. Cutting edge: inhaled antigen upregulates retinaldehyde dehydrogenase in lung CD103+ but not plasmacytoid dendritic cells to induce Foxp3 de novo in CD4+ T cells and promote airway tolerance. J Immunol. 2013;191(1):25–9.
Bateman ED, Hurd SS, Barnes PJ, Bousquet J, Drazen JM, FitzGerald M, Gibson P, Ohta K, O’Byrne P, Pedersen SE, et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur Respir J. 2008;31(1):143–78.
Holgate ST, Arshad HS, Roberts GC, Howarth PH, Thurner P, Davies DE. A new look at the pathogenesis of asthma. Clin Sci (Lond). 2010;118(7):439–50.
Romagnani S. The increased prevalence of allergy and the hygiene hypothesis: missing immune deviation, reduced immune suppression, or both? Immunology. 2004;112(3):352–63.
American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology: Asthma Statistics. 2015.
Asthma Society of Canada: What is Asthma 2015.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Asthma. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/asthma/signs.
Barnes PJ. Immunology of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(3):183–92.
Hamid Q, Tulic MK, Liu MC, Moqbel R. Inflammatory cells in asthma: mechanisms and implications for therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111(1 Suppl):S5–S12. discussion S12–17
Murdoch JR, Lloyd CM. Chronic inflammation and asthma. Mutat Res. 2010;690(1–2):24–39.
Maddox L, Schwartz DA. The pathophysiology of asthma. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:477–98.
Movassagh H, Khadem F, Gounni AS. Semaphorins and their roles in airway biology: potential as therapeutic targets. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018;58(1):21–7.
Kolodkin AL, Matthes DJ, O’Connor TP, Patel NH, Admon A, Bentley D, Goodman CS. Fasciclin IV: sequence, expression, and function during growth cone guidance in the grasshopper embryo. Neuron. 1992;9(5):831–45.
Luo Y, Raible D, Raper JA. Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell. 1993;75(2):217–27.
Roth L, Koncina E, Satkauskas S, Cremel G, Aunis D, Bagnard D. The many faces of semaphorins: from development to pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66(4):649–66.
Yazdani U, Terman JR. The semaphorins. Genome Biol. 2006;7(3):211.
Kumanogoh A, Kikutani H. Immunological functions of the neuropilins and plexins as receptors for semaphorins. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(11):802–14.
Takamatsu H, Takegahara N, Nakagawa Y, Tomura M, Taniguchi M, Friedel RH, Rayburn H, Tessier-Lavigne M, Yoshida Y, Okuno T, et al. Semaphorins guide the entry of dendritic cells into the lymphatics by activating myosin II. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(7):594–600.
Morote-Garcia JC, Napiwotzky D, Kohler D, Rosenberger P. Endothelial Semaphorin 7A promotes neutrophil migration during hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(35):14146–51.
Choi YI, Duke-Cohan JS, Chen W, Liu B, Rossy J, Tabarin T, Ju L, Gui J, Gaus K, Zhu C, et al. Dynamic control of beta1 integrin adhesion by the plexinD1-sema3E axis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(1):379–84.
Movassagh H, Shan L, Mohammed A, Halayko AJ, Gounni AS. Semaphorin 3E deficiency exacerbates airway inflammation, Hyperresponsiveness, and remodeling in a mouse model of allergic asthma. J Immunol. 2017;198(5):1805–14.
Takegahara N, Takamatsu H, Toyofuku T, Tsujimura T, Okuno T, Yukawa K, Mizui M, Yamamoto M, Prasad DV, Suzuki K, et al. Plexin-A1 and its interaction with DAP12 in immune responses and bone homeostasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(6):615–22.
Takamatsu H, Okuno T, Kumanogoh A. Regulation of immune cell responses by semaphorins and their receptors. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010;7(2):83–8.
Chen H, Xie GH, Wang WW, Yuan XL, Xing WM, Liu HJ, Chen J, Dou M, Shen LS. Epigenetically downregulated Semaphorin 3E contributes to gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(24):20449–65.
Klagsbrun M, Shimizu A. Semaphorin 3E, an exception to the rule. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(8):2658–60.
Shimizu I, Yoshida Y, Moriya J, Nojima A, Uemura A, Kobayashi Y, Minamino T. Semaphorin3E-induced inflammation contributes to insulin resistance in dietary obesity. Cell Metab. 2013;18(4):491–504.
Hughes A, Kleine-Albers J, Helfrich MH, Ralston SH, Rogers MJ. A class III semaphorin (Sema3e) inhibits mouse osteoblast migration and decreases osteoclast formation in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012;90(2):151–62.
Movassagh H, Shan L, Halayko AJ, Roth M, Tamm M, Chakir J, Gounni AS. Neuronal chemorepellent Semaphorin 3E inhibits human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133(2):560–7.
Choi YI, Duke-Cohan JS, Ahmed WB, Handley MA, Mann F, Epstein JA, Clayton LK, Reinherz EL. PlexinD1 glycoprotein controls migration of positively selected thymocytes into the medulla. Immunity. 2008;29(6):888–98.
Wanschel A, Seibert T, Hewing B, Ramkhelawon B, Ray TD, van Gils JM, Rayner KJ, Feig JE, O’Brien ER, Fisher EA, et al. Neuroimmune guidance cue Semaphorin 3E is expressed in atherosclerotic plaques and regulates macrophage retention. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(5):886–93.
Gay CM, Zygmunt T, Torres-Vazquez J. Diverse functions for the semaphorin receptor PlexinD1 in development and disease. Dev Biol. 2011;349(1):1–19.
Zhang Y, Singh MK, Degenhardt KR, Lu MM, Bennett J, Yoshida Y, Epstein JA. Tie2Cre-mediated inactivation of plexinD1 results in congenital heart, vascular and skeletal defects. Dev Biol. 2009;325(1):82–93.
Chauvet S, Cohen S, Yoshida Y, Fekrane L, Livet J, Gayet O, Segu L, Buhot MC, Jessell TM, Henderson CE, et al. Gating of Sema3E/PlexinD1 signaling by neuropilin-1 switches axonal repulsion to attraction during brain development. Neuron. 2007;56(5):807–22.
Gu C, Yoshida Y, Livet J, Reimert DV, Mann F, Merte J, Henderson CE, Jessell TM, Kolodkin AL, Ginty DD. Semaphorin 3E and plexin-D1 control vascular pattern independently of neuropilins. Science. 2005;307(5707):265–8.
Mazzotta C, Romano E, Bruni C, Manetti M, Lepri G, Bellando-Randone S, Blagojevic J, Ibba-Manneschi L, Matucci-Cerinic M, Guiducci S. Plexin-D1/Semaphorin 3E pathway may contribute to dysregulation of vascular tone control and defective angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:221.
Oh WJ, Gu C. The role and mechanism-of-action of Sema3E and Plexin-D1 in vascular and neural development. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013;24(3):156–62.
Cariboni A, Andre V, Chauvet S, Cassatella D, Davidson K, Caramello A, Fantin A, Bouloux P, Mann F, Ruhrberg C. Dysfunctional SEMA3E signaling underlies gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron deficiency in Kallmann syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(6):2413–28.
Christensen C, Ambartsumian N, Gilestro G, Thomsen B, Comoglio P, Tamagnone L, Guldberg P, Lukanidin E. Proteolytic processing converts the repelling signal Sema3E into an inducer of invasive growth and lung metastasis. Cancer Res. 2005;65(14):6167–77.
Kolodkin AL, Levengood DV, Rowe EG, Tai YT, Giger RJ, Ginty DD. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell. 1997;90(4):753–62.
Casazza A, Finisguerra V, Capparuccia L, Camperi A, Swiercz JM, Rizzolio S, Rolny C, Christensen C, Bertotti A, Sarotto I, et al. Sema3E-Plexin D1 signaling drives human cancer cell invasiveness and metastatic spreading in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(8):2684–98.
Casazza A, Kigel B, Maione F, Capparuccia L, Kessler O, Giraudo E, Mazzone M, Neufeld G, Tamagnone L. Tumour growth inhibition and anti-metastatic activity of a mutated furin-resistant Semaphorin 3E isoform. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4(3):234–50.
Bellon A, Luchino J, Haigh K, Rougon G, Haigh J, Chauvet S, Mann F. VEGFR2 (KDR/Flk1) signaling mediates axon growth in response to semaphorin 3E in the developing brain. Neuron. 2010;66(2):205–19.
Bousquet J, Chanez P, Lacoste JY, Barneon G, Ghavanian N, Enander I, Venge P, Ahlstedt S, Simony-Lafontaine J, Godard P, et al. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1990;323(15):1033–9.
Louis R, Lau LC, Bron AO, Roldaan AC, Radermecker M, Djukanovic R. The relationship between airways inflammation and asthma severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161(1):9–16.
Woodruff PG, Khashayar R, Lazarus SC, Janson S, Avila P, Boushey HA, Segal M, Fahy JV. Relationship between airway inflammation, hyperresponsiveness, and obstruction in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108(5):753–8.
Hamid Q, Tulic M. Immunobiology of asthma. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:489–507.
Green RH, Brightling CE, McKenna S, Hargadon B, Parker D, Bradding P, Wardlaw AJ, Pavord ID. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360(9347):1715–21.
Jayaram L, Pizzichini MM, Cook RJ, Boulet LP, Lemiere C, Pizzichini E, Cartier A, Hussack P, Goldsmith CH, Laviolette M, et al. Determining asthma treatment by monitoring sputum cell counts: effect on exacerbations. Eur Respir J. 2006;27(3):483–94.
Jatakanon A, Uasuf C, Maziak W, Lim S, Chung KF, Barnes PJ. Neutrophilic inflammation in severe persistent asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160(5 Pt 1):1532–9.
Shaw DE, Berry MA, Hargadon B, McKenna S, Shelley MJ, Green RH, Brightling CE, Wardlaw AJ, Pavord ID. Association between neutrophilic airway inflammation and airflow limitation in adults with asthma. Chest. 2007;132(6):1871–5.
Wenzel SE, Szefler SJ, Leung DY, Sloan SI, Rex MD, Martin RJ. Bronchoscopic evaluation of severe asthma. Persistent inflammation associated with high dose glucocorticoids. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(3 Pt 1):737–43.
Qiu Y, Zhu J, Bandi V, Guntupalli KK, Jeffery PK. Bronchial mucosal inflammation and upregulation of CXC chemoattractants and receptors in severe exacerbations of asthma. Thorax. 2007;62(6):475–82.
Choi JS, Jang AS, Park JS, Park SW, Paik SH, Park JS, Uh ST, Kim YH, Park CS. Role of neutrophils in persistent airway obstruction due to refractory asthma. Respirology. 2012;17(2):322–9.
Shiang C, Mauad T, Senhorini A, de Araujo BB, Ferreira DS, da Silva LF, Dolhnikoff M, Tsokos M, Rabe KF, Pabst R. Pulmonary periarterial inflammation in fatal asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39(10):1499–507.
Anees W, Huggins V, Pavord ID, Robertson AS, Burge PS. Occupational asthma due to low molecular weight agents: eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic variants. Thorax. 2002;57(3):231–6.
Martin RJ, Cicutto LC, Smith HR, Ballard RD, Szefler SJ. Airways inflammation in nocturnal asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;143(2):351–7.
Tan WC, Koh TH, Hay CS, Taylor E. The effect of inhaled budesonide on the diurnal variation in airway mechanics, airway responsiveness and serum neutrophil chemotactic activity in Asian patients with predominant nocturnal asthma. Respirology. 1998;3(1):13–20.
Gagliardo R, Chanez P, Gjomarkaj M, La Grutta S, Bonanno A, Montalbano AM, Di Sano C, Albano GD, Gras D, Anzalone G, et al. The role of transforming growth factor-beta1 in airway inflammation of childhood asthma. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2013;26(3):725–38.
Konradsen JR, James A, Nordlund B, Reinius LE, Soderhall C, Melen E, Wheelock AM, Lodrup Carlsen KC, Lidegran M, Verhoek M, et al. The chitinase-like protein YKL-40: a possible biomarker of inflammation and airway remodeling in severe pediatric asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132(2):328–335.e325.
McDougall CM, Helms PJ. Neutrophil airway inflammation in childhood asthma. Thorax. 2006;61(9):739–41.
Movassagh H, Saati A, Nandagopal S, Mohammed A, Tatari N, Shan L, Duke-Cohan JS, Fowke KR, Lin F, Gounni AS. Chemorepellent Semaphorin 3E negatively regulates neutrophil migration in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 2017;198(3):1023–33.
Linden A. Role of interleukin-17 and the neutrophil in asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001;126(3):179–84.
Saffar AS, Dragon S, Ezzati P, Shan L, Gounni AS. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulate induction of Mcl-1 and survival in glucocorticoid-treated human neutrophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121(2):492–498.e410.
Trevor JL, Deshane JS. Refractory asthma: mechanisms, targets, and therapy. Allergy. 2014;69(7):817–27.
Movassagh H, Shan L, Duke-Cohan JS, Chakir J, Halayko AJ, Koussih L, Gounni AS. Downregulation of semaphorin 3E promotes hallmarks of experimental chronic allergic asthma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):98953–63.
Paul WE, Zhu J. How are T(H)2-type immune responses initiated and amplified? Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(4):225–35.
Kopf M, Schneider C, Nobs SP. The development and function of lung-resident macrophages and dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2015;16(1):36–44.
Lambrecht BN, Hammad H. Taking our breath away: dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3(12):994–1003.
Steinman RM, Banchereau J. Taking dendritic cells into medicine. Nature. 2007;449(7161):419–26.
van Helden MJ, Lambrecht BN. Dendritic cells in asthma. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013;25(6):745–54.
Guilliams M, Ginhoux F, Jakubzick C, Naik SH, Onai N, Schraml BU, Segura E, Tussiwand R, Yona S. Dendritic cells, monocytes and macrophages: a unified nomenclature based on ontogeny. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(8):571–8.
Furuhashi K, Suda T, Hasegawa H, Suzuki Y, Hashimoto D, Enomoto N, Fujisawa T, Nakamura Y, Inui N, Shibata K, et al. Mouse lung CD103+ and CD11bhigh dendritic cells preferentially induce distinct CD4+ T-cell responses. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012;46(2):165–72.
Plantinga M, Guilliams M, Vanheerswynghels M, Deswarte K, Branco-Madeira F, Toussaint W, Vanhoutte L, Neyt K, Killeen N, Malissen B, et al. Conventional and monocyte-derived CD11b(+) dendritic cells initiate and maintain T helper 2 cell-mediated immunity to house dust mite allergen. Immunity. 2013;38(2):322–35.
Curreli S, Wong BS, Latinovic O, Konstantopoulos K, Stamatos NM. Class 3 semaphorins induce F-actin reorganization in human dendritic cells: role in cell migration. J Leukoc Biol. 2016;100(6):1323–34.
Busse WW. The relationship of airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation: airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma: its measurement and clinical significance. Chest. 2010;138(2 Suppl):4S–10S.
Movassagh H, Shan L, Duke-Cohan JS, Halayko AJ, Uzonna JE, Gounni AS. Semaphorin 3E alleviates hallmarks of house dust mite-induced allergic airway disease. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(7):1566–76.
Chapoval SP, Dasgupta P, Smith EP, DeTolla LJ, Lipsky MM, Kelly-Welch AE, Keegan AD. STAT6 expression in multiple cell types mediates the cooperative development of allergic airway disease. J Immunol. 2011;186(4):2571–83.
Leigh R, Ellis R, Wattie JN, Hirota JA, Matthaei KI, Foster PS, O’Byrne PM, Inman MD. Type 2 cytokines in the pathogenesis of sustained airway dysfunction and airway remodeling in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;169(7):860–7.
Sahoo A, Alekseev A, Obertas L, Nurieva R. Grail controls Th2 cell development by targeting STAT6 for degradation. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4732.
Erazo A, Kutchukhidze N, Leung M, Christ AP, Urban JF Jr, Curotto de Lafaille MA, Lafaille JJ. Unique maturation program of the IgE response in vivo. Immunity. 2007;26(2):191–203.
Wu LC, Zarrin AA. The production and regulation of IgE by the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(4):247–59.
Hakonarson H, Herrick DJ, Serrano PG, Grunstein MM. Mechanism of cytokine-induced modulation of beta-adrenoceptor responsiveness in airway smooth muscle. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(11):2593–600.
Hakonarson H, Halapi E, Whelan R, Gulcher J, Stefansson K, Grunstein MM. Association between IL-1beta/TNF-alpha-induced glucocorticoid-sensitive changes in multiple gene expression and altered responsiveness in airway smooth muscle. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001;25(6):761–71.
Kim J, Oh WJ, Gaiano N, Yoshida Y, Gu C. Semaphorin 3E-Plexin-D1 signaling regulates VEGF function in developmental angiogenesis via a feedback mechanism. Genes Dev. 2011;25(13):1399–411.
Suchting S, Freitas C, le Noble F, Benedito R, Breant C, Duarte A, Eichmann A. The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 negatively regulates endothelial tip cell formation and vessel branching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(9):3225–30.
Fukushima Y, Okada M, Kataoka H, Hirashima M, Yoshida Y, Mann F, Gomi F, Nishida K, Nishikawa S, Uemura A. Sema3E-PlexinD1 signaling selectively suppresses disoriented angiogenesis in ischemic retinopathy in mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(5):1974–85.
Hellstrom M, Phng LK, Hofmann JJ, Wallgard E, Coultas L, Lindblom P, Alva J, Nilsson AK, Karlsson L, Gaiano N, et al. Dll4 signalling through Notch1 regulates formation of tip cells during angiogenesis. Nature. 2007;445(7129):776–80.
Zygmunt T, Gay CM, Blondelle J, Singh MK, Flaherty KM, Means PC, Herwig L, Krudewig A, Belting HG, Affolter M, et al. Semaphorin-PlexinD1 signaling limits angiogenic potential via the VEGF decoy receptor sFlt1. Dev Cell. 2011;21(2):301–14.
Torres-Vazquez J, Gitler AD, Fraser SD, Berk JD, Van NP, Fishman MC, Childs S, Epstein JA, Weinstein BM. Semaphorin-plexin signaling guides patterning of the developing vasculature. Dev Cell. 2004;7(1):117–23.
Rahimi N. VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2: two non-identical twins with a unique physiognomy. Fronti Biosci. 2006;11:818–29.
Krueger J, Liu D, Scholz K, Zimmer A, Shi Y, Klein C, Siekmann A, Schulte-Merker S, Cudmore M, Ahmed A, et al. Flt1 acts as a negative regulator of tip cell formation and branching morphogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. Development. 2011;138(10):2111–20.
Tatari N, Movassagh H, Shan L, Koussih L, Gounni AS. Semaphorin 3E inhibits house dust mite-induced angiogenesis in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Am J Pathol. 2019;189(4):762–72.
White MJ, Risse-Adams O, Goddard P, Contreras MG, Adams J, Hu D, Eng C, Oh SS, Davis A, Meade K, et al. Novel genetic risk factors for asthma in African American children: precision medicine and the SAGE II study. Immunogenetics. 2016;68(6–7):391–400.
Modena BD, Bleecker ER, Busse WW, Erzurum SC, Gaston BM, Jarjour NN, Meyers DA, Milosevic J, Tedrow JR, Wu W, et al. Gene expression correlated with severe asthma characteristics reveals heterogeneous mechanisms of severe disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(11):1449–63.
Movassagh H, Shan L, Chakir J, McConville JF, Halayko AJ, Koussih L, Gounni AS. Expression of semaphorin 3E is suppressed in severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140(4):1176–9.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research grant (MOP # 115115) and the Research Manitoba Chair to A. S. G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Koussih, L., Gounni, A.S. (2021). Semaphorin3E/plexinD1 Axis in Asthma: What We Know So Far!. In: Wang, YX. (eds) Lung Inflammation in Health and Disease, Volume II. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1304. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68748-9_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68748-9_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-68747-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-68748-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)