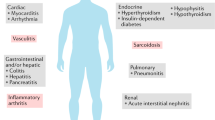
Abstract
With expanding use of immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), the incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) is increasing, posing a new clinical challenge for practitioners. The spectrum and incidence of irAEs differ by the immune checkpoint molecule that is blocked, such that CTLA-4 inhibitors are associated with colitis and hypophysitis, while PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors with pneumonitis and thyroiditis. However, despite ICI type, irAEs can affect every organ system in the body. Improved irAE outcomes are related to their timely recognition and management. This chapter explores what is known about the epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, management, and outcomes of non-rheumatic irAEs. In addition, we include an examination of late-breaking research into the prevention and management of irAEs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):158–68.
Haanen JB, Carbonnel F, Robert C, Kerr KM, Peters S, Larkin J, Jordan K. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(suppl_4):iv119–42.
US Dept of Health and Human Services. Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE). Version 5.0. US Dept of Health and Human Services. 2017. https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf
Eggermont AM, Chiarion-Sileni V, Grob JJ, Dummer R, Wolchok JD, Schmidt H. Prolonged survival in stage III melanoma with Ipilimumab adjuvant therapy. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1845–55.
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, et al. Improved survival with Ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):711–23.
Xing P, Zhang F, Wang G, Xu Y, Li C, Wang S, Guo Y, Cai S, Wang Y, Li J. Incidence rates of immune-related adverse events and their correlation with response in advanced solid tumours treated with NIVO or NIVO+ IPI: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):341.
Carlino MS, Long GV. Ipilimumab combined with Nivolumab: a standard of Care for the Treatment of advanced melanoma? Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(16):3992–8.
Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, Postow MA, Rizvi NA, Lesokhin AM, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:122–33.
Morganstein DL, Lai Z, Spain L, Diem S, Levine D, Mace C, et al. Thyroid abnormalities following the use of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 and programmed death receptor protein-1 inhibitors in the treatment of melanoma. Clin Endocrinol. 2017;86(4):614–20.
Naidoo J, Wang X, Woo KM, Iyriboz T, Halpenny D, Cunningham J, et al. Pneumonitis in patients treated with anti–programmed Death-1/programmed death ligand 1 therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(7):709–17.
Abdel-Rahman O, El Halawani H, Fouad M. Risk of endocrine complications in cancer patients treated with immune check point inhibitors: a meta-analysis. Future Oncol. 2016;12(3):413–25.
Connolly C, Bambhania K, Naidoo J. Immune-related adverse events: a case-based approach. Front Oncol. 2019;9(530):1–15
Thompson JA, Schneider BJ, Brahmer J, Andrews S, Armand P, Bhatia S, et al. Management of immunotherapy-related toxicities, version 1.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2019;17(3):255–89.
Haanen JBAG, Carbonnel F, Robert C, Kerr KM, Peters S, Larkin J, et al. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(Supplement_4):iv264–6.
Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, Bingham CO, Brogdon C, Dadu R, et al. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):95.
Wang DY, Salem JE, Cohen JV, Chandra S, Menzer C, Ye F, Zhao S, Das S, Beckermann KE, Ha L, Rathmell WK. Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(12):1721–8.
Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ, Atkins MB, Brassil KJ, Caterino JM, et al. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1714–68.
Aarli JA. The immune system and the nervous system. Sur Prog. 1983;229:137–54.
Larkin J, Chmielowski B, Lao CD, Hodi FS, Sharfman W, Weber J, et al. Neurologic serious adverse events associated with Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab alone in advanced melanoma, including a case series of encephalitis. Oncologist. 2017;22(6):709–18.
Kamath SD, Kumthekar PU. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) metastatic disease. Frontiers in oncology. 2018;8(414):1–7.
Bot I, Blank CU, Boogerd W, Brandsma D. Neurological immune-related adverse events of ipilimumab. Pract Neurol. 2013;13(4):278–80.
Cuzzubbo S, Javeri F, Tissier M, Roumi A, Barlog C, Doridam J, et al. Neurological adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: review of the literature. Eur J Cancer. 2017;73:1–8.
Nguyen BH, Kuo J, Budiman A, Christie H, Ali S. Two cases of clinical myasthenia gravis associated with pembrolizumab use in responding melanoma patients. Melanoma Res. 2017;27(2):152–4.
Hottinger AF. Neurologic complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Curr Opin Neurol. 2016;29(6):806–12.
Wick W, Hertenstein A, Platten M. Neurological sequelae of cancer immunotherapies and targeted therapies. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(12):e529–41.
Cuzzubbo S, Tissier M. Neurological adverse events associated with the immune checkpoint inhibitors: review of the literature and characterization of the neurological patterns. Neuro-Oncology. 2016;18(suppl_4):iv25–6.
Fellner A, Makranz C, Lotem M, Bokstein F, Taliansky A, Rosenberg S, et al. Neurologic complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Neuro-Oncol. 2018;137(3):601–9.
Dubey D, David W, Amato A, Reynolds K, Clement N, Chute D, et al. Varied phenotypes and management of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated neuropathies. Neurology. 2019;93(11):e1093–103.
Blackmon JT, Viator TM, Conry RM. Central nervous system toxicities of anti-cancer immune checkpoint blockade. J Neurol Neuromed. 2016;1(4):39–45.
Mandel JJ, Olar A, Aldape KD, Tremont-Lukats IW. Lambrolizumab induced central nervous system (CNS) toxicity. J Neurol Sci. 2014;344(0):229–31.
Feng S, Coward J, McCaffrey E, Coucher J, Kalokerinos P, O'Bryne K. Pembrolizumab-induced encephalopathy: a review of neurological toxicities with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(11):1626–35.
Liao B, Shroff S, Kamiya-Matsuoka C, Tummala S. Atypical neurological complications of ipilimumab therapy in patients with metastatic melanoma. Neuro-Oncology. 2014;16(4):589–93.
Lancaster E. The diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune encephalitis. J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(1):1–13.
Shah S, Dunn-Pirio A, Luedke M, Morgenlander J, Skeen M, Eckstein C. Nivolumab-induced autoimmune encephalitis in two patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Case Rep Neurolog Med. 2018:1–4.
Zafar Z, Vogler C, Hudali T, Bhattarai M. Nivolumab-associated acute demyelinating encephalitis: a case report and literature review. Clin Med Res. 2019;17(1–2):29–33.
Segreti J, Harris AA. Acute bacterial meningitis. Infect Dis Clin N Am. 1996;10(4):797–809.
Logan SA, MacMahon E. Viral meningitis. BMJ. 2008;336(7634):36–40.
Dubey D, Pittock SJ, Kelly CR, McKeon A, Lopez-Chiriboga AS, Lennon VA, Gadoth A, Smith CY, Bryant SC, Klein CJ, Aksamit AJ. Autoimmune encephalitis epidemiology and a comparison to infectious encephalitis. Ann Neurol. 2018;83(1):166–77.
Williams TJ, Benavides DR, Patrice K, Dalmau JO, Ávila d, Ribeiro AL, Le DT, et al. Association of Autoimmune Encephalitis with Combined Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment for metastatic Cancer. JAMA Neurol. 2016;73(8):928–33.
Johnson DB, Manouchehri A, Haugh AM, Quach HT, Balko JM, Lebrun-Vignes B, et al. Neurologic toxicity associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a pharmacovigilance study. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):134.
Gaudy-Marqueste C, Monestier S, Franques J, Cantais E, Richard M, Grob J. A severe case of ipilimumab-induced guillain-barré syndrome revealed by an occlusive enteric neuropathy: a differential diagnosis for ipilimumab-induced colitis. J Immunother. 2013;36(1):77–8.
Sepúlveda M, Martinez-Hernandez E, Gaba L, Victoria I, Sola-Valls N, Falgàs N, et al. Motor polyradiculopathy during pembrolizumab treatment of metastatic melanoma. Muscle Nerve. 2017;56(6):E162–7.
Mansoukis G, Koch J, Sommerville RB, EL-Dokla A, Harms MB, AL-Lozi MT, et al. Multifocal radiculopathy during Ipilimumab treatment of melanoma. Muscle Nerve. 2013;48:440–4.
Supakornnumporn S, Katirji B. Guillain-Barre syndrome triggered by immune checkpoint inhibitors: a case report and literature review. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2017;19(2):80–3.
Spain L, Tippu Z, Larkin JM, Carr A, Turajlic S. How we treat neurological toxicity from immune checkpoint inhibitors. ESMO open. 2019;4(Suppl 4):1–5.
Thaipisuttikul I, Chapman P, Avila E. Peripheral neuropathy associated with Ipilimumab: a report of two cases. J Immunother. (Hagerstown, Md.: 1997). 2015;38(2):77.
Chen X, Haggiagi A, Tzatha E, DeAngelis LM, Santomasso B. Electrophysiological findings in immune checkpoint inhibitor-related peripheral neuropathy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019;130(8):1440–5.
Wijdicks EF, Klein CJ. Guillain-barre syndrome. In: Mayo Clinic Proceedings 1 Mar 2017, vol. 92, no. 3. Elsevier. p. 467–79.
Dalakas MC. Neurological complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors: what happens when you ‘take the brakes off’the immune system. Therapeutic advances in neurological disorders. 2018;11:1–9.
Suzuki S, Ishikawa N, Konoeda F, Seki N, Fukushima S, Takahashi K, et al. Nivolumab-related myasthenia gravis with myositis and myocarditis in Japan. Neurology. 2017;89(11):1127–34.
Makarious D, Horwood K, Coward JIG. Myasthenia gravis: an emerging toxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Eur J Cancer. 2017;82:128–36.
Garcia CA, El-Ali A, Rath TJ, Contis LC, Gorantla V, Drappatz J, Davar D. Neurologic immune-related adverse events associated with adjuvant ipilimumab: report of two cases. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):83.
Fukasawa Y, Sasaki K, Natsume M, Nakashima M, Ota S, Watanabe K, Takahashi Y, Kondo F, Kozuma K, Seki N. Nivolumab-induced myocarditis concomitant with myasthenia gravis. Case Rep Oncol. 2017;10:809–12.
Gonzalez NL, Puwanant A, Lu A, Marks SM, Živković SA. Myasthenia triggered by immune checkpoint inhibitors: new case and literature review. Neuromuscul Disord. 2017;27(3):266–8.
Johnson DB, et al. Myasthenia gravis induced by Ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(33):e122–4.
Chen JH, et al. Coexisting myasthenia gravis, myositis, and polyneuropathy induced by ipilimumab and nivolumab in a patient with non-small-cell lung cancer: a case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(50):e9262.
Becquart O, Lacotte J, Malissart P, Nadal J, Lesage C, Guillot B, et al. Myasthenia gravis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother. 2019;42(8):309–12.
Bennett DLH, Mills KR, Riordan-Eva P, Barnes PRJ, Rose MR. Anti-MuSK antibodies in a case of ocular myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77(4):564–5.
Montes V, Sousa S, Pita F, Guerreiro R, Carmona C. Myasthenia gravis induced by ipilimumab in a patient with metastatic melanoma. Frontiers in neurology. 2018;9(150)1–3.
Romi F. Thymoma in myasthenia gravis: from diagnosis to treatment. Autoimmun Dis. 2011:1–5.
Trouth AJ, Dabi A, Solieman N, Kurukumbi M, Kalyanam J. Myasthenia gravis: a review. Autoimmun Dis. 2012:1–10.
Maggi L, Mantegazza R. Treatment of myasthenia gravis. Clin Drug Investig. 2011;31(10):691–701.
Dalvin LA, Shields CL, Orloff M, Sato T, Shields JA. Checkpoint inhibitor immune therapy: systemic indications and ophthalmic side effects. Retina. 2018;38(6):1063–78.
de Andrade FA, Fiorot SH, El B, Provenzano J, Martins VJ, Levy RA. The autoimmune diseases of the eyes. Autoimmun Rev. 2016;15(3):258–71.
Chang CJ, Chen SJ, Hwang DK, Liu CJ. Bilateral anterior uveitis after immunotherapy for malignant melanoma. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2018;8(3):173–5. https://doi.org/10.4103/tjo.tjo_88_17.
Fang T, Marberley DA, Ethminan M. Ocular adverse events with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2019;31:319–22.
Conrady C, Conrady C, Larochelle M, Larochelle M, Pecen P, Pecen P, et al. Checkpoint inhibitor-induced uveitis: a case series. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2018;256(1):187–91.
Aaberg MT, Aaberg TM. Pembrolizumab administration associated with posterior uveitis. Retinal Cases Brief Rep. 2016;11(4):1–351.
Kim JM, Materin MA, Sznol M, Kluger HM, Weiss S, Chow J, et al. Ophthalmic immune-related adverse events of immunotherapy: a single-site case series. Ophthalmology. 2019;126(7):1058–62.
Pasadhika S, Rosenbaum JT. Update on the use of systemic biologic agents in the treatment of non-infectious uveitis. BTT. 2014;8:67–81.
Friedman CF, Proverbs-Singh TA, Postow MA. Treatment of the immune-related adverse effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(10):1346–53.
Cadranel J, Canellas A, Matton L, Darrason M, Parrot A, Naccache JM, Lavolé A, Ruppert AM, Fallet V. Pulmonary complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir Rev. 2019;28(153):190058.
Nishino M, Giobbie-Hurder A, Hatabu H, Ramaiya NH, Hodi FS. Incidence of programmed cell death 1 inhibitor–related pneumonitis in patients with advanced Cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(12):1607–16.
Balaji A, Zhang J, Wills B, Marrone KA, Elmariah H, Yarchoan M, et al. Immune-related adverse events requiring hospitalization: Spectrum of toxicity, treatment, and outcomes. J Oncol Pract. 2019;15(9):e825–34.
Suresh K, Psoter KJ, Voong KR, Shankar B, Forde PM, Ettinger DS, et al. Impact of checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis on survival in NSCLC patients receiving immune checkpoint immunotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. 14(3):494–502.
Postow MA, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, Robert C, Grossmann K, McDermott D, et al. Nivolumab and Ipilimumab versus Ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(21):2006–17.
Chuzi S, Tavora F, Cruz M, Costa R, Chae YK, Carneiro BA, et al. Clinical features, diagnostic challenges, and management strategies in checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis. Cancer Manag Res. 2017;9:207–13.
Balaji A, Verde F, Suresh K, Naidoo J. Pneumonitis from anti–PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Cancer Netw. 2017;31(10):739–46.
Rashdan S, Minna JD, Gerber DE. Diagnosis and management of pulmonary toxicity associated with cancer immunotherapy. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6(6):472–8.
Barjaktarevic IZ, Qadir N, Suri A, Santamauro JT, Stover D. Organizing pneumonia as a side effect of Ipilimumab treatment of melanoma. Chest. 2013;143(3):858–61.
Tirumani SH, Ramaiya NH, Keraliya A, Bailey ND, Ott PA, Hodi FS, et al. Radiographic profiling of immune-related adverse events in advanced melanoma patients treated with Ipilimumab. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015;3(10):1185–92.
Suresh K, Naidoo J, Zhong Q, Xiong Y, Mammen J, de Flores MV, et al. The alveolar immune cell landscape is dysregulated in checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis. J Clin Investig. 2019;129(10):4305–15.
Koelzer VH, Rothschild SI, Zihler D, Wicki A, Willi B, Willi N, et al. Systemic inflammation in a melanoma patient treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors—an autopsy study. J Immunother Cancer. 2016;4(1):13.
Naidoo J, Cappelli L, Lipson EJ, Forde PM, Sharfman WH, Zhang J, Mammen J, Moseley K, Suresh K, Mehta S, Sander I. A multidisciplinary toxicity team for cancer immunotherapy-related adverse events. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2019;17(6):712–20.
Trinh S, Le A, Gowani S, La-Beck NM. Management of immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: a Minireview of current clinical guidelines. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2019;6(2):154–60.
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, Akerley W. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):711–23.
Soularue E, Lepage P, Colombel JF, Coutzac C, Faleck D, Marthey L, Collins M, Chaput N, Robert C, Carbonnel F. Enterocolitis due to immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review. Gut. 2018;67(11):2056–67.
Cabanillas G. Immune related adverse events and their treatment in melanoma patients receiving ipilimumab. JCO. 2017;35(15_suppl):e14598-e14598.
Gupta A, De Felice KM, Loftus EV, Khanna S. Systematic review: colitis associated with anti-CTLA-4 therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;42(4):406–17.
Reddy HG, Schneider BJ, Tai AW. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated colitis and hepatitis. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018;9:9.
Weber JS. Practical management of immune-related adverse events from immune checkpoint protein antibodies for the oncologist. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2012:174–7.
Zeimer M, Koukoulioti E, Simon JC, Berg T. Managing immune checkpoint-inhibitor-induced severe autoimmune-like hepatitis by liver-directed topical steroids. J Hepatol. 2017;66(3):657–9.
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ, Powell SF, Cheng SY. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(22):2078–92.
Kähler KC, Hassel JC, Heinzerling L, Loquai C, Mössner R, Ugurel S, et al. Management of side effects of immune checkpoint blockade by anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 antibodies in metastatic melanoma. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016;14(7):662–81.
Abu-Sbeih H, Tang T, Lu Y, Thirumurthi S, Altan M, Jazaeri AA, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced pancreatic injury. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):31.
George J, Bajaj D, Sankaramangalam K, Yoo JW, Joshi NS, Gettinger S, et al. Incidence of pancreatitis with the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in advanced cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology. 2019;19(4):587–94.
Su Q, Zhang X, Zhang C, Hou Y, Yao Y, Cao B. Risk of immune-related pancreatitis in patients with solid tumors treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: systematic assessment with meta-analysis. J Immunol Res. 2018:e1027323.
Abu-Sbeih H, Faleck DM, Ricciuti B, Mendelsohn RB, Naqash AR, Cohen JV, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with preexisting inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Oncol. 2019:JCO1901674.
Dubin K, Callahan MK, Ren B, Khanin R, Viale A, Ling L, et al. Intestinal microbiome analyses identify melanoma patients at risk for checkpoint-blockade-induced colitis. Nat Commun. 2016;7(1):1–8.
Papaconstantinou HT, Thomas JS. Bacterial colitis. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2007;20(1):18–27.
Kim KW, Ramaiya NH, Krajewski KM, Shinagare AB, Howard SA, Jagannathan JP, et al. Ipilimumab-associated colitis: CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200(5):W468–74.
Cramer P, Bresalier R. Gastrointestinal and hepatic complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017;19(1):1–9.
Geukes Foppen MH, Rozeman EA, van Wilpe S, Postma C, Snaebjornsson P, van Thienen JV, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibition-related colitis: symptoms, endoscopic features, histology and response to management. ESMO Open. 2018;3(1):e000278.
Grover S, Rahma OE, Hashemi N, Lim RM. Gastrointestinal and hepatic toxicities of checkpoint inhibitors: algorithms for management. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2018;(38):13–19.
Bergqvist V, Hertervig E, Gedeon P, Kopljar M, Griph H, Kinhult S, Carneiro A, Marsal J. Vedolizumab treatment for immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced enterocolitis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017;66(5):581–92.
Cheung V, Gupta T, Payne M, Middleton MR, Collier JD, Simmons A, et al. Immunotherapy-related hepatitis: real-world experience from a tertiary Centre. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2019;10(4):364–71.
Wolchok JD, Hoos A, O'Day S, Weber JS, Hamid O, Lebbé C, Maio M, Binder M, Bohnsack O, Nichol G, Humphrey R, Hodi FS. Guidelines for the evaluation of immune therapy activity in solid tumors: immune-related response criteria. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:7412–20.
Gauci M, Baroudjian B, Zeboulon C, Pages C, Poté N, Roux O, et al. Immune-related hepatitis with immunotherapy: are corticosteroids always needed? J Hepatol. 2018;69(2):548–50.
Suzman DL, Pelosof L, Rosenberg A, Avigan MI. Hepatotoxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors: an evolving picture of risk associated with a vital class of immunotherapy agents. Liver Int. 2018;38(6):976–87.
Tsung I, Dolan R, Lao CD, Fecher L, Riggenbach K, Yeboah-Korang A, et al. Liver injury is most commonly due to hepatic metastases rather than drug hepatotoxicity during pembrolizumab immunotherapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;50(7):800–8.
Widmann G, Nguyen VA, Plaickner J, Jaschke W. Imaging features of toxicities by immune checkpoint inhibitors in Cancer therapy. Curr Radiol Rep. 2017;5(11):1–10.
Hsu C, Marshall JL, He AR. Workup and Management of Immune‐Mediated Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Toxicities That Develop During Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment. The oncologist. 2020;25(2):105–111.
Zen Y, Yeh MM. Hepatotoxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors: a histology study of seven cases in comparison with autoimmune hepatitis and idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Mod Pathol. 2018;31(6):965–73.
Zhang HC, Luo W, Wang Y. Acute liver injury in the context of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related colitis treated with infliximab. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):47.
Chmiel KD, Suan D, Liddle C, Nankivell B, Ibrahim R, Bautista C, et al. Resolution of severe ipilimumab-induced hepatitis after antithymocyte globulin therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(9):237.
Sanjeevaiah A, Kerr T, Beg MS. Approach and management of checkpoint inhibitor-related immune hepatitis. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018;9(1):220–4.
Delanoy N, Michot J, Comont T, Kramkimel N, Lazarovici J, Dupont R, et al. Haematological immune-related adverse events induced by anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy: a descriptive observational study. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6(1):e48–57.
Kohlmann J, Wagenknecht D, Simon J, Ziemer M. Immune-related pancreatitis associated with checkpoint blockade in melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2019;29(5):549–52.
Friedman CF, Clark V, Raikhel AV, Barz T, Shoushtari AN, Momtaz P, et al. Thinking critically about classifying adverse events: incidence of pancreatitis in patients treated with Nivolumab + Ipilimumab. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109(4):1–3.
Saito H, Ono K. Nivolumab-induced pancreatitis: an immune-related adverse event. Radiology. 2019;293(3):521.
Shiuan E, Beckermann KE, Ozgun A, Kelly C, McKean M, McQuade J, et al. Thrombocytopenia in patients with melanoma receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):8.
Calvo R. Hematological side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors: the example of immune-related thrombocytopenia. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:454.
Tanios GE, Doley PB, Munker R. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia associated with the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer: 68 cases from the Food and Drug Administration database and review. Eur J Haematol. 2019;102:157–62.
Michot JM, Lazarovici J, Tier A, Champiat S, Voisin AL, Ebbo M, et al. Haematological immune-related adverse events with immune checkpoint inhibitos, how to manage? Eur J Cancer. 2019;122:72–90.
Papazafiropoulou A, Papanas N, Pappas S, Maltezos E, Mikhailidis DP. Effects of oral hypoglycemic agents on platelet function. J Diabetes Complicat. 2015;29(6):846–51.
Karakas Y, Yuce D, Kılıckap S. Immune thrombocytopenia induced by Nivolumab in a metastatic non-small cell lung Cancer patient. Oncol Res Treat. 2017;40(10):621–2.
Neunert C, Lim W, Crowther M, Cohen A, Solberg L, Crowther MA. The American Society of Hematology 2011 evidence-based practice guideline for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2011;117(16):4190–207.
Varricchi G, Galdiero M, Marone G, Criscuolo G, Triassi M, Bonaduce D, et al. Cardiotoxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors. ESMO Open. 2017;2:e000247. https://doi.org/10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000247.
Salem J, Manouchehri A, Moey M, Lebrun-Vignes B, Bastarache L, Pariente A, et al. Cardiovascular toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: an observational, retrospective, pharmacovigilance study. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:1579–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30608-9.
Johnson DB, Balko JM, Compton ML, Chalkias S, Gorham J, Xu Y, et al. Fulminant myocarditis with combination immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1749–55. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1609214.
Yang S, Asnani A. Cardiotoxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Curr Probl Cancer. 2018;42:422–32.
Semper H, Muehlberg F, Schulz-Menger J, Allewelt M, Grohé C. Drug-induced myocarditis after nivolumab treatment in a patient with PDL1- negative squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer. 2016;99:117–9.
Geisler BP, Raad RA, Esaian D, Sharon E, Schwartz DR Apical ballooning and cardiomyopathy in a melanoma patient treated with ipilimumab: a case of takotsubo-like syndrome.
de Almeida DVP, Gomes JR, Haddad FJ, Buzaid AC. Immune-mediated pericarditis with pericardial tamponade during nivolumab therapy. J Immunother. 2018;41:329–31.
Upadhrasta S, Elias H, Patel K, Zheng L. Managing cardiotoxicity associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2019;5(1):6–14.
Läubli H, Balmelli C, Bossard M, Pfister O, Glatz K, Zippelius A. Acute heart failure due to autoimmune myocarditis under pembrolizumab treatment for metastatic melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2015;3:11.
Lyon AR, Yousaf N, Battisti NM, Moslehi J, Larkin J. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and cardiovascular toxicity. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(9):e447–58.
Villadolid J, Amin A. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: update on management of immune-related toxicities. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4(5):560–75.
Spain L, Diem S, Larkin J. Management of toxicities of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016;44:51–60.
Larkin J, et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):23–34.
Robert C, Schachter J, Long G, Arance A, Grob J, Mortier L, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2521–32. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1503093.
Ito J, Fujimoto D, Nakamura A, Nagano T, Uehara K, Imai Y, Tomii K. Aprepitant for refractory nivolumab-induced pruritus. Lung Cancer. 2017;109:58–61.
Cortazar FB, et al. Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2016;90(3):638–47.
Wanchoo R, Karam S, Uppal NN, Barta VS, Deray G, Devoe C, et al. Adverse renal effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors: a narrative review. Am J Nephrol. 2017;45(2):160–9.
Fadel F, El Karoui K, Knebelmann B. Anti-CTLA4 antibody-induced lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(2):211–2.
Thajudeen B, et al. Ipilimumab granulomatous interstitial nephritis. Am J Ther. 2015;22(3):e84–7.
Shirali A, Perazella M, Gettinger S. Association of acute interstitial nephritis with programmed cell death 1 inhibitor therapy in lung cancer patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016;68:287–91. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.02.057.
El Majzoub I, Qdaisat A, Thein K, Win M, Han M, Jacobson K, et al. Adverse effects of immune checkpoint therapy in cancer patients visiting the emergency department of a comprehensive cancer center. Ann Emerg Med. 2019;73:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.04.019.
Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, Hodi FS, Min L, Krop IE, Tolaney SM. Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(2):173–82.
Kapke J, Shaheen Z, Kilari D, Knudson P, Wong S. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated type 1 diabetes mellitus: case series, review of the literature, and optimal management. Case Rep Oncol. 2017;10(3):897–909.
Usui Y, Udagawa H, Matsomoto S, Imai K, Ohashi K, Ishibashi M, et al. Association of serum anti-GAD antibody and HLA haplotypes with type 1 diabetes mellitus triggered by Nivolumab in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12:e41–3.
Larsabal M, Marti A, Jacquemin C, Rambert J, Thiolat D, Dousset L, et al. Vitiligo-like lesions occurring in patients receiving anti-programmed cell death−1 therapies are clinically and biologically distinct from vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:863–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.10.044.
Das S, Johnson DB. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7:1–11.
Johnson D, Sullivan R, Menzies A. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in challenging populations. Cancer. 2017;123:1904–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30642.
Cappelli L, Dorak M, Bettinotti M, Bingham C, Shah A. Association of HLA-DRB1 shared epitope alleles and immune checkpoint inhibitor induced inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology. 2018;58:476–80. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key358.
Suresh K, Voong K, Shankar B, Forde P, Ettinger D, Marrone K, et al. Pneumonitis in non–small cell lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint immunotherapy: incidence and risk factors. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13:1930–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.08.2035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Balaji, A., Shankar, B., Naidoo, J. (2021). Non-Rheumatic Immune-Related Adverse Events. In: Suarez-Almazor, M.E., Calabrese, L.H. (eds) Rheumatic Diseases and Syndromes Induced by Cancer Immunotherapy. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56824-5_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56824-5_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-56823-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-56824-5
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)