Abstract
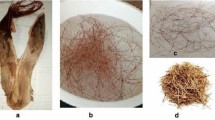
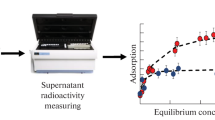
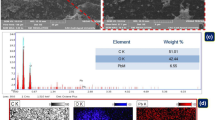
This paper focuses on Phragmites australis pretreated fibers which were used to improve their adsorption capacities of the anionic surfactant sodium dodecylben-zene sulfonate (SDBS) in batch system. The pretreatment of the biomass was performed using NaOH, C2H6O, and H3PO4. The obtained fibers were charac-terized and reaction mechanisms were suggested. The functional groups of the pretreated fibers were identified with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The preliminary results of the research show that fibers treated with H3 PO4 present the biggest amount of SDBS, adsorbed up to 72.7%, and show that the highest surfactant removal was attained at pH2. The kinetic rate of pseudo-second-order and Brouers–Sotolongo isotherm modeling is the most appropriate to describe the present biosorption phenomenon.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kersraoui, A., Bouzaabia, S., Seffen, M.: The combination of Luffa cylindrical fibers and metal oxides offers a highly performing hybrid fiber material in water decontamination. J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 11524–11534 (2018)
Chen, S., Cheow, Y.L., Ng, S.L., Ting, A.: Mechanisms for metal removal established via electron microscopy and spectroscopy: a case study on metal tolerant fungi Penicillium simplicissimum. J. Hazardous Mater., 394–402 (2019)
Dallel, R., Kesraoui, A., Seffen, M.: Biosorption of cationic dye onto “Phragmites australis” fibers: characterization and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 7247–7256 (2018)
Jincheng, M., Wang, D., Yang, X., Zhang, Z., Yang, B., Zhang, Ch.: Adsorption of surfactant on stratum rocks: exploration of low adsorption surfactants for reservoir stimulation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 1–8 (2018)
Zhang, F., Li, S., Zhang, Q., Liu, J., Zeng, S., Liu, M., Sun, D.: Adsorption of different types of surfactants on graphene oxide. J. Molecul. Liquids., 338–346. (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dallel, R., Baati, R., Seffen, M. (2021). Adsorption of Anionic Surfactant on Phragmites Australis: Pretreatment and Reaction Mechanisms. In: Ksibi, M., et al. Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition). EMCEI 2019. Environmental Science and Engineering(). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_128
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_128
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-51209-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-51210-1
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)