Abstract
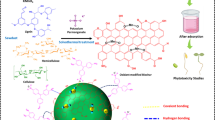
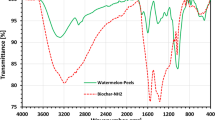
This research looks at the potential use of natural biomass of fibers plant with raw leaf release (Tl) and sulphuric acid treated fibers (Tls) as adsorbents for the removal of Pb (II) ions in water. The properties of the materials were evaluated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR), nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms and thermogravimetric analysis/differential thermogravimetry (TGA/DTG). investigations were used to describe the fundamental physicochemical characteristics of Tl both before and after acid treatment. Was the subject of bath adsorption tests Pb (II). The initial concentration of Pb (II) ions, reaction time, adsorbent dosage, and pH of the ions were all optimized. The calculated adsorption capacities of Tl and Tls on Pb (II) were 32.64 and 44.65 mg g−1, respectively, according to adsorption isotherm studies. Under ideal biosorption circumstances, which include pH = 5, a biosorbent mass of 0.1 g, and an initial Pb2+ ion concentration of 10 ppm, calculations using the response surface methodology revealed a maximum biosorption efficiency of Pb2+ of 77.6% for Tl and 98.7% for Tls. Desorption research findings demonstrated the potential for promising regenerations, as the percentage removal of Pb (II) from the initial value was sustained at more than 60% even after three adsorption–desorption cycles. Furthermore, the adsorption expenses for Pb (II) removal using Tl and Tls were assumed to be 2.14 and 6.71 USD kg−1, respectively. Based on these findings, Tl and Tls treated substances could be utilized as low-cost, environmentally friendly, and effective adsorbents for the removal of Pb (II) from water. G°, S°, and H° thermodynamic parameters demonstrated that the adsorption process was viable, spontaneous, and exothermic.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin Y, Teng C, Yu S, Song T, Dong L, Liang J, Bai X, Liu X, Hu X, Qu J (2018) Batch and fixed-bed biosorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solution using immobilized Pleurotus ostreatus spent substrate. Chemosphere 191:799–808
Ghaedi AM, Ghaedi M, Vafaei A, Iravani N, Keshavarz M, Rad M, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2015) Adsorption of copper (II) using modified activated carbon prepared from Pomegranate wood: optimization by bee algorithm and response surface methodology. J Mol Liq 206:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.02.029
Dallel R, Kesraoui A, Seffen M (2018) Biosorption of cationic dye onto “Phragmites australis” fibers: characterization and mechanism. J Environ Chem Eng 6:7247–7256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.024
Regti A, Lakbaibi Z, Ben El Ayouchia H, El Haddad M, Laamari MR, El Himri M, Haounati R (2021) Hybrid methods combining computational and experimental measurements for the uptake of eriochrome black T dye utilising fish scales. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1929199
Haounati R, Ouachtak H, El Haouti R, Akhouairi S, Largo F, Akbal F, Benlhachemi A, Jada A, Addi AA (2021) Elaboration and properties of a new SDS/CTAB@Montmorillonite organoclay composite as a superb adsorbent for the removal of malachite green from aqueous solutions. Sep Purif Technol 255:117335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117335
Kang J-K, Lee S-C, Kim S-B (2018) Enhancement of selective Cu(II) sorption through preparation of surface-imprinted mesoporous silica SBA-15 under high molar concentration ratios of chloride and copper ions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 272:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.06.038
Gupta S, Sharma SK, Kumar A (2019) Biosorption of Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution using modified Aloe barbadensis Miller leaf powder. Water Sci Eng 12:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2019.04.003
Ouachtak H, Akhouairi S, Haounati R, Addi AA, Jada A, Taha ML, Douch J (2020) 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid removal from water by goethite modified natural sand column fixed-bed: experimental study and mathematical modeling. Desalin Water Treat 194:439–449. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25562
Haounati R, El Guerdaoui A, Ouachtak H, El Haouti R, Bouddouch A, Hafid N, Bakiz B, Santos DMF, Labd Taha M, Jada A, Ait Addi A (2021) Design of direct Z-scheme superb magnetic nanocomposite photocatalyst Fe3O4/Ag3PO4@Sep for hazardous dye degradation. Sep Purif Technol 277:119399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119399
Vishan I, Saha B, Sivaprakasam S, Kalamdhad A (2019) Evaluation of Cd(II) biosorption in aqueous solution by using lyophilized biomass of novel bacterial strain Bacillus badius AK: biosorption kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. Environ Technol Innov 14:100323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100323
Rangabhashiyam A, Lata S, Balasubramanian P (2018) Biosorption characteristics of methylene blue and malachite green from simulated wastewater onto Carica papaya wood biosorbent. Surf Interfaces 10:197–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2017.09.011
Kadiri L, Ouass A, Essaadaoui Y, Rifi EH, Lebkiri A (2018) Coriandrum sativum seeds as a green low-cost biosorbent for methylene blue dye removal from aqueous solution: spectroscopic, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Mediterr J Chem 7:204–216. https://doi.org/10.13171/mjc731810911-kadiri
Kankılıç GB, Metin AÜ, Tüzün İ (2016) Phragmites australis: an alternative biosorbent for basic dye removal. Ecol Eng 86:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.10.024
Tan B, Ching Y, Poh S, Abdullah L, Gan S (2015) A review of natural fiber reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) based composites: application and opportunity. Polymers 7:2205–2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7111509
Kozlov VA, Nikiforova TE, Loginova VA, Koifman OI (2015) Mechanism of protodesorption—exchange of heavy metal cations for protons in a heterophase system of H2O–H2SO4–MSO4—cellulose sorbent. J Hazard Mater 299:725–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.004
El-Sheikh AH, Alshamaly HS (2020) Cadmium removal from organic acid-bearing soil-washing water by magnetic biosorption: effect of various factors and adsorption isothermal study. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104188
Zhang K, Khan A, Sun P, Zhang Y, Taraqqi-A-Kamal A, Zhang Y (2020) Simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and oxidization of organic pollutants by rice husk derived biochar and the interactive influences of coexisting Cr(VI). Sci Total Environ 706:135763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135763
Bediako JK, Wei W, Yun Y-S (2016) Conversion of waste textile cellulose fibers into heavy metal adsorbents. J Ind Eng Chem 43:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.07.048
Flauzino Neto WP, Silvério HA, Dantas NO, Pasquini D (2013) Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from agro-industrial residue – soy hulls. Ind Crops Prod 42:480–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.06.041
Maisyarah MA, Shiun LJ, Nasir AF, Haslenda H, Shin HW (2019) Characteristics of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin of md2 pineapple biomass. Chem Eng Trans 72:79–84. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1972014
Bazargan-Lari R, Zafarani HR, Bahrololoom ME, Nemati A (2014) Removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions by low-cost natural hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:1642–1648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.11.009
Banerjee M, Basu RK, Das SK (2018) Cr(VI) adsorption by a green adsorbent walnut shell: adsorption studies, regeneration studies, scale-up design and economic feasibility. Process Saf Environ Prot 116:693–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.03.037
Barquilha CER, Cossich ES, Tavares CRG, Silva EA (2019) Biosorption of nickel(II) and copper(II) ions by Sargassum sp. in nature and alginate extraction products. Bioresour Technol Rep 5:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2018.11.011
Albert Q, Leleyter L, Lemoine M, Heutte N, Rioult J-P, Sage L, Baraud F, Garon D (2018) Comparison of tolerance and biosorption of three trace metals (Cd, Cu, Pb) by the soil fungus Absidia cylindrospora. Chemosphere 196:386–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.156
Meitei MD, Prasad MNV (2014) Adsorption of Cu (II), Mn (II) and Zn (II) by Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleiden: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Ecol Eng 71:308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.07.036
do Nascimento JM, de Oliveira JD, Rizzo ACL, Leite SGF (2019) Biosorption Cu (II) by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Rep 21:00315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00315
Tabaraki R, Nateghi A (2014) Multimetal biosorption modeling of Zn2+, Cu2+ and Ni2+ by Sargassum ilicifolium. Ecol Eng 71:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.07.031
Shi Y, He J, Yang X, Zhou W, Wang J, Li X, Liu C (2019) Sorption of U(VI) onto natural soils and different mineral compositions: the batch method and spectroscopy analysis. J Environ Radioact 203:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2019.03.011
Yan J, Zhu Y, Qiu F, Zhao H, Yang D, Wang J, Wen W (2016) Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies for removal of methyl orange using a novel β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene oxide-isophorone diisocyanate composites. Chem Eng Res Des 106:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2015.12.023
Bensalah J, Berradi M, Habsaoui A, Allaoui M, Essebaai H, El Khattabi O, Lebkiri A, Rifi E-H (2021) Kinetic and thermodynamic study of the adsorption of cationic dyes by the cationic artificial resin Amberlite®IRC50. Mater Today Proc 45:7468–7472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.028
El Alouani M, Alehyen S, El Achouri M, Taibi M (2018) Removal of cationic dye–methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption on fly ash based geopolymer. J Mater Environ Sci 9:32–46. https://doi.org/10.26872/jmes.2018.9.1.5
Zheng L, Meng P (2016) Preparation, characterization of corn stalk xanthates and its feasibility for Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 58:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.06.017
Basu M, Guha AK, Ray L (2017) Adsorption behavior of cadmium on husk of lentil. Process Saf Environ Prot 106:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.11.025
Jabar JM, Adebayo MA, Owokotomo IA, Odusote YA, Yılmaz M (2022) Synthesis of high surface area mesoporous ZnCl2–activated cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) leaves biochar derived via pyrolysis for crystal violet dye removal. Heliyon 8:e10873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10873
Adebayo MA, Jabar JM, Amoko JS, Openiyi EO, Shodiya OO (2022) Coconut husk-raw clay-Fe composite: preparation, characteristics and mechanisms of Congo red adsorption. Sci Rep 12:14370. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-18763-y
Kong Z, Li M, Chen J, Bao Y, Fan B, Francis F, Dai X (2016) Processing factors of triadimefon and triadimenol in barley brewing based on response surface methodology. Food Control 64:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.12.021
Subha B, Song YC, Woo JH (2015) Optimization of biostimulant for bioremediation of contaminated coastal sediment by response surface methodology (RSM) and evaluation of microbial diversity by pyrosequencing. Mar Pollut Bull 98:235–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.06.042
Saelee K, Yingkamhaeng N, Nimchua T, Sukyai P (2016) An environmentally friendly xylanase-assisted pretreatment for cellulose nanofibrils isolation from sugarcane bagasse by high-pressure homogenization. Ind Crops Prod 82:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.11.064
Argun ME, Dursun S, Karatas M (2009) Removal of Cd(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) from water using modified pine bark. Desalination 249:519–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.01.020
Norfahana A, Chuo Sing C, Siti Hamidah M-S, Umi AA, Khairul Faizal P, Kelly Yong TL (2020) Trends in adsorption mechanisms of fruit peel adsorbents to remove wastewater pollutants (Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II)). J Water Environ Technol 18:290–313. https://doi.org/10.2965/jwet.20-004
Xuan Z, Tang Y, Li X, Liu Y, Luo F (2006) Study on the equilibrium, kinetics and isotherm of biosorption of lead ions onto pretreated chemically modified orange peel. Biochem Eng J 31:160–164
Reddy DHK, Harinath Y, Seshaiah K, Reddy AVR (2010) Biosorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions using chemically modified Moringa oleifera tree leaves. Chem Eng J 162:626–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.06.010
Largo F, Haounati R, Ouachtak H, Hafid N, Jada A, Ait Addi A (2023) Design of organically modified sepiolite and its use as adsorbent for hazardous Malachite Green dye removal from water. Water Air Soil Pollut 183:234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06185-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
El Amri, A., Hsisou, R., Jebli, A. et al. Acid Activation of Natural Reed Filter Biomass (Typha latifolia) Application to Pb (II) Uptake from Aqueous Solutions: Kinetic, Thermodynamic Equilibrium Studies and Optimization Studies. Chemistry Africa 7, 345–365 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00733-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00733-0