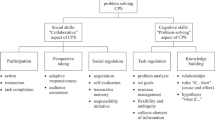
Several studies have analyzed the problem solving activities in face-to-face groups, but this is not yet sufficiently investigated in virtual groups.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Jong, T., & Ferguson-Hessler, M. G. M. (1996). Types and qualities of knowledge. Educational Psychologist, 31(2), 105-113.
Dörner, D., Kreuzig, H. W., Reither, F., & Stäudel, T. (1983). Lohhausen. Vom Umgang mit Unbestimmtheit und Komplexität. Bern: Huber.
Fischer, F., & Waibel, M. C. (2002). Wenn virtuelle Lerngruppen nicht so funktionieren wie sie eigentlich sollten. In U. Rinn & J. Wedekind (Ed.), Referenzmodelle netzbasierten Lehrens und Lernens. Virtuelle Komponenten der Präsenzlehre (pp. 35-50). Münster: Waxmann.
Gruenfeld, D. H., & Hollingshead, A. B. (1993). Sociocognition in work groups: The evolution of group integrative complexity and its relation to task performance. Small Group Research, 24 383-405.
Hayes, J. R. (1989). The complete problem solver. Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Mabry, E. A., & Attridge, M. D. (1990). Small group interaction and outcome correlates for structured and unstructured tasks. Small Group Research, 21 315-332.
Putz-Osterloh, W. (1983). über Determinanten komplexer Problemlöseleistungen und Möglichkeiten zu ihrer Erfassung. Sprache und Kognition, 2 100-116.
Reinmann, G., & Mandl, H. (2006). Unterrichten und Lernumgebungen gestalten. In A. Krapp & B. Weidenmann (Ed.), Pädagogische Psychologie (pp. 613-658). Weinheim: Beltz Psychologie Verlags Union.
Resnick, L. B., Salmon, M., Zeitz, C. M., Wathen, S. H., & Holowchak, M. (1993). Reasoning in conversation. Cognition and Instruction, 11, 347-364.
Stempfle, J., & Badke-Schaub, P. (2002). Kommunikation und Problemlösen in Gruppen: eine Prozessanalyse. Gruppendynamik und Organisationsberatung, 33(1), 57-81.
Wetzel, J. (1995). Problemlösen in Gruppen: Auswirkungen von psychologischen Trainingsmaβnahmen und Expertenbeteiligung unter kooperativen und kompetitiven Arbeitsbedingungen. Dissertation. Technische Universität Carolo-Wilhelmina, Braunschweig.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hasenbein, M., Kopp, B., Mandl, H. (2008). Collaborative Problem Solving with Cases in a Virtual Professional Training. In: Zumbach, J., Schwartz, N., Seufert, T., Kester, L. (eds) Beyond Knowledge: The Legacy of Competence. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8827-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8827-8_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-8826-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-8827-8
eBook Packages: Humanities, Social Sciences and LawEducation (R0)