Abstract
Background: Some in vitro studies warn combining different metals in orthopedic surgery. The aim of this study is to determine the impact of combining titanium and stainless steel on bone healing and the clinical course of patients undergoing internal fxation of femoral fractures.
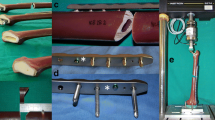
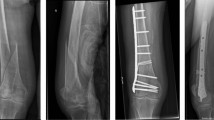
Materials and Methods: 69 patients with femoral fractures had polyaxial locking plate osteosynthesis. The locking plate was made of a titanium alloy. Two different cohorts were defned: (a) sole plating and (b) additional stainless steel cerclage wiring. Postoperative radiographs and clinical followup were performed at 6 weeks, 3 months and 12 months.
Results: Cohorts A and B had 36 and 33 patients, respectively. Patient demographics and comorbidities were similar in both groups. In two cases in cohort A, surgical revision was necessary. No complication could be attributed to the combination of titanium and stainless steel.
Conclusion: The combination of stainless steel cerclage wires and titanium plates does not compromise fracture healing or the postoperative clinical course.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoffmeier KL, Hofmann GO, Muckley T. Choosing a proper working length can improve the lifespan of locked plates: A biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2011;26;405–9.
Disegi JA. Titanium alloys for fracture fixation implants. Injury 2000;31(Suppl 4):14–7.
Carls J, Kohn D, Rossig S. A comparative study of two cerclage systems. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1999;119;67–7.
Bostrom MP, Asnis SE, Ernberg JJ, Wright TM, Giddings VL, Berberian WS, et al. Fatigue testing of cerclage stainless steel wire fixation. J Orthop Trauma 1994;8;422–8.
Shaw JA, Daubert HB. Compression capability of cerclage fixation systems: A biomechanical study. Orthopedics 1988;11;1169–7.
Mazzocca AD, Caputo AE, Browner BD. Principles of internal fixation. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2000. p. 195–7.
Disegi JA, Eschbach L. Stainless steel in bone surgery. Injury 2000;31(Suppl 4):2–6.
Perren SM, Mathys R, Pohler O. Implants and materials in fracture fixation. Dübendorf: AO Foundation; 2000.
Takai S, Yoshino N, Kusaka Y, Watanabe Y, Hirasawa Y. Dissemination of metals from a failed patellar component made of titanium-base alloy. J Arthroplasty 2003;18;931–5.
Witt JD, Swann M. Metal wear and tissue response in failed titanium alloy total hip replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1991;73;559–6.
Barbosa M. Corrosion mechanisms of metallic biomaterials. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publisher B.V.; 1999.
Griffin CD, Buchanan RA, Lemons JE. In vitro electrochemical corrosion study of coupled surgical implant materials. J Biomed Mater Res 1983;17;489–500.
Serhan H, Slivka M, Albert T, Kwak SD. Is galvanic corrosion between titanium alloy and stainless steel spinal implants: A clinical concern? Spine J 2004;4;379–87.
Venugopalan R, Lucas LC. Evaluation of restorative and implant alloys galvanically coupled to titanium. Dent Mater 1998;14;165–72.
Jennett B, Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet 1975;1;480–4.
Franz KL. Stand der Beurteilungsmöglichkeit der Prognose nach SHT- Vorbedingungen für eine Aussage über die Prognose. Neuro Trauma News 1998;9;4–5.
Erhardt JB, Grob K, Roderer G, Hoffmann A, Forster TN, Kuster MS. Treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures with the non-contact-bridging-plate: A new angular stable implant. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2008;128;409–16.
Duncan CP, Masri BA. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. AAOS Instr Course Lect 1995;44;293–304.
Rorabeck CH, Taylor JW. Classification of periprosthetic fractures complicating total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 1999;30;209–14.
Henderson CE, Lujan TJ, Kuhl LL, Bottlang M, Fitzpatrick DC, Marsh JL. 2010 (Mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award): Healing complications are common after locked plating for distal femur fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2011;469;1757–65.
O’Toole RV, Gobezie R, Hwang R, Chandler AR, Smith RM, Estok DM 2nd, et al. Low complication rate of LISS for femur fractures adjacent to stable hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006;450;203–10.
Ricci WM, Loftus T, Cox C, Borrelli J. Locked plates combined with minimally invasive insertion technique for the treatment of periprosthetic supracondylar femur fractures above a total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma 2006;20;190–6.
Wick M, Muller EJ, Kutscha-Lissberg F, Hopf F, Muhr G. Periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fractures: LISS or retrograde intramedullary nailing? Problems with the use of minimally invasive technique. Unfallchirurg 2004;107;181–8.
Kaab MJ, Stockle U, Schutz M, Stefansky J, Perka C, Haas NP. Stabilisation of periprosthetic fractures with angular stable internal fixation: A report of 13 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2006;126;105–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Zayat, B.F., Ruchholtz, S., Efe, T. et al. Results of titanium locking plate and stainless steel cerclage wire combination in femoral fractures. IJOO 47, 454–458 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.118200
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.118200