Abstract
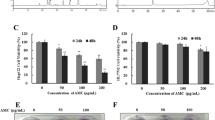
Asparagus cochinchinensis Merrill (Liliaceae) has been traditionally used for the treatment of cancer in Korea and China, but its anticancer activity and underlying mechanism remain to be defined. Anticancer activities were investigated on fractions obtained from A. cochinchinensis 70% ethanol extract (ACE-EtOH) in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Ethylacetate fraction from A. cochinchinensis extract (ACE-EA), more effective than other fractions, induced apoptosis of HepG2 (IC50=72.33±0.34 μg/mL), as revealed by apoptotic feature observation, increased capase-3 activity and Poly ADP ribose polymerase cleavage, and decreased expression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein in a dose-dependent manner. Protein levels of autophagyrelated molecules, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 α and beclin 1, appeared to be induced by ACE-EA, suggesting ACE-EA exhibits anti-cancer activity with induction via both apoptosis and autophagy signaling pathways in HepG2 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, and Cressman EN (2008) Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 48, 2047–2063.
Chen YN, Cheng CC, Chen JC, Tsauer W, and Hsu SL (2003) Norcantharidin-induced apoptosis is via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase and c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase signaling pathways in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Br J Pharmacol 140, 461–470.
Chen J, Xiao XQ, Deng CM, Su XS, and Li GY (2006) Downregulation of xIAP expression by small interfering RNA inhibits cellular viability and increases chemosensitivity to methotrexate in human hepatoma cell line HepG2. J Chemother 18, 525–531.
Cheung CS, Chung KK, Lui JC, Lau CP, Hon PM, Chan JY, Fung KP, and Au SW (2007) Leachianone A as a potential anti-cancer drug by induction of apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Cancer Lett 253, 224–235.
Choi J, Yip-Schneider M, Albertin F, Wiesenauer C, Wang Y, and Schmidt CM (2008) The effect of doxorubicin on MEK-ERK signaling predicts its efficacy in HCC. J Surg Res 150, 219–226.
Chung TW, Moon SK, Chang YC, Ko JH, Lee YC, Cho G, Kim SH, Kim JG, and Kim CH (2004) Novel and therapeutic effect of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma cells: complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by dual mechanism. FASEB J 18, 1670–1681.
Huang KC (1993) In The Pharmacology Of Chinese Herbs, p. 361, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA.
Hui KM (2009) Human hepatocellular carcinoma: expression profiles-based molecular interpretations and clinical applications. Cancer Lett 286, 96–102.
Iida Y, Oh KB, Saito M, Matsuoka H, and Kurata H (2000) In vitro synergism between nyasol, an active compound isolated from Anemarrhena asphodeloides, and azole agents against Candida albicans. Planta Med 66, 435–438.
Kiyono K, Suzuki HI, Matsuyama H, Morishita Y, Komuro A, Kano MR, Sugimoto K, and Miyazono K (2009) Autophagy is activated by TGF-beta and potentiates TGFbeta-mediated growth inhibition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 69, 8844–8852.
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD (2000) Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science 290, 1717–1721.
Lauricella M, Emanuele S, D’Anneo A, Calvaruso G, Vassallo B, Carlisi D, Portanova P, Vento R, and Tesoriere G (2006) JNK and AP-1 mediate apoptosis induced by bortezomib in HepG2 cells via FasL/caspase-8 and mitochondriadependent pathways. Apoptosis 11, 607–625.
Lee DY, Choo BK, Yoon T, Cheon MS, Lee HW, Lee AY, and Kim HK (2009) Anti-inflammatory effects of Asparagus cochinchinensis extract in acute and chronic cutaneous inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol 121, 28–34.
Lin HM, Tseng HC, Wang CJ, Chyau CC, Liao KK, Peng PL, and Chou FP (2007) Induction of autophagy and apoptosis by the extract of Solanum nigrum Linn in HepG2 cells. J Agric Food Chem 55, 3620–3628.
Llovet JM and Bruix J (2008) Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 48, 1312–1327.
Oketch-Rabah HA, Dossaji SF, Christensen SB, Frydenvang K, Lemmich E, Cornett C, Olsen CE, Chen M, Kharazmi A, and Theander T (1997) Antiprotozoal compounds from Asparagus africanus. J Nat prod 60, 1017–1022.
Parekh P, Motiwale L, Naik N, and Rao KV (2011) Downregulation of cyclin D1 is associated with decreased levels of p38 MAP kinases, Akt/PKB and Pak1 during chemopreventive effects of resveratrol in liver cancer cells. Exp Toxicol Pathol, 63, 167–173.
Paruthiyil S, Cvoro A, Zhao X, Wu Z, Sui Y, Staub RE, Baggett S, Herber CB, Griffin C, Tagliaferri M, Harris HA, Cohen I, Bjeldanes LF, Speed TP, Schaufele F, and Leitman DC (2009) Drug and cell type-specific regulation of genes with different classes of estrogen receptor beta-selective agonists. PLoS One 4, e6271.
Sandra T and Amato JG (2010) Targeting cancer cells through autophagy for anticancer therapy. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22, 246–251.
Shi JG, Li GQ, Huang SY, Mo SY, Wang Y, Yang YC, and Hu WY (2004) Furostanol oligoglycosides from Asparagus cochinchinensis. J Asian Nat Prod Res 6, 99–105.
Song MC, Yang HJ, Bang MH, Kim DK, Jeong TS, Kim JP, and Baek NI (2007) Antioxidant and antiatherogenic activity of cis-Hinokiresinol from Trapa pseudoincisa. Arch Pharm Res 30, 1392–1397.
Tsuchihara K, Fujii S, and Esumi H (2009) Autophagy and cancer: dynamism of the metabolism of tumor cells and tissues. Cancer Lett 278, 130–138.
Yang CX, Huang SS, Yang XP, and Jia ZJ (2004) Nor-lignans and steroidal saponins from Asparagus gobicus. Planta Med 70, 446–451.
Zhang HJ, Sydara K, Tan GT, Ma C, Southavong B, Soejarto DD, Pezzuto JM, and Fong HH (2004) Bioactive constituents from Asparagus cochinchinensis. J Nat Prod 67, 194–200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Park† and M.S. Cheon† contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, M., Cheon, M.S., Kim, S.H. et al. Anticancer activity of Asparagus cochinchinensis extract and fractions in HepG2 cells. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 54, 188–193 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2011.031
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2011.031