Abstract
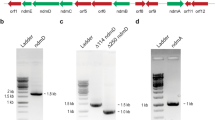
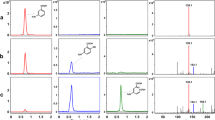
A gene encoding Catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (CD-2,3) was cloned from 3,4-dichloroaniline degrading bacterium Pseudomonas sp. KB35B. Comparison of the deduced amino acids of the CD-2,3 with other CD-2,3 proteins revealed that only three amino acids (Q116, N142 and V215) were particularly different in the CD-2,3 of KB35B. To elucidate how these differences are related with the biochemical properties of the protein, these amino acids were converted into the corresponding residue of other CD-2,3 proteins or Gly, respectively. The effects of amino acid conversion on the catalytic properties of the altered enzymes were then determined, and the results showed that Q116 is a critical amino acid involved in both substrate affinity and catalysis since the conversion of Q116 into other amino acids resulted in the change of both Km and Vmax. However, the substitution of N142 showed only change of Vmax, suggesting that this domain may involve in substrate catalysis. The mutation of V215 domain led to the deficiency of expression, implying that this amino acid is essential for the expression of the CD-2,3.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD-2,3:
-
catechol 2,3-dioxygenase
- 3,4-DCA:
-
3,4-dichloroaniline
- IPTG:
-
isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, and Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25, 3389–3402.
Choi JH, Kim TK, Kim YM, Kim WC, Joo GJ, Lee KY, and Rhee IK (2005) Cloning and characterization of a short chain alcohol dehydrogenase gene for cyclohexanol oxidation in Rhodococcus sp. TK6. J Microbiol Biotechnol 15, 1186–1196.
Choi JH, Kim TK, Kim YM, Kim WC, Park K, and Rhee IK (2006) Cloning and characterization of a gene cluster for cyclohexanone oxidation in Rhodococcus sp. TK6. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16, 511–518.
Gheewala SH and Annachhatre AP (1997) Biodegradation of aniline. Water Sci Technol 36, 53–63.
Jeong JJ, Kim JH, Kim CK, Hwang IG, and Lee K (2003) 3- and 4-alkylphenol degradation pathway in Pseudomonas sp. strain KL28: genetic organization of the lap gene cluster and substrate specificities of phenol hydroxylase and catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. Microbiology 149, 3265–3277.
Kazuki F, Neuls ED, Ryberg JM, and Suh DY (2007) Mutational analysis of conserved outer sphere arginine residues of chalcone synthase. J Biochem 142, 731–739.
Kim JE, Fernandes E, and Bollag JM (1997) Enzymatic coupling of the herbicide bentazon with humus monomer and characterization of reaction products. Environ Sci Technol 31, 2392–2398.
Kim YM, Jung SH, Chung YH, Yu CB, and Rhee IK (2008) Cloning and characterization of a cyclohexanone monooxygenase gene from Arthrobacter sp. L661. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 13, 40–47.
Kim YM, Park K, Joo GJ, Jeong EM, Kim JE, and Rhee IK (2004) Glutathione-dependent biotransformation of the fungicide chlorothalonil. J Agric Food Chem 52, 4192–4196.
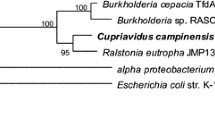
Kim YM, Park K, Kim WC, Shin JH, Kim JE, Park HD, and Rhee IK (2007) Cloning and characterization of a catechol-degrading bacterium Pseudomonas sp. KB35B. J Agric Food Chem 55, 4722–4727.
Lo HH, Valentovic M, Brown PI, and Rankin GO (1994) Effect of chemical form, route of administration and vehicle on 3,5-dichloroaniline-induced nephrotoxicity in the Fischer 344 rat. J Appl Toxicol 14, 417–422.
Nakanishi Y, Murakami S, Shinke R, and Aoki K (1991) Induction, purification, and characterization of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from aniline-assimilating Pseudomonas sp. FK-8-2. Agric Biol Chem 55, 1281–1289.
Neurath H (1943) The role of glycine in protein structure. J Am Chem Soc 65, 2039–2041.
Park A, Lamb HK, Nichols C, Moore JD, Brown KA, Cooper A, Charles IG, Stammers DK, and Hawkins AR (2008) Biophysical and kinetic analysis of wild-type and site-directed mutants of the isolated and native dehydroquinate synthase domain of the AROM protein. Protein Sci 13, 2108–2119.
Rodarie D and Jouanneau Y (2001) Genetic and biochemical characterization of the biphenyl dioxygenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain B4. J Microbiol Biotechnol 11, 763–771.
Sota M, Yano H, Ono A, Miyazaki R, Ishii H, Genka H, Top EM, and Tsuda M (2006) Genomic and functional analysis of the IncP-9 naphthalene-catabolic plasmid NAH7 and its transposon Tn4655 suggests catabolic gene spread by a tyrosine recombinase. J Bacteriol 188, 4057–4067.
Tixier C, Sancelme M, Ait-Aissa S, Bonnemoy F, Cuer A, Truffaut N, and Veschambre H (2002) Biotransformation of phenylurea herbicides by a soil bacterial strain, Arthrobacter sp. N2: structure, ecotoxicity and fate of diuron metabolite with soil fungi. Chemosphere 46, 519–526.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YK., Eom, SH., Hwang, HJ. et al. Cloning and mutational analysis of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from 3,4-dichloroaniline degrading bacterium Pseudomonas sp. KB35B. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 52, 258–263 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2009.046
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2009.046