Abstract
Contingency awareness during conditioning describes the phenomenon of becoming consciously aware of the association between a conditioned stimulus (CS) and an unconditioned stimulus (US). Despite the fact that contingency awareness is necessary for associative learning in some conditioning paradigms, its role in contextual fear conditioning, a variant that uses a context-CS (CTX) instead of a cue, has not been characterized thus far. We investigated if contingency awareness is a prerequisite for contextual fear conditioning and if subjects classified as aware differ from unaware subjects on a hemodynamic, autonomic, and behavioral level. We used a computer-generated picture context as CTX and slightly painful electric stimulation as US while we recorded brain responses by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), and obtained skin conductance responses (SCR) and verbal ratings of emotional valence and arousal. SCR analyses revealed that only aware subjects became conditioned to the US-associated CTX (CTX+). Brain activity related to the CTX+ was more strongly pronounced in fear-associated areas like the insula in the aware relative to the unaware group. Finally, the hippocampus was functionally connected to the cingulate cortex and posterior medial frontal gyrus in aware subjects relative to unaware subjects. These task-related differential connectivity patterns suggest that information exchange between the hippocampus and regions involved in the expression of conditioned fear and decision uncertainty is crucial for the acquisition of contingency knowledge. This study demonstrates the importance of contingency awareness for contextual fear conditioning and points to the hippocampus as a potential mediator for contingency learning in contextual learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Classical conditioning is one of the most widely used paradigms in psychology to investigate associative learning processes in humans and other animals (Buchel & Dolan, 2000; Fullana et al., 2015). In a conditioning procedure an initially neutral stimulus (conditioned stimulus; CS) is learned to predict a biologically relevant event (unconditioned stimulus; US) after repeated CS/US pairings and as a result evokes a conditioned response (CR), if presented alone (Pavlov, 1927). In fear conditioning the US is aversive and repeated pairings results in fear responses to the CS (Watson & Rayner, 1920). Common variants of classical conditioning are delay, trace, and contextual conditioning. In delay conditioning CS and US overlap, whereas in trace conditioning a temporal gap is interposed between CS offset and US onset. Contextual conditioning is characterized by the fact that a context, which is comprised of several individual features (these can be spatial, temporal, etc.) that must be assembled into a unified representation, is associated with the US (Maren, Phan, & Liberzon, 2013; Rudy, 2009). CRs are commonly assessed by measuring skin conductance responses (SCR), heart rate, or fear-potentiated startle (Hamm, Greenwald, Bradley, & Lang, 1993). Human subjects usually become consciously aware (i.e., develop declarative knowledge) of the CS/US contingency during conditioning. However, the development of contingency awareness depends on the processing demands of the respective conditioning paradigm (Carter, Hofstotter, Tsuchiya, & Koch, 2003; Clark & Squire, 1998; Knuttinen, Power, Preston, & Disterhoft, 2001; LaBar & Disterhoft, 1998; Manns, Clark, & Squire, 2002). Single-cue conditioning produces only very few unaware subjects, whereas more complex conditioning schemes such as differential conditioning (where one stimulus – CS+ – is associated with the US while the other – CS- – is not) prevent more subjects from becoming aware (Carter et al., 2003). The question whether declarative knowledge of the relationship between CS und US is necessary for successful conditioning has sparked a considerable debate amongst scientists (Clark, Manns, & Squire, 2002; Lovibond, Liu, Weidemann, & Mitchell, 2011; Lovibond & Shanks, 2002; Manns et al., 2002; Mitchell, De Houwer, & Lovibond, 2009; Schultz & Helmstetter, 2010; Smith, Clark, Manns, & Squire, 2005; Weidemann, Best, Lee, & Lovibond, 2013).
Several brain regions are involved in contingency awareness including for example the ventral striatum/nucleus accumbens (Klucken, Kagerer, et al., 2009a; Klucken, Tabbert, et al., 2009b). The most consistent reports, however, come from studies implicating the hippocampus and the frontal cortex in the formation of declarative knowledge of the learned association. Clark and Squire (1998) examined healthy controls and amnesic patients with damage to the hippocampal formation who underwent delay conditioning and trace conditioning. They found that, in controls, awareness was relevant for trace but not for delay conditioning. Accordingly, the patients acquired delay conditioning but failed to acquire trace conditioning. An inability to develop contingency awareness was also observed in hippocampal-damaged patients undergoing standard cue conditioning without temporal offset between of CS and US (Bechara et al., 1995). Furthermore, activity in the hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus was linked to the acquisition of contingency knowledge during fear conditioning in healthy subjects (Carter et al., 2003; Carter, O'Doherty, Seymour, Koch, & Dolan, 2006; Knight, Waters, & Bandettini, 2009; Tabbert et al., 2011). Carter et al. (2006) also reported a correlation of trial-by-trial US expectancy ratings and responses in the middle frontal gyrus. Other neuroimaging studies demonstrated an engagement of prefrontal areas (Andreatta et al., 2015; McIntosh, Rajah, & Lobaugh, 1999) related to contingency awareness. McIntosh, Rajah, and Lobaugh (2003) found interactions of these areas with the medial temporal lobe (MTL), which were specific to aware subjects during associative learning in a task that required subjects to learn which one of two tones predicts a visual stimulus. If hippocampus/parahippocampus and prefrontal cortex support contingency awareness, the memory functions they subserve also might differ between aware and unaware subjects. There is some evidence that supports this notion, with one study showing a trend toward higher working memory capacity in aware compared to unaware subjects (Cosand et al., 2008). This is consistent with the fact that executing a working memory task during conditioning impairs contingency awareness (Tabbert, Stark, Kirsch, & Vaitl, 2006), an effect that is more pronounced in hippocampus-dependent procedures (trace conditioning) compared to procedures that do not rely on the hippocampus (delay conditioning) (Carter et al., 2003).
The role of contingency awareness was intensively studied in tone-cue trace and delay conditioning (e.g., Carter et al., 2006; Clark & Squire, 1998) as well as in standard visual-cue conditioning (e.g., Klucken, Tabbert, et al., 2009b; Knight et al., 2009) paradigms. However, up to now, we do not know which brain systems are involved in contingency learning while subjects undergo contextual conditioning.
In this study we sought to elucidate the role of contingency awareness during contextual fear conditioning using two feature-identical picture contexts of which one served as the CTX+ while the other served as the CTX- (Baeuchl, Meyer, Hoppstädter, Diener, & Flor, 2015) during functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and simultaneous recording of SCRs. In addition, subjects rated CTXs on emotional valence and arousal before and after conditioning. Specifically, we aimed to identify differences in brain activation and functional connectivity patterns between aware and unaware subjects with a focus on hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Furthermore, we wanted to address the questions if contingency-unaware subjects would also be conditioned by expressing CRs during the experiment. In addition, we were interested if both groups also differed in their memory performance in neuropsychological tests. We predicted that relative to the aware group, unaware subjects would not become conditioned, would not show activity in brain regions associated with the anticipation of aversive events (e.g., insula) and contingency awareness (hippocampus and prefrontal cortex), and would achieve lower scores on tests of visual and working memory, indicating an important role of awareness in contextual conditioning.
Materials and methods
Participants
We investigated 100 healthy adults who signed informed consent prior to data collection. Subjects were recruited via invitation letters, sent out to a sample of residents of Mannheim, Germany, which were randomly selected by the cities' registration office. Individuals who showed interest in participating in the study underwent a telephone screening where they were asked if they have a history of or are currently suffering from, neurological impairments, mental disorder, or drug abuse. Two subjects were excluded due to excessive head movements (abrupt displacements > 0.4 mm (translation) or > 0.4° (rotation) in more than 5% of scans; see Functional MRI preprocessing and BOLD activity analyses) and two subjects were excluded because they incorrectly indicated that the US was associated with the safe context CTX- (see Stimulus ratings and group allocation). This left 96 subjects for the fMRI analyses (52 male, age range: 19–49 years; mean age: 30.27 ± 9.03 standard deviation (SD)). For SCR analyses, a further ten subjects had to be excluded because they were categorized as SCR non-responders (see SCR analyses). All participants were right-handed (Edinburgh Handedness Inventory: LQ > 72; Oldfield (1971)) German native speakers who had normal or corrected-to-normal vision. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty Mannheim of Heidelberg University and adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Experimental design
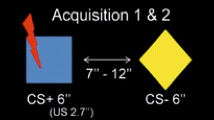
The stimulus material was comprised of two context pictures and was taken from a previous study (Baeuchl et al. (2015); see Fig. 1). Context pictures were designed to induce configural processing for successful differential context conditioning to occur. This was established by using 3D pictures of the same rooms containing the same cues, which were positioned in distinct spatial arrangements. The design of the contexts was based on configural learning theories that postulate that the representation of contexts rely on the integration of multiple cues into a unified representation (Eichenbaum, 2004; Moses & Ryan, 2006; Rudy & Sutherland, 1995).
The event-related fMRI experiment consisted of three conditions: CTX- in which one of the context pictures was never associated with an unconditioned aversive electric stimulus (US), CTX+paired where the US was administered during the presentation of the other context picture, and CTX+unpaired in which the latter context picture was not paired with the US. Hence, our differential conditioning procedure followed a partial reinforcement scheme in which the US is administered in 50% of CTX+ trials. The assignment of the pictures to CTX+ and CTX- was counterbalanced between subjects. The condition CTX+unpaired was created to investigate hemodynamic responses evoked by the CTX+ without the confounding effects of the US. The pictures were presented for the duration of 4 s and appeared in a pseudo-randomized order with every picture being shown 40 times during the entire experimental run. The same stimulus (e.g., CTX+) occurred maximally three times in a row and the US was never administered in two consecutive trials. The trial sequence was identical for all subjects. Inter-stimulus intervals were randomly jittered between 4–8 s resulting in trial lengths of 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 s (Fig. 2). The electric stimulus was administered to the right thumb via a pair of surface electrodes, and occurred within an interval of 0.5–3.5 s during the presentation of the CTX+. US onset was randomized within the described interval to ensure that the participants perceived the occurrence of the US as unpredictable, a prerequisite for inducing contextual fear in aversive context conditioning (Grillon, Baas, Lissek, Smith, & Milstein, 2004). The US consisted of a train of six electric pulses that were applied in a frequency of 12.2 Hz over the duration of 480 ms. US intensity was individually adjusted to be aversive but not too painful. Pain threshold and pain tolerance levels were assessed by applying a series of electrical stimuli of ascending intensity to the thumb of the right hand until the subject indicated that the stimulus was "becoming painful" (pain threshold), and then further until the subject could not bear to receive a stimulus of a higher intensity (pain tolerance). This procedure was repeated three times and the pain threshold and pain tolerance were determined by the mean value of the last stimuli of the last two stimulus series. For the experiment, the magnitude of the stimulation was initially set at 80% of the difference between the individually assessed pain threshold and pain tolerance level. The electric stimulus of this magnitude had to be rated for pain intensity and unpleasantness on a 9-point scale ranging from 1 = not painful/not unpleasant to 9 = very painful/very unpleasant. The magnitude of the stimulation was adjusted if ratings for painfulness and unpleasantness were below 6 points on both scales (painfulness rating – mean: 7.28 ± 0.64 SD; unpleasantness rating – mean: 7.33 ± 0.67 SD). For two subjects one of the scales was rated 4.5 and 5, respectively. We did not raise the magnitude of the electric stimulation in these cases because the other scale was rated with 7 points and subjects already reported the stimulation to be quite painful. Pain intensity and unpleasantness ratings were repeated directly after the experiment. To check whether subjects adapted to the electric stimuli over time, we calculated separate paired t-tests, comparing the pre- and post-experimental ratings on intensity and unpleasantness. The results were considered significant if p < 0.05, adjusted for multiple comparisons using the Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) procedure (Benjamini & Hochberg, 1995). Prior to the experiment subjects were instructed to view the pictures attentively during the session while they would occasionally receive a painful stimulus. No information was given that the painful stimulus would occur only during presentation of one of the context pictures. The net scanning time for our paradigm amounted to 13.2 min. In the literature, the distinction is often made that cue conditioning results in fear responses, while contextual (fear) conditioning results in anxiety responses (Tovote, Fadok, & Luthi, 2015), although this notion has been called into question recently (Perusini & Fanselow, 2015). Since context exposure happens for a relatively short time in our task and the overall experiment has a short duration, we do not assume that our subjects will develop sustained levels of arousal and hence will refer to the CTX+ evoked responses as “fear” instead of “anxiety” responses in this study. The experimental procedure included neither a habituation (presentation of CTXs and US without pairing prior to acquisition) nor an extinction phase (presentation of CTX+ and CTX- without delivery of US during CTX+ after the acquisition phase).Footnote 1
The design involved three conditions using two contextual stimuli: during the CTX- condition (40 trials) one of the contexts was never associated with aversive electrical stimulation (US), while in the CTX+paired condition (20 trials), the US was presented in the second context and in the CTX+unpaired condition (20 trials) the second context was presented without the US being administered. Each context presentation lasted for 4 s and the inter-stimulus interval varied randomly between 4 and 8 s (var. ISI)
Neuropsychological testing
The subjects participated in a neuropsychological test session in which they performed the Mehrfachwahl-Wortschatz-Intelligenztest (MWT-B) (Lehrl, 2005), a multiple-choice vocabulary-intelligence test and the logical memory subtests (I and II) of the Wechsler-Memory-Scale revised (WMS-R) (Härting et al., 2000), followed by ten computerized tasks taken from the Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB; Cambridge Cognition Ltd., Cambridge, UK). Testing took place on a separate day to the fMRI experiment and always occurred prior to the scanning day. Subjects completed the CANTAB tests simple reaction time (SRT) and rapid visual processing (RVP) that assess attention, intra-/extradimensional set shift (IED), spatial span (SSP) and stockings of Cambridge (SOC), which assess executive function, working memory, and planning, the stop signal task (SST) that assesses response inhibition and tests on delayed matching to sample (DMS), pattern recognition memory (PRM) and paired associates learning (PAL), which assess visual memory. For the current work, we examined only those neuropsychological tests that are relevant to the question whether contingency-aware and -unaware subjects differ in their performance on visual memory and working memory tasks that are sensitive to changes in medial temporal- and frontal-lobe functioning. Therefore, we compared both groups of subjects in their performance on PAL, DMS, PRM, and SSP using two sample t-tests. For each CANTAB task one measure was used to compare performance between groups: (1) PAL total errors (eight shapes, adjusted), which assesses performance at the most difficult stage of the task (with an adjustment for subjects who have not reached this stage). This score is especially suited for measuring memory and learning in high-functioning individuals; (2) DMS% correct (all delays), which represents the number of occasions the subject selected the correct stimulus after the sample has been hidden, for all delays; (3) PRM% correct, which is an indicator of overall performance on visual short term recognition memory; (4) SSP span length, which represents the longest sequence successfully recalled by the subject and indexes working memory capacity. Where possible, the standard score was used instead of the raw score. Outliers in the test scores (3 SDs from the mean; 0.69% of data) were excluded before statistical comparison. The results were considered significant if p < 0.05 (FDR adjusted).
Skin conductance response (SCR)
Skin conductance was recorded continuously from the thenar and hypothenar of the left hand using two Ag/AgCl electrodes and a sampling rate of 5,000 Hz. Before mounting of the electrodes, the skin was prepared with an isotonic saline solution (0.9% saline) and electrode paste was applied to the electrodes, which contained 0.5% saline in a neutral base. The signal was amplified using a BRAINAMP ExG MR device in combination with a GSR MR module (BRAIN PRODUCTS, Gilching, Germany).
MRI data acquisition
MRI data collection was performed at two recording sites in Mannheim and Heidelberg with identical set-ups, using a 3-Tesla MAGNETOM Trio scanner and a 32-channel phased-array head coil (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). Functional images were obtained in a descending order using a T2*-weighted echo-planar imaging sequence (33 axial slices, co-planar with AC-PC; TR = 1800 ms; TE = 30 ms; FA = 73°; FOV = 192 × 192 mm; matrix size = 64 × 64 mm; voxel size = 3 × 3 × 3 mm). Each functional scan resulted in 452 volumes of which the first five were discarded to allow for magnetic saturation. Additionally, T1-weighted anatomical, magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MP-RAGE) images were acquired (TR = 2,300 ms; TE = 3 ms; FA = 9°; FOV = 256 × 256 × 192 mm; voxel size = 1 × 1 × 1 mm). The stimuli were delivered using Presentation (version 14.9; Neurobehavioral Systems, Inc., Albany, USA).
Stimulus ratings and group allocation
Directly before and after the experiment, while lying in the MR scanner, the subjects verbally rated the two contextual pictures on emotional valence and arousal using a 9-point scale ranging from “1” (very pleasant/not arousing) to “9” (very unpleasant/very arousing). Additionally, after the experiment, the subjects were asked about the perceived likelihood that the US occurred during the presentation of each picture (contingency awareness) on a 9-point scale ranging from “1” (very unlikely) to “9” (very likely). The subjects were classified as aware of the CTX+/US contingency if they gave a contingency awareness rating of CTX+/US that was > 50% higher than their rating of CTX-/US (difference ≥ 5 points). All other subjects were coded as unaware. This criterion is similar to that applied by Lovibond et al. (2011), who also used a 50% cut-off on questions related to contingency awareness. Two subjects were excluded from this group allocation procedure because their rating of CTX-/US was > 50% higher than their rating of CTX+/US. This classification procedure resulted in a contingency-aware group with 41 subjects (20 male, age range: 19–48 years; mean age: 28.98 ± 7.30 SD) and a contingency-unaware group with 55 subjects (32 male, age range: 19–49 years; mean age: 31.24 ± 10.08 SD). Differences in contingency awareness were not equally distributed along the scale but seemed to follow a bimodal distribution with two distinct peaks at the values 0 and 6 (see Fig. 3). To assess the bimodality of the data, we fitted the rating differences to a unimodal and a bimodal distribution using the “gmdistribution.fit” function in Matlab (version 7.14, MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA, USA), which estimates the parameters of a model consisting of n mixed Gaussian distributions (whereby n is the number of modes/peaks). We compared the fitted models on the basis of the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), a procedure for model selection (models with small BIC values are more likely to be the true model). The bimodal distribution model compared to the unimodal distribution model would be favored if it had a ∆BIC > 2 (Kass & Raftery, 1995). To verify if stimulus ratings on the dimensions arousal and valence differed between CTX+ and CTX- within a group and, in a further step, between the two groups, we proceeded as follows. First, values of the pre-experimental ratings were subtracted from the post-experimental values, whereby resulting “difference values” > 0 imply that subjects assessed the respective stimulus to be more arousing or unpleasant after the experiment compared to before. Then we calculated two-way mixed effects ANOVAs on these difference values for both the valence and arousal ratings, with awareness as between-subjects factor and CTX type as within-subject factor. Finally, paired t-tests were calculated to compare ratings on arousal and valence for CTX+ and CTX- within each group. The results were considered significant if p < 0.05 and FDR correction was applied where appropriate.
The participants rated the visual contexts (CTX+ and CTX-) after the experiment on the perceived likelihood that the aversive event (US) occurred during their presentation. CTX- ratings were subtracted from CTX+ ratings yielding a bimodal-looking distribution of rating differences. The subjects were classified as contingency aware if they had a rating difference of ≥ +5 points and as contingency unaware if they had a rating difference of < 5 points
SCR analyses
The skin conductance response (SCR) was assessed as a peripheral indicator of conditioning. The raw data were down-sampled to 10 Hz and outliers (3 SDs from the mean; 0.64% of the data) were rectified via linear interpolation. We analyzed event-related SCRs in a response window of 1– 8 s after stimulus presentation, using the software package Ledalab (version 3.4.6; http://www.ledalab.de/). We applied a continuous decomposition analysis (CDA), which is based on deconvolution of the original data into continuous tonic and phasic activity to reduce the possible impact of superposition effects (Benedek & Kaernbach, 2010). The magnitude of the SCRs was quantified for each trial in each subject using the time integral of the deconvoluted phasic activity over the whole response window (μS*s). Subjects were classified as SCR non-responders if they showed significant SCR responses (deflections > 0.01 μS within response window) for CTX+paired in less than 66% of trials. This criterion was chosen based on previous experience from working with SCR datasets of other fear conditioning studies in our lab. Ten subjects who met this criterion were excluded, leaving 86 subjects for further SCR analyses. A constant value of 1 was added to all remaining SCRs before they were logarithmically transformed in order to normalize the data. SCRs of CTX+unpaired and CTX- trials were split into three non-overlapping time bins. Since CTX+unpaired contained 20 and CTX- contained 40 trials, bin sizes were chosen to be 7 or 14 sample points for the first and last bin and 6 or 12 sample points for the second bin, respectively. The data were then averaged within each time bin. A three-way mixed effects ANOVA was calculated on these averaged SCRs with awareness as a between-subjects factor and CTX type and time bin as within-subjects factors. In addition, within-group comparisons between CTX+unpaired and CTX- were carried out for both groups using separate paired t-tests. Results were considered significant if p < 0.05 and FDR correction was applied where appropriate.
Functional MRI preprocessing and BOLD activity analyses
MRI data were preprocessed and analyzed using SPM 8 (Statistical Parametric Mapping; http://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/). The functional images were realigned to the first image of the sequence to correct for head motion. The maximum absolute displacements of the head over the course of the experiment (motion drifts) across all subjects were 1.4 mm, 4.8 mm, and 4.9 mm (x,y,z translations) and 3.5°, 1.6°, and 2.4° (transverse, longitudinal, and vertical axis of rotation). The estimated realignment parameters (translations and rotations of the head) obtained from this procedure were examined for abrupt displacements (motion “spikes” relative to preceding scan) in all subjects using custom-made scripts in Matlab. If such a spike exceeded 0.4 mm (translation) or 0.4° (rotation) the affected scan was interpolated by the mean of the preceding and subsequent scan. In this way a total of 20 scans from six subjects were interpolated, which corresponds to less than 0.05% of all scans. This step was carried out because the realignment procedure, while sensitive to the effects of slow drifts, cannot account for the effects of sudden head movements (Lemmin et al., 2010). After this step, the realignment procedure was repeated for data sets that contained interpolated scans. Next, all functional data were slice-time corrected to the middle slice using SPM’s Fourier phase shifting interpolation. The anatomical image was co-registered to the mean functional image and segmented into gray matter and white matter using the New Segment algorithm. The segmented images were used to normalize the functional images to the standard space of the Montreal Neurological Institute (ICBM 152 MNI template) via SPM’s DARTEL toolbox. Functional images were resampled to the original acquisition resolution of 3-mm cubic voxels and spatially smoothed (8-mm FWHM Gaussian kernel). Blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) responses were analyzed within the framework of the general linear model (GLM). To this end, the time series of all conditions (CTX+paired, CTX+unpaired, and CTX-) were modeled as stick function regressors and convolved with the canonical hemodynamic response function. These three regressors depict BOLD responses that were relatively constant throughout the course of the experiment (sustained activity). Previous studies identified a decay of neural responses in the amygdala (Büchel, Morris, Dolan, & Friston, 1998; LaBar, Gatenby, Gore, LeDoux, & Phelps, 1998; Quirk, Armony, & LeDoux, 1997) and hippocampus (Baeuchl et al., 2015; Büchel, Dolan, Armony, & Friston, 1999; Büchel et al., 1998; Knight, Cheng, Smith, Stein, & Helmstetter, 2004; Marschner, Kalisch, Vervliet, Vansteenwegen, & Buchel, 2008) during fear conditioning. Therefore, we created additional regressors by parametrically modulating the main effect regressors of our three conditions with a demeaned linear decaying function to obtain BOLD effects that decreased over time (transient activity). The same approach was employed in previous contextual fear conditioning studies to capture transient activity in the medial temporal lobe (Baeuchl et al., 2015; Marschner et al., 2008). Since head movements can severely affect functional connectivity estimates even after standard motion correction methods are applied (Power, Barnes, Snyder, Schlaggar, & Petersen, 2012; Van Dijk, Sabuncu, & Buckner, 2012), we modeled residual movement effects as described in Lund, Norgaard, Rostrup, Rowe, and Paulson (2005) by including a Volterra expansion to the six rigid-body motion parameters as covariates of no interest in the design matrix of the GLM. The Volterra expansion includes the linear and quadratic effect of the motion parameters and the linear and quadratic effect of the first derivative of the motion parameters, resulting in 24 covariates of no interest. This expansion accounts for higher order effects of motion, including spin history effects (Friston, Williams, Howard, Frackowiak, & Turner, 1996). The data were high-pass filtered with a cut-off of 128 s and corrected for temporal autocorrelation using the AR(1) model.
On the single subject level, contrasts were set up such that they reflected sustained and transient activity during contextual fear conditioning: CTX+unpaired(sustained) > CTX-(sustained) and CTX+unpaired(transient)> CTX-(transient). Single-subject contrast images were first entered into separate random-effects one-sample t-test within-group analyses for sustained and transient effects in aware and unaware subjects, respectively. Then, single-subject contrast images were employed for group comparisons via two-sample t-tests, yielding the following contrasts: Contingency Aware(sustained) > Contingency Unaware(sustained) and Contingency Aware(transient)> Contingency Unaware(transient). Group contrast design matrices additionally included the mean-centered covariates “age” and “scanner site.” Statistical maps were considered significant if they survived a family-wise error corrected (FWE) cluster-level threshold of p < 0.05 as determined by the CorrClusTh algorithm (version 1.3; www2.warwick.ac.uk/fac/sci/statistics/staff/academic-research/nichols/scripts/spm). For sustained activity, we used a whole-brain cluster-defining threshold of p < 0.001, which resulted in cluster-sizes of k= 64, k= 70, and k = 72 for the aware and unaware group and the group comparison, respectively. For transient activity, we carried out anatomical region of interest (ROI) analyses since we were primarily interested in BOLD responses within the medial temporal lobe (MTL). The anatomical ROI comprises bilateral hippocampus and bilateral amygdala and was created using the Anatomy toolbox (version 2.0, Eickhoff et al., 2005). The cluster-defining threshold of this ROI-analysis was set to p < 0.005, which resulted in cluster-sizes of k = 45, k = 48, and k = 48 for the aware and unaware group and the group comparison, respectively.
Psychophysiological interaction
We employed psychophysiological interaction analyses (PPI; Friston et al., 1997; Gitelman, Penny, Ashburner, & Friston, 2003) to investigate whether functional interactions between brain regions were differentially modulated by the experimental task in contingency-aware subjects relative to contingency unaware subjects. PPI identifies regionally specific responses in terms of an interaction of a seed-region (extracted first eigenvariate of a ROI) with an experimental factor (e.g., the task), using the difference in regression coefficients. Because interactions in the brain do not occur on a hemodynamic but on a neural level, the PPI algorithm implemented in SPM 8 deconvolves the BOLD time-series of the seed-region (Gitelman et al., 2003). We selected two seed-regions for two independent analyses, defined by the peak activation within the right hippocampus in the transient activity contingency-aware group contrast and the peak activation within the right middle frontal gyrus in the sustained activity between-group comparison. Seed masks were created by constructing spherical ROIs with a diameter of 6 mm around the center of the hippocampal (MNI coordinates: 30, -18, -21) and middle frontal gyrus (33, 57, 18) peak. Time series data were then extracted from these seeds as the first eigenvariate of the filtered and adjusted response in all voxels. Interaction regressors were created by computing the element-wise product of the experimental event time course (contrast: CTX+unpaired > CTX-) and the seed-region time series. The effects of these interaction regressors were tested against baseline on a single-subject level, yielding contrast images for the two separate analyses using the hippocampal seed (PPI: HC) and the middle frontal gyrus seed (PPI: MFG). Single subject contrast images were entered into random-effects two-sample t-test analyses for group comparisons yielding the following contrasts: Contingency Aware(PPI: seed HC)> Contingency Unaware(PPI: seed HC) and Contingency Aware(PPI: seed MFG)> Contingency Unaware(PPI: seed MFG). The results were considered significant if p < 0.05 (FWE corrected on cluster-level; see Functional MRI preprocessing and BOLD activity analyses), using a whole-brain cluster defining threshold of p < 0.005 which resulted in a cluster size of k = 193.
Results
Stimulus ratings
Ratings on intensity (t(95) = 12.929, p < 0.001) and unpleasantness (t(95) = 10.488, p < 0.001) of the US were significantly lower after compared to before the experiment. Fitting a unimodal (BIC = 523.24) and a bimodal (BIC = 462.23) model to the contingency awareness rating differences confirmed the assumption that the data followed a bimodal distribution. Since the model with the smaller BIC is preferred in model selection and the difference between both models was > 10, this constitutes strong evidence for bimodality of the data (Kass & Raftery, 1995). A two-way mixed-effects ANOVA on the post minus pre-experimental differences in the valence rating revealed a main effect of CTX type (F(1,94) = 20.888, p < 0.001) and an interaction between awareness and CTX type (F(1,94) = 9.731, p < 0.003). A second two-way mixed-effects ANOVA on the arousal rating differences yielded a main effect of CTX type (F(1,94) = 15.491, p < 0.001) and an interaction between awareness and CTX type (F(1,94) = 19.712, p < 0.001). Paired t-tests showed that contingency-aware subjects had higher ratings for CTX+ than CTX- on valence (t(40) = 4.658, p < 0.001) and arousal (t(40) = 4.7512, p < 0.001) whereas contingency-unaware subjects did not (for detailed results see Table 1).
Neuropsychological assessment
On the PAL task contingency-unaware subjects committed significantly more errors on the eight shapes stage than contingency-unaware subjects (t(93) = 2.071, p = 0.041). Contingency-aware subjects also performed significantly better on the PRM task at the immediate (t(93) = 2.361, p = 0.020) as well as the delayed (t(92) = 2.905, p = 0.005) recognition phase compared to unaware subjects. In addition, contingency-aware compared to contingency-unaware subjects showed a trend towards a higher percentage of correct responses in their performance on the DMS (t(94) = 1.666, p = 0.099). The span length on the SSP was on average significantly higher in the contingency-aware group compared to the unaware group, in both the forward (t(94) = 2.967, p = 0.004) and the backward (t(94) = 3.470, p = 0.001) mode, indicating higher working memory capacity in the former group. Figure 4 depicts the mean scores of the CANTAB tests for contingency-aware and contingency-unaware subjects.
SCR results
A three-way mixed-effects ANOVA on SCRs revealed a main effect of time bin (F(2,420) = 56.050, p < 0.001) as well as two-way interactions between awareness and CTX type (F(1,420) = 13.345, p < 0.001) and between CTX type and time bin (F(2,420) = 17.306, p < 0.001). Paired t-tests comparing CTX+unpaired > CTX- showed that contingency-aware subjects did not demonstrate significant differences between the two conditions in the first (t(37) = -0.455, p = 0.651) and third time bin (t(37) = 1.218, p = 0.230), while in the second time bin SCRs were significantly larger for CTX+unpaired than for CTX- (t(37) = 2.860, p = 0.007). Contingency-unaware subjects on the other hand showed a different response pattern. CTX- evoked larger SCR responses than CTX+unpaired in the first (t(47) = -5.276, p < 0.001) and third time bin (t(47) = -4.113, p < 0.001), while SCRs did not significantly differ between the two conditions in the second time bin (t(47) = 1.763, p = 0.085). Mean SCR amplitudes across all three time bins for both groups are depicted in Fig. 5. These results suggest that successful conditioning occurred after one-third of the experiment and only in those subjects that were aware of the CTX+/US contingency.
Mean skin conductance response (SCR) amplitudes (log([μS*s]+1)) for CTX+unpaired and CTX- trials in the contingency-aware group and the contingency-unaware group, respectively. SCRs are divided into three non-overlapping time bins with separate statistical tests computed in every bin. Error bars denote the standard error of the mean. *p < 0.01
Functional MRI results
Sustained effects
We first examined sustained BOLD responses within the contingency-aware and contingency-unaware group and then compared both groups using the following contrast: Contingency Aware(sustained) > Contingency Unaware(sustained). Single subject contrast images for these analyses were taken from the contrast estimates for CTX+unpaired(sustained) > CTX-(sustained), which reflect the effects of fear conditioning. Brain activity that was significant in the contingency-aware group was found in several regions including bilateral insula, bilateral inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), left anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), left superior medial gyrus (SMG), and bilateral inferior parietal lobule (IPL). Detailed results for this analysis are reported in Table 3 and are depicted in Fig. 6. No significant BOLD responses were detected in the unaware group. Group comparisons yielded significantly stronger activations for aware than unaware subjects in the bilateral insula, bilateral inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), right middle frontal gyrus (MFG), left superior medial gyrus (SMG), and bilateral inferior parietal lobule (IPL). Detailed results for this comparison can be found in Table 2 and are depicted in Fig. 7.
Sustained brain activity for the contrast CTX+unpaired > CTX- in the contingency-aware group. Results are significant at the cluster-level (p < 0.05, FWE corrected). Plane coordinates are in MNI space. Table 2 lists detailed information of the results
Stronger brain activation in contingency-aware subjects relative to contingency-unaware subjects. Contrast images used for the group comparison were taken from the contrast CTX+unpaired(sustained) > CTX-(sustained). Results are significant at the cluster-level (p < 0.05, FWE corrected). Plane coordinates are in MNI space. A list of all significant activations for this contrast can be found in Table 2
Transient effects
For contingency-aware subjects we observed significant transient activity in clusters in the right hippocampus and left amygdala/hippocampus; however, the latter cluster did not reach significance on the cluster level (FWE corrected p = 0.155, cluster size k = 19). A list of the within-group results of contingency-aware subjects can be found in Table 3, while the activations are depicted in Fig. 8. The same analysis did not yield any significant cluster-level corrected results for contingency-unaware subjects with the largest cluster significant on the voxel-level found in the subiculum (FWE corrected p = 0.315, cluster size k = 6). The comparison of transient brain activity in contingency-aware versus contingency-unaware subjects (Contingency Aware(transient) > Contingency Unaware(transient)) did not yield significant differences between the groups after applying an FWE-corrected threshold on the cluster level. All analyses used contrast images from the contrast estimates of CTX+unpaired(transient) > CTX-(transient) and were confined to a ROI of the MTL region.
Transient brain activity (linearly decaying over time) for the contrast CTX+unpaired > CTX- in the contingency-aware group. Results are significant at the cluster-level (p < 0.05, FWE corrected within bilateral MTL ROI). Plane coordinates are in MNI space. Table 2 lists detailed information of the results
Functional connectivity results
The right hippocampal seed region was functionally connected to two clusters, largely residing in the superior medial gyrus/posterior medial frontal cortex and the anterior/mid cingulate cortex, respectively. Detailed results of the PPI group comparison of the hippocampal seed region are reported in Table 3 and depicted in Fig. 9. The right middle frontal gyrus did not show any significant connections to the rest of the brain that survived a cluster-threshold correction (Fig. 9).
Differential modulating effect of the task on functional connectivity of the hippocampus with the rest of the brain (psychophysiological interaction analysis) in contingency-aware subjects relative to contingency-unaware ones. Results are significant at the cluster-level (p < 0.05, FWE corrected). Plane coordinates are in MNI space. A list of all significant interaction effects for this contrast can be found in Table 3
Discussion
This study investigated the role of contingency awareness in contextual fear conditioning. Our results demonstrate marked differences between aware and unaware subjects in almost all variables under study. The conditioning procedure evoked significant autonomic responses related to CTX+unpaired only in the aware group, and this effect was also present in the stimulus ratings that revealed higher arousal and unpleasantness ratings for CTX+ than for CTX- in aware subjects compared to unaware ones. Sustained brain activity in regions typically engaged in fear conditioning like the insula, inferior parietal lobule, and superior medial gyrus (Alvarez, Biggs, Chen, Pine, & Grillon, 2008; Baeuchl et al., 2015; Etkin, Egner, & Kalisch, 2011; Marschner et al., 2008; Pohlack, Nees, Ruttorf, Schad, & Flor, 2012) was significantly stronger in the aware than in the unaware group. Transient hippocampal responses, which were found only in aware subjects, were not significantly different between the groups. A task-related increase in functional connectivity between hippocampus and cingulate cortex/posterior medial frontal cortex was observed in the aware relative to unaware subjects. Finally, awareness was also related to superior performance in tests of visual and working memory. Taken together, these findings suggest that the development of declarative knowledge of the CTX/US contingency is necessary for differential contextual fear conditioning and that the hippocampus and regions of the frontal cortex contribute to contingency learning.
Contingency awareness
The current study assessed contingency awareness post-experimentally by asking the subjects whether they perceived the US as co-occurring with the CTX, assigning them to the aware group in case the CTX+/US ratings were > 50% higher than their CTX-/US ratings and to the unaware group if this was not the case. The question how contingency awareness can be reliably determined in conditioning experiments has been debated in the literature. Lovibond and Shanks (2002) criticized post-conditioning questionnaires (PCQ) as a means to measure awareness by arguing that they might be subject to forgetting. To alleviate the problem of forgetting, Lovibond and Shanks (2002) proposed that if a PCQ is used it should be administrated directly after learning, use a recognition rather than a recall format and employ a continuous rating scale. The contingency awareness rating procedure of the current study fulfilled these criteria. Although our results suggest that awareness is necessary for differential contextual conditioning, the precise nature of the relationship between contingency awareness and associative learning remains elusive.
Behavior
Analyses of the post- minus pre-experimental stimulus rating differences yielded a main effect for CTX type and an interaction between awareness and CTX type, both for the arousal and valence rating alike. In combination with the within-group contrasts these results showed that affective conditioning occurred only in aware subjects. CTX+ acquired, relative to CTX-, negative emotional valence and was perceived as more arousing as a function of conditioning in the aware group. These behavioral effects were absent in unaware subjects.
Phasic changes of differential SCRs were taken as indicators of autonomic conditioning and examined over three time bins. As hypothesized, results from the SCR analyzes demonstrated that fear learning developed in aware but not in unaware subjects. Significant differential responses (CTX+unpaired > CTX-) were observed in the aware group in the second time bin, while SCR differences between conditions did not reach significance in the first and third time bin. These findings illustrate learning-related changes after one-third of the experiment and a habituation effect toward the end. The subjects habituated to the US, as indicated by significantly lower pain intensity and unpleasantness ratings after compared to before the experiment. This habituation was probably also responsible for the diminution of SCR responses in CTX+unpaired trials. We detected the same differential SCR pattern in a previous study in which we analyzed only aware subjects using the same design (Baeuchl et al., 2015). In contrast, unaware subjects displayed a quite different behavior. Their SCRs in response to CTX+unpaired were not significantly higher than those for CTX- in the second time bin but SCRs related to the CTX- were of higher magnitude within the first and third time bin relative to CTX+unpaired. Since they were not able to predict which CTX would be accompanied by a US, unaware subjects might have fallen for the gambler’s fallacy (Burns & Corpus, 2004), expecting that the US should occur during CTX- presentation after they perceived that the US was administered during the CTX+ in previous trials. However, since we did not obtain online US expectancy ratings that would have allowed us to verify if unaware subjects indeed expected the US to occur during CTX- presentation, this interpretation remains speculative.
All neuropsychological tests of visual and working memory indicated significantly better performance of the aware relative to the unaware group. As these tests are sensitive to medial temporal and frontal lobe functioning, the resulting group differences lend further support for the involvement of those brain structures in acquiring contingency awareness during conditioning. An adequate level of visual and working memory capacity might be necessary to maintain representations of previous events during the experiment, in order to become aware of the fact that the US only occurs during CTX+ presentation.
FMRI and PPI
Sustained BOLD responses that were larger in contingency aware than in contingency-unaware subjects (with the single subject contrast CTX+unpaired > CTX-) included the bilateral insula, bilateral inferior frontal gyrus, bilateral inferior parietal lobule, left superior medial gyrus, right middle frontal gyrus, and right thalamus. Interestingly, there was a large overlap between the findings of the group comparison and the activations found in the aware group alone, while we did not obtain any significant within-group results in the unaware group. These brain regions also largely overlap with those described in a previous study using the same paradigm, where all subjects were aware of the contingency (Baeuchl et al., 2015), and are commonly implicated in successful contextual fear conditioning in healthy controls (Alvarez et al., 2008; Lang et al., 2009; Marschner et al., 2008; Pohlack et al., 2012). Hence, relative to aware subjects, unaware subjects lacked activity in the insula, involved in the anticipation of painful events (Ploghaus et al., 1999), and superior medial gyrus, linked to the appraisal and expression of fear (Etkin et al., 2011). This is in line with the fact that unaware subjects did not show higher autonomic responses to CTX+ unpaired relative to CTX-. More pronounced activity within inferior frontal gyrus and inferior parietal lobule in the aware group might be explained by the contribution of these brain regions to directing attention toward the US-associated context, as they are commonly engaged during attentional processing (Simon et al., 2004). MFG activity during acquisition was previously only reported in differential trace conditioning paradigms (Carter et al., 2006; Knight et al., 2004) where it had been directly related to contingency awareness (Carter et al., 2006). In addition, we found significant transient responses in the right hippocampus in the aware group. However, this transient brain activity in the MTL was not significantly stronger in the aware relative to the unaware group. Although this result confirms that the hippocampus is necessary for successful contextual conditioning, it does not allow conclusions to be drawn about potential differences in hippocampal activity between the two groups (see Nieuwenhuis, Forstmann, & Wagenmakers, 2011). Previous studies that also found transient hippocampal responses during conditioning explained them in terms of an associative learning effect. Marschner et al. (2008) interpret declining hippocampal responses during contextual conditioning as a learning-related reduction of a prediction error, since the occurrence of the US during CTX+ presentation is no longer surprising.
A psychophysiological interaction (PPI) analysis with the right hippocampus as a seed region (Contingency Aware(PPI: seed HC) > Contingency Unaware(PPI: seed HC)) revealed significant group differences of task-related hippocampal connectivity with the midcingulate cortex (MCC)/anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and superior medial gyrus (SMG)/posterior medial frontal cortex (pMFC). Despite the fact that PPI does not explicitly model directionality, its interaction term leads to different models for the influence of region A on region B than for region B on region A. In this light, our PPI findings could indicate an information flow from hippocampus to the cingulate cortex and pMFC. A meta-analysis of fear-conditioning studies indicated that regions of the dorsal ACC/MCC belong to a core fear network, which is activated regardless of how fear was learnt (Mechias, Etkin, & Kalisch, 2010). Group-specific task-related modulation of the connection from the hippocampus to the cingulate cortex in aware relative to unaware subjects suggests that contextual information formed in the hippocampus may need to be relayed to the cortex in order for fear conditioning to occur. This is consistent with the fact that activity in the dorsal ACC is positively correlated with autonomic arousal (Critchley et al., 2003), especially during fear conditioning (Milad et al., 2007). Another meta-analysis of studies on cognitive control outlined that more dorsally located areas in the SMG/pMFC are frequently associated with pre-response conflict and decision uncertainty (Ridderinkhof, Ullsperger, Crone, & Nieuwenhuis, 2004). Hippocampal input to these brain areas during contextual conditioning might be necessary to disambiguate uncertainties about CTX-US relationships.
Limitations
The work presented in this paper is subject to several limitations. Online US expectancy ratings have the advantage of providing additional information about the time point at which the contingency is learned. It might be interesting to investigate potential changes of BOLD activity and/or functional network activity after the exact point in time when subjects become aware. The usage of an offline PCQ as employed in our study does not allow for this possibility. MRI data acquisition in this study was carried out on two different scanner sites with the same MRI sequences, scanner hardware and spatial setup. Studies exploring the effects of multiple scanner sites observed scanner site related biases that particularly affected the brainstem and thalamus (Chen et al., 2014). Although we have included scanner site as a covariate in our GLM and multi-site MRI recordings have been shown to be reliable when data are recorded with similar acquisition parameters (Cannon et al., 2014; Ewers et al., 2006; Jovicich et al., 2006), we cannot rule out the possibility that our data are affected by these multi scanner site acquisition issues.
Although there is evidence that MTL activity decreases over time during cue, trace, and contextual conditioning (Alvarez et al., 2008; Baeuchl et al., 2015; Büchel et al., 1999; Knight et al., 2004; LaBar et al., 1998; Marschner et al., 2008; Quirk et al., 1997), the assumption of a linear decay of MTL responses might not provide the best fit to the data. A suboptimal fit of our linear model of decreasing BOLD activity to the data might have underpowered the statistical group-comparison of MTL responses, which makes it difficult to judge whether aware and unaware subjects genuinely do not differ in hippocampal activity or whether a lack of power is responsible for the obtained null-result.
We found no significant amygdala activation in our within-group analysis of transient brain responses, although we observed a trend in a cluster that included the left anterior hippocampus and amygdala. This was surprising as the amygdala is frequently implicated in the acquisition of conditioned fear (Greco & Liberzon, 2016). Notably, contextual fear conditioning studies do not always reliably elicit amygdala activation (Alvarez et al., 2008; Stout et al., 2018) and a similar result of amygdala activation that showed a trend toward significance was obtained by Marschner et al. (2008). Since they too assumed a linear decay of MTL responses, it might be that time-varying amygdala activity is less well represented by this model than hippocampal responses.
We also failed to detect activity in the ventral striatum in our study, a region found to be involved in context conditioning (Pohlack et al., 2012) and contingency awareness (Klucken, Kagerer, et al., 2009a). Future studies need to address whether the ventral striatum fulfills a general role in fear conditioning or whether its involvement is more dependent on the specifics of a conditioning paradigm (e.g., stimulus type and stimulus duration).
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate the importance of contingency awareness for contextual fear conditioning. There were striking differences between subjects classified as aware and those classified as unaware. Furthermore, these differences not only showed that contingency awareness is necessary for contextual conditioning, but also shed light on potential mechanisms for contingency learning. Hence, our study contributes to the current debate on the necessity of contingency awareness during associative learning and extends it to contextual conditioning paradigms.
Notes
Our experiment was part of a larger scanning procedure where every subject underwent a scanning session on two different days and completed two experimental paradigms per session. The order in which experiments were presented to each subject was counterbalanced within – and between sessions.
References
Alvarez, R. P., Biggs, A., Chen, G., Pine, D. S., & Grillon, C. (2008). Contextual fear conditioning in humans: cortical-hippocampal and amygdala contributions. J Neurosci, 28(24), 6211-6219. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1246-08.2008
Andreatta, M., Glotzbach-Schoon, E., Muhlberger, A., Schulz, S. M., Wiemer, J., & Pauli, P. (2015). Initial and sustained brain responses to contextual conditioned anxiety in humans. Cortex, 63, 352-363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2014.09.014
Baeuchl, C., Meyer, P., Hoppstädter, M., Diener, C., & Flor, H. (2015). Contextual fear conditioning in humans using feature-identical contexts. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 121, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2015.03.001
Bechara, A., Tranel, D., Damasio, H., Adolphs, R., Rockland, C., & Damasio, A. R. (1995). Double dissociation of conditioning and declarative knowledge relative to the amygdala and hippocampus in humans. Science, 269(5227), 1115-1118.
Benedek, M., & Kaernbach, C. (2010). A continuous measure of phasic electrodermal activity. J Neurosci Methods, 190(1), 80-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.04.028
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, J. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological). 57(1), 289-300.
Buchel, C., & Dolan, R. J. (2000). Classical fear conditioning in functional neuroimaging. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 10(2), 219-223.
Büchel, C., Dolan, R. J., Armony, J. L., & Friston, K. J. (1999). Amygdala-hippocampal involvement in human aversive trace conditioning revealed through event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci, 19(24), 10869-10876.
Büchel, C., Morris, J., Dolan, R. J., & Friston, K. J. (1998). Brain systems mediating aversive conditioning: an event-related fMRI study. Neuron, 20(5), 947-957.
Burns, B. D., & Corpus, B. (2004). Randomness and inductions from streaks: "gambler's fallacy" versus "hot hand". Psychon Bull Rev, 11(1), 179-184.
Cannon, T. D., Sun, F., McEwen, S. J., Papademetris, X., He, G., van Erp, T. G. M., … Toga, A. W. (2014). Reliability of neuroanatomical measurements in a multisite longitudinal study of youth at risk for psychosis. Human Brain Mapping, 35(5), 2424-2434. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22338
Carter, R. M., Hofstotter, C., Tsuchiya, N., & Koch, C. (2003). Working memory and fear conditioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 100(3), 1399-1404. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0334049100
Carter, R. M., O'Doherty, J. P., Seymour, B., Koch, C., & Dolan, R. J. (2006). Contingency awareness in human aversive conditioning involves the middle frontal gyrus. Neuroimage, 29(3), 1007-1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.09.011
Chen, J. Y., Liu, J. Y., Calhoun, V. D., Arias-Vasquez, A., Zwiers, M. P., Gupta, C. N., … Turner, J. A. (2014). Exploration of scanning effects in multi-site structural MRI studies. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 230, 37-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.04.023
Clark, R. E., Manns, J. R., & Squire, L. R. (2002). Classical conditioning, awareness, and brain systems. Trends Cogn Sci, 6(12), 524-531.
Clark, R. E., & Squire, L. R. (1998). Classical conditioning and brain systems: the role of awareness. Science, 280(5360), 77-81.
Cosand, L. D., Cavanagh, T. M., Brown, A. A., Courtney, C. G., Rissling, A. J., Schell, A. M., & Dawson, M. E. (2008). Arousal, working memory, and conscious awareness in contingency learning. Conscious Cogn, 17(4), 1105-1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2008.04.007
Critchley, H. D., Mathias, C. J., Josephs, O., O'Doherty, J., Zanini, S., Dewar, B. K., … Dolan, R. J. (2003). Human cingulate cortex and autonomic control: converging neuroimaging and clinical evidence. Brain, 126(Pt 10), 2139-2152. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awg216
Eichenbaum, H. (2004). Hippocampus: cognitive processes and neural representations that underlie declarative memory. Neuron, 44(1), 109-120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.028
Eickhoff, S. B., Stephan, K. E., Mohlberg, H., Grefkes, C., Fink, G. R., Amunts, K., & Zilles, K. (2005). A new SPM toolbox for combining probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps and functional imaging data. Neuroimage, 25(4), 1325-1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.12.034
Etkin, A., Egner, T., & Kalisch, R. (2011). Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends Cogn Sci, 15(2), 85-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2010.11.004
Ewers, M., Teipel, S. J., Dietrich, O., Schonberg, S. O., Jessen, F., Heun, R., … Hampel, H. (2006). Multicenter assessment of reliability of cranial MRI. Neurobiology of Aging, 27(8), 1051-1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.05.032
Friston, K. J., Buechel, C., Fink, G. R., Morris, J., Rolls, E., & Dolan, R. J. (1997). Psychophysiological and modulatory interactions in neuroimaging. Neuroimage, 6(3), 218-229. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1997.0291
Friston, K. J., Williams, S., Howard, R., Frackowiak, R. S., & Turner, R. (1996). Movement-related effects in fMRI time-series. Magn Reson Med, 35(3), 346-355.
Fullana, M. A., Harrison, B. J., Soriano-Mas, C., Vervliet, B., Cardoner, N., Avila-Parcet, A., & Radua, J. (2015). Neural signatures of human fear conditioning: an updated and extended meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Molecular Psychiatry, 21(4), 500-508. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.88
Gitelman, D. R., Penny, W. D., Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2003). Modeling regional and psychophysiologic interactions in fMRI: the importance of hemodynamic deconvolution. Neuroimage, 19(1), 200-207.
Greco, J. A., & Liberzon, I. (2016). Neuroimaging of Fear-Associated Learning. Neuropsychopharmacology, 41(1), 320-334. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.255
Grillon, C., Baas, J. P., Lissek, S., Smith, K., & Milstein, J. (2004). Anxious responses to predictable and unpredictable aversive events. Behavioral Neuroscience, 118(5), 916-924. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7044.118.5.916
Hamm, A. O., Greenwald, M. K., Bradley, M. M., & Lang, P. J. (1993). Emotional Learning, Hedonic Change, and the Startle Probe. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 102(3), 453-465. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843x.102.3.453
Härting, C., Markowitsch, H.-J., Neufeld, H., Calabrese, P., Seisinger, K., & Kessler, J. (2000). Wechsler Memory Scale - Revised Edition, German Edition. Manual. Bern: Huber.
Jovicich, J., Czanner, S., Greve, D., Haley, E., van der Kouwe, A., Gollub, R., … Dale, A. (2006). Reliability in multi-site structural MRI studies: Effects of gradient non-linearity correction on phantom and human data. Neuroimage, 30(2), 436-443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.09.046
Kass, R. E., & Raftery, A. E. (1995). Bayes factors. J Am Stat Assoc, 90(430), 773-795.
Klucken, T., Kagerer, S., Schweckendiek, J., Tabbert, K., Vaitl, D., & Stark, R. (2009a). Neural, Electrodermal and Behavioral Response Patterns in Contingency Aware and Unaware Subjects during a Picture-Picture Conditioning Paradigm. Neuroscience, 158(2), 721-731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.09.049
Klucken, T., Tabbert, K., Schweckendiek, J., Merz, C. J., Kagerer, S., Vaitl, D., & Stark, R. (2009b). Contingency learning in human fear conditioning involves the ventral striatum. Human Brain Mapping, 30(11), 3636-3644. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20791
Knight, D. C., Cheng, D. T., Smith, C. N., Stein, E. A., & Helmstetter, F. J. (2004). Neural substrates mediating human delay and trace fear conditioning. J Neurosci, 24(1), 218-228. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0433-03.2004
Knight, D. C., Waters, N. S., & Bandettini, P. A. (2009). Neural substrates of explicit and implicit fear memory. Neuroimage, 45(1), 208-214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.015
Knuttinen, M. G., Power, J. M., Preston, A. R., & Disterhoft, J. F. (2001). Awareness in classical differential eyeblink conditioning in young and aging humans. Behavioral Neuroscience, 115(4), 747-757.
LaBar, K. S., & Disterhoft, J. F. (1998). Conditioning, awareness, and the hippocampus. Hippocampus, 8(6), 620-626. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1998)8:6<620::AID-HIPO4>3.0.CO;2-6
LaBar, K. S., Gatenby, J. C., Gore, J. C., LeDoux, J. E., & Phelps, E. A. (1998). Human amygdala activation during conditioned fear acquisition and extinction: a mixed-trial fMRI study. Neuron, 20(5), 937-945.
Lang, S., Kroll, A., Lipinski, S. J., Wessa, M., Ridder, S., Christmann, C., … Flor, H. (2009). Context conditioning and extinction in humans: differential contribution of the hippocampus, amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Eur J Neurosci, 29(4), 823-832. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06624.x
Lehrl, S. (2005). Mehrfachwahl-Wortschatz-Intelligenztest (MWT-B). Balingen: Spitta Verlag.
Lemmin, T., Ganesh, G., Gassert, R., Burdet, E., Kawato, M., & Haruno, M. (2010). Model-based attenuation of movement artifacts in fMRI. J Neurosci Methods, 192(1), 58-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.07.013
Lovibond, P. F., Liu, J. C., Weidemann, G., & Mitchell, C. J. (2011). Awareness is necessary for differential trace and delay eyeblink conditioning in humans. Biol Psychol, 87(3), 393-400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.05.002
Lovibond, P. F., & Shanks, D. R. (2002). The role of awareness in Pavlovian conditioning: empirical evidence and theoretical implications. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process, 28(1), 3-26.
Lund, T. E., Norgaard, M. D., Rostrup, E., Rowe, J. B., & Paulson, O. B. (2005). Motion or activity: their role in intra- and inter-subject variation in fMRI. Neuroimage, 26(3), 960-964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.02.021
Manns, J. R., Clark, R. E., & Squire, L. R. (2002). Standard delay eyeblink classical conditioning is independent of awareness. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process, 28(1), 32-37.
Maren, S., Phan, K. L., & Liberzon, I. (2013). The contextual brain: implications for fear conditioning, extinction and psychopathology. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14(6), 417-428. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3492
Marschner, A., Kalisch, R., Vervliet, B., Vansteenwegen, D., & Buchel, C. (2008). Dissociable roles for the hippocampus and the amygdala in human cued versus context fear conditioning. J Neurosci, 28(36), 9030-9036. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1651-08.2008
McIntosh, A. R., Rajah, M. N., & Lobaugh, N. J. (1999). Interactions of prefrontal cortex in relation to awareness in sensory learning. Science, 284(5419), 1531-1533.
McIntosh, A. R., Rajah, M. N., & Lobaugh, N. J. (2003). Functional connectivity of the medial temporal lobe relates to learning and awareness. J Neurosci, 23(16), 6520-6528.
Mechias, M. L., Etkin, A., & Kalisch, R. (2010). A meta-analysis of instructed fear studies: implications for conscious appraisal of threat. Neuroimage, 49(2), 1760-1768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.09.040
Milad, M. R., Quirk, G. J., Pitman, R. K., Orr, S. P., Fischl, B., & Rauch, S. L. (2007). A role for the human dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in fear expression. Biol Psychiatry, 62(10), 1191-1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.04.032
Mitchell, C. J., De Houwer, J., & Lovibond, P. F. (2009). The propositional nature of human associative learning. Behav Brain Sci, 32(2), 183-198; discussion 198-246. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X09000855
Moses, S. N., & Ryan, J. D. (2006). A comparison and evaluation of the predictions of relational and conjunctive accounts of hippocampal function. Hippocampus, 16(1), 43-65. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20131
Nieuwenhuis, S., Forstmann, B. U., & Wagenmakers, E. J. (2011). Erroneous analyses of interactions in neuroscience: a problem of significance. Nat Neurosci, 14(9), 1105-1107. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2886
Oldfield, R. C. (1971). The Assessment and Analysis of Handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia, 9(1), 97-113. https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4
Pavlov, I. P. (1927). Conditioned reflexes: an investigation of the physiological activity of the cerebral cortex. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
Perusini, J. N., & Fanselow, M. S. (2015). Neurobehavioral perspectives on the distinction between fear and anxiety. Learning & Memory, 22(9), 417-425. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.039180.115
Ploghaus, A., Tracey, I., Gati, J. S., Clare, S., Menon, R. S., Matthews, P. M., & Rawlins, J. N. (1999). Dissociating pain from its anticipation in the human brain. Science, 284(5422), 1979-1981.
Pohlack, S. T., Nees, F., Ruttorf, M., Schad, L. R., & Flor, H. (2012). Activation of the ventral striatum during aversive contextual conditioning in humans. Biol Psychol, 91(1), 74-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2012.04.004
Power, J. D., Barnes, K. A., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2012). Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage, 59(3), 2142-2154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.018
Quirk, G. J., Armony, J. L., & LeDoux, J. E. (1997). Fear conditioning enhances different temporal components of tone-evoked spike trains in auditory cortex and lateral amygdala. Neuron, 19(3), 613-624.
Ridderinkhof, K. R., Ullsperger, M., Crone, E. A., & Nieuwenhuis, S. (2004). The role of the medial frontal cortex in cognitive control. Science, 306(5695), 443-447. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1100301
Rudy, J. W. (2009). Context representations, context functions, and the parahippocampal-hippocampal system. Learn Mem, 16(10), 573-585. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.1494409
Rudy, J. W., & Sutherland, R. J. (1995). Configural association theory and the hippocampal formation: an appraisal and reconfiguration. Hippocampus, 5(5), 375-389. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.450050502
Schultz, D. H., & Helmstetter, F. J. (2010). Classical conditioning of autonomic fear responses is independent of contingency awareness. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process, 36(4), 495-500. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020263
Simon, O., Kherif, F., Flandin, G., Poline, J. B., Riviere, D., Mangin, J. F., … Dehaene, S. (2004). Automatized clustering and functional geometry of human parietofrontal networks for language, space, and number. Neuroimage, 23(3), 1192-1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.09.023
Smith, C. N., Clark, R. E., Manns, J. R., & Squire, L. R. (2005). Acquisition of differential delay eyeblink classical conditioning is independent of awareness. Behavioral Neuroscience, 119(1), 78-86. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7044.119.1.78
Stout, D. M., Glenn, D. E., Acheson, D. T., Spadoni, A. D., Risbrough, V. B., & Simmons, A. N. (2018). Neural measures associated with configural threat acquisition. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 150, 99-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2018.03.012
Tabbert, K., Merz, C. J., Klucken, T., Schweckendiek, J., Vaitl, D., Wolf, O. T., & Stark, R. (2011). Influence of contingency awareness on neural, electrodermal and evaluative responses during fear conditioning. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 6(4), 495-506. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsq070
Tabbert, K., Stark, R., Kirsch, P., & Vaitl, D. (2006). Dissociation of neural responses and skin conductance reactions during fear conditioning with and without awareness of stimulus contingencies. Neuroimage, 32(2), 761-770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.03.038
Tovote, P., Fadok, J. P., & Luthi, A. (2015). Neuronal circuits for fear and anxiety. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 16(6), 317-331. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3945
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., … Joliot, M. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage, 15(1), 273-289. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.0978
Van Dijk, K. R., Sabuncu, M. R., & Buckner, R. L. (2012). The influence of head motion on intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage, 59(1), 431-438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.07.044
Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 3, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0069608
Weidemann, G., Best, E., Lee, J. C., & Lovibond, P. F. (2013). The role of contingency awareness in single-cue human eyeblink conditioning. Learn Mem, 20(7), 363-366. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.029975.112
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by a grant from the German Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, 01GQ1003B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baeuchl, C., Hoppstädter, M., Meyer, P. et al. Contingency awareness as a prerequisite for differential contextual fear conditioning. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 19, 811–828 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-018-00666-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-018-00666-z