Abstarct
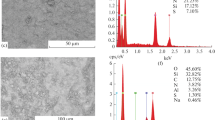
A selective sorbent based on the diatomite of local origin modified with aluminum compounds has been studied by the methods of powder X-ray diffraction; FTIR; and differential thermal, adsorption-structural (BET), and chemical analyses. The surface modification of diatomite is carried out by heating it in an NaOH solution and its subsequent treatment with a solution of aluminum salt and ammonia. The amorphous surface silica partially dissolves during the treatment with NaOH and forms an aluminosilicate compound at the addition of an aluminum salt. The obtained material is deposited both on the surface of the diatomite and on the inner surface of the macro- and larger mesopores, which leads to the development of the specific surface area of 81.8 m2/g, which is 2.5 times larger than the corresponding value in the initial diatomite (37.5 m2/g). The precipitated aluminosilicate compound with the concentration equal to 0.34 g of Al/g of aluminosilicate contributes to the development of a porous structure in the treated diatomite, so the volume of the mesopores increases from 0.029 to 0.079 cm3/g and that of the micropores from 0.012 to 0.027 cm3/g. The qualitative changes in the composition of the obtained sorbent are confirmed by the emergence of new lines in the X-ray diffraction patterns, which are characteristic for aluminosilicates, and additional peaks in the infrared spectra corresponding to the stretching vibrations of Si-O-Al. The selectivity of the obtained adsorbent with respect to fluoride ions increases significantly, specifically, its adsorption capacity increases from 8.9 to 57.6 mg of F/g at the initial fluorine concentration equal to 0.15 mol/L.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eskandarpour, A., Onyango, M.S., Ochieng, A., and Asai, S., Removal of Fluoride Ions from Aqueous Solution at Low pH Using Schwertmannite, J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, vol. 152, pp. 571–579.
Gopal, V. and Elango, K.P., Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies of Adsorption of Fluoride Onto Plaster Of Paris, J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, vol. 141, pp. 98–105.
Srimurali, M., Pragathi, A., and Karthikeyan, J., A Study on Removal of Fluorides from Drinking Water onto Low-Cost Materials, Environ. Poll., 1998, vol. 99, pp. 285–289.
Fan, X., Parker, D.J., and Smith, M.D., Adsorption Kinetics of Fluoride on Low Cost Materials, Water Res., 2003, vol. 37, pp. 4929–4937.
Agarwal, M., Rai, K., Shrivastav, R., and Dass, S., A Study on Fluoride Sorption by Montmorillonite and Kaolinite, Water Air Soil Pollut., 2002, vol. 141, pp. 247–261.
Abe, I., Iwasaki, S., Tokimoto, T., Kawasaki, N., Nakamura, T., and Tanada, S., Adsorption of Fluoride Ions onto Carbonaceous Materials, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2004, vol. 275, pp. 35–39.
Chidambaram, S., Ramanathan, A.L., and Vasudevan, S., Fluoride Removal Studies in Water Using Natural Materials, Water SA, 2003, vol. 29,no. 3, pp. 339–343.
Ayoob, S., Gupta, A.K., Bhakat, P.B., and Bhat, V.T., Investigations on the Kinetics and Mechanisms of Sorptive Removal of Fluoride from Water Using Alumina Cement Granules, J. Chem. Eng., 2008, vol. 140, pp. 6–14.
Tor, A., Removal of Fluoride from an Aqueous Solution by Using Montmorillonite, Desalination, 2006, vol. 201, pp. 267–276.
Sujana, M.G., Thakur, R.S., and Rao, S.B., Removal of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution by Using Alum Sludge, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1998, vol. 206, pp. 94–101.
Bakr, H.E.G.M.M., Diatomite: Its Characterization, Modifications and Applications, Asian J. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 2,no. 3, pp. 121–136.
Korunic, Z., Diatomaceous Earths, a Group of Natural Insecticides, J. Stored Prod. Res., 1998, vol. 34, pp. 87–97.
Aytas, S., Akyil, S., Aslani, M.A.A., and Aytekin, U., Removal of Uranium from Aqueous Solution by Diatomite (Kieselguhr), J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 1999, vol. 240,no. 3, pp. 973–976.
Badii, K. and Ardejani, F.D., M. Saberi A., Shafaei, S.Z., Adsorption of Acid Blue 25 Dye in Aqueous Solutions, Indian J. Chem. Technol., 2010, vol. 17, pp. 7–16.
Wu, J., Yang, Y.S., and Lin, J., Advanced Tertiary Treatment of Municipal Wastewater Using Raw and Modified Diatomite, J. Hazard. Mater., 2005, vol. B127, pp. 196–203.
Song, H., Jiang, H., Liu, X., and Meng, G., Nano TiO2 Deposited on Crude Mineral and the Photoactivity to the Degradation of Chloroform, Am. J. Environ. Sci., 2006, vol. 2,no. 2, pp. 60–65.
Jia, Y., Han, W., Xiong, G., and Yang, W., Diatomite as High Performance and Environmental Friendly Catalysts for Phenol Hydroxylation with H2O2, Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater., 2007, vol. 8, pp. 106–109.
Zhang, Z. and Wang, Z., Diatomite-Supported Pd Nanoparticles: An Efficient Catalyst for Heck and Suzuki Reactions, J. Org. Chem., 2006, vol. 71,no. 19, pp. 7485–748.
Nenadovic, S., Nenadovic, M., Kovacevic, R., Matovic, Lj., Matovic, B., and Jovanovic, Z., Influence of Diatomite Microstructure on its Adsorption Capacity for Pb(II), Sci. Sinter., 2009, vol. 41, pp. 309–317.
Ubonchonlakat, K., Sikong, L., and Phochanugoon, S., Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide Coating on Diatomite by Sol-Gel Method, Proc. Technology and Innovation for Sustainable Development. Conference Faculty of Engineering, K. Kaen University, Thailand, 2008, pp. 500–503.
Lingaraju, D., Ramji, K., Devi, M.P., and Rao, N.B.M., Synthesis, Fictionalization and Characterization of Silica Hybrid Nanocomposites, International Journal of Nanotechnology and Applications, 2010, vol. 4,no. 1, pp. 21–30.
Rangsriwatananon, K., Chaisena, A., and Thongkasam, C., Thermal and Acid Treatment on Natural Raw Diatomite Influencing in Synthesis of Sodium Zeolites, J. Porous Mater., 2008, vol. 15, pp. 499–505.
Losev, S.S., Application of Natural Silica, Diatomite Celite 545, for Quantitative Determination of Co+2 Ions, Visnik UzhNU, Seriya Khimiya, 2009, no. 22, pp. 228–122.
Chen, Z., Li, H., and Wang, L., Enhancement in Activity of a Vanadium Catalyst for the Oxidation of Sulfur Dioxide by Radio Frequency Plasma, J. Natur. Gas Chem., 2003, vol. 12, pp. 195–200.
Ilia, I.K., Stamatakis, M.G., and Perraki, Th.S., Mineralogy and Technical Properties of Clayey Diatomites from North and Central Greece, Cent. Eur. J. Geosci., 2009, vol. 1,no. 4, pp. 393–403.
Mohamedbakr, H. and Burkitbaev, M., Elaboration and Characterization of Natural Diatomite in Aktyubinsk Kazakhstan, The Open Mineralogy Journal, 2009, vol. 3, pp. 12–16.
Khraisheh, M.A.M., Al-Ghouti, M.A., Allen, S.J., and Ahmad, M.N., Effect of OH and Silanol Groups in the Removal of Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Diatomite, Water Res., 2005, vol. 39, pp. 922–932.
Goren, R., Baykara, T., Marsoglu, M., Effects of Purification and Heat Treatment on Pore Structure and Composition of Diatomite, Br. Ceramic Trans., 2002, vol. 101, pp. 177–180.
Khraisheh, M.A.M., Al-Degs, YahyaS., and Mcminn, W.A.M., Remediation of Wastewater Containing Heavy Metals Using Raw and Modified Diatomite, Chem. Eng. J., 2004, no. 2, pp. 177–184.
Al-Degs, Y., Khraisheh, M.A.M., and Tutunji, M.F., Sorption of Lead Ions on Diatomite and Manganese Oxides Modified Diatomite, Water Res., 2001, vol. 35, pp. 3724–3728.
Al-Ghouti, M., Khraisheh, M.A.M., Ahmad, M.N.M., and Allen, S., Thermodynamic Behavior and the Effect of Temperature on the Removal of Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Modified Diatomite: A Kinetic Study, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2005, vol. 287, pp. 6–13.
Wu, J., Yang, Y.S., and Lin, J., Advanced Tertiary Treatment of Municipal Wastewater Using Raw and Modified Diatomite, J. Hazard. Mater., 2005, vol. 127, pp. 196–203.
Xiong, W. and Peng, J., Development and Characterization of Ferrihydrite-Modiffied Diatomite as a Phosphorus Adsorbent, Water Res., 2008, vol. 42, pp. 4869–4877.
Hsien, K.J., Tsai, W.T., and Su, T.Y., Preparation of Diatomite-TiO Composite for Photodegradation of Bisphenol-A in Water, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 2009, vol. 51, pp. 63–69.
Buzaeva, M.V., Reducing Environmental Threat of Waste Waters Containing the Products of Decomposition of Lubrication and Coolant Fluids by Means of Chemically Modified Diatomite, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. Dissertation, Ul’yanovsk, 2006.
Bogdevich, O.P., Izmailova, D.N., and Bolotin, O.A., Application of Modified Sorbents for Elimination of Tri- and Pentavalent Arsenic Ions from Aqueous Solutions, Buletinul Institutului De Geofizica I Geologie Al ASM, 2006, no. 1, pp. 118–125.
Grigoryan, K.G., Arutunyan, G.A., Baginova, L.G., and Grigoryan, G.O., Synthesis of Calcium Hydromonosilicate from Diatomite under Hydrothermal Conditions and Its Transformation into Wollastonite, Khimicheskaya Tekhnologiya, 2008, vol. 9, pp. 101–103.
Hadjar, H., Hamdi, B., Jaber, M., Brendle, J., Kessaissia, Z., Balard, H., and Donnet, J.B., Elaboration and Characterization of New Mesoporous Materials from Diatomite and Charcoal, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 2008, vol. 107, pp. 219–226.
Zelentsov, V., Datsko, T., and Dvornikova, E., Studiul aplicabilitatii diatomitului modificat pentru inlaturarea ionilor de fluor din apele naturale, Comunicri tiinifice. Simpozion Internaional “Mediul i Industria”, Romania, Bucharest, 2005, vol. 1, pp. 213–218.
Zelentsov, V.I., Datsko, T.Ya., and Dvornikova, E.E., Fluorine Adsorption by Aluminum Oxihydrates Subjected to Thermal Treatment, Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem., 2008, vol. 44,no. 1, pp. 64–68.
Zelentsov, V.I., Datsko, T., and Dvornikova, E., Adsorbia fluorului de ctre oxidul de aluminiu, Proc. of the 33rd Annual Congress of the American Romanian Academy of Arts and Sciences (ARA), Sibiu, Romania, 2009, vol. 2, pp. 392–395.
Zelentsov, V. and Datsko, T., Active Pore Materials Based on Sludge of Cr-Ni Alloy Electrochemical Machining, Moldavian J. Phys. Sci., 2006, vol. 5,no. 2, pp. 162–168.
Yeun, C. Wu and Anan Nitya, Water Defluoridation with Activated Alumina, J. Environ. Eng. Div., 1979, vol. 105,no. 2, pp. 357–367.
Meenakshi and Maheshwari, R.C., Fluoride in Drinking Water and its Removal, J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, vol. 137,no. 1, pp. 456–463.
Ghorai, S. and Pant, K.K., Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Breakthrough Studies for Adsorption of Fluoride on Activated Alumina, Separ. Purif. Technol., 2005, vol. 42,no. 3, pp. 265–267.
Tripathy, S.S., Bersillon, J.-L., and Gopal, K., Removal of Fluoride from Drinking Water by Adsorption onto Alum-Impregnated Activated Alumina, Separ. Purif. Technol., 2006, vol. 50,no. 3, pp. 310–317.
Lounici, H., Belhocinea, D., Grib, H., Drouiche, M., Paussb, A., and Mameri, N., Fluoride Removal with Electroactivated Alumina, Desalination, 2004, vol. 161, pp. 287–293.
Krishna, B., Sanat, K.S., and Uday, C.G., Adsorption of Fluoride from Aqueous Solution by a Synthetic Iron(III)-Aluminum(III) Mixed Oxide, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2007, vol. 46,no. 16, pp. 5346–5356.
Zelentsov, V., Datsko, T., and Dvornikova, E., Procedeu de obinere a sorbentului pe baza de diatomit pentru purificare de ionii de fluor, MD 3973C2, 2010-07-31.
Bilinkis, G.M., Peres, F.S., and Kogos, A.Yu., Major Relationships in Occurrence of Diatomites in Moldova, Geol. Zh., 1987, vol. 47,no. 4, pp. 15–22.
Bilinkis, G.M., Geodinamika krainego yugo-zapada Vostochno-Evropeiskoi platformy v epokhu morfogeneza (Geodynamics of Utmost South-West of Eastern-European Platform in Epoch of Morphogenesis), Chishinau: Biznes-Elita, Lextoria, 2004, pp. 14–16.
Bolotin, O.A., Romanov, L.F., Dubinovskii, V.L., Syutkin, S.V, and Angelov, P.E., Selection of Activation Parameters of Moldavian Diatomites for Obtaining Sorbents for Water Treatment, Abstracts of Papers, The Third International Conference Ecological Chemistry, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova, 2005, p. 47.
Shin, E.W., Han, J.S., Jang, M., Min, S.-H., Park, J.K., and Rowell, R.M., Phosphate Adsorption on Aluminum-Impregnated Mesoporous Silicates: Surface Structure and Behaviour of Adsorbents, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, vol. 38, pp. 912–917.
Parks, G.A. and de Bruyn, P.L., The Zero Point of Charge of Oxides, J. Phys. Chem, 1962, vol. 66, pp. 967–973.
Yopps, J.A. and Fuerstenau, D.W., The Zero Point of Charge of Alpha-Alumina, J. Colloid Sci., 1964, vol. 19,no. 1, pp. 61–71.
Nayak, P.S. and Singh, B.K., Instrumental Characterization of Clay by XRF, XRD and FTIR, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2007, vol. 30,no. 3, pp. 235–238.
IUPAC Manual of Symbols and Terminology, Appendix 2, Pt.1, Colloid and Surface Chemistry, Pure Appl. Chem., 1972, vol. 31, p. 578.
Greg, S. and Sing, K., Adsorbtsiya, udel’naya poverkhnost’, poristost’ (Adsorption, Specific Surface, and Porosity), Moscow: Mir, 1984, 306.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © T.Ya. Datsko, V.I. Zelentsov, E.E. Dvornikova, 2011, published in Elektronnaya Obrabotka Materialov, 2011, no. 6, pp. 59–68.
About this article
Cite this article
Datsko, T.Y., Zelentsov, V.I. & Dvornikova, E.E. Physicochemical and adsorption-structural properties of diatomite modified with aluminum compounds. Surf. Engin. Appl.Electrochem. 47, 530–539 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375511060081
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375511060081