Abstract
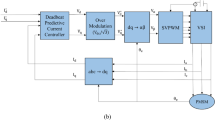
The characteristics of a wound-rotor asynchronous machine (a double-fed machine) upon positive slides are studied in the present article. The double-fed machine (DFM) allows one to adjust the internal and external flows of the active and reactive power at any rotor speed. This feature of the DFM enables one to build various electromechanical systems, such as power-efficient electric drives for transport systems, power generators with variable shaft speed, power-efficient load stands for electric machines and combustion engines, and power-efficient stands for testing an asynchronous machine with the wound rotor without the additional load. The main modes of DFM operation, which are motor and generator modes of operation at a speed below a synchronous one, are studied. The analysis that has been carried out allows one to determine the main properties of the DFM: the direction of the rotor and stator active power flows proves that the positive power feedback appears at positive sliding; the motor mode of DFM operation occurs at the negative modulation phase, while the generator mode takes place at the positive one; the active power transformed in the machine is proportional to the modulation phase; and the sign of reactive power in the stator circuit depends on the relationship between the rotor voltage and the slide. A virtual model of the DFM is constructed in the SimPower System of Matlab-Simulink. It is used for studying the static and dynamic characteristics of the DFM. These characteristics confirm the theoretical results of the analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zherve, G.K., Promyshlennye ispytaniya elektricheskikh mashin (Industrial Tests for Electrical Machines), Leningrad: Energoizdat 1984.
Botvinnik, M.M. and Shakaryan, Yu.G., Upravlyaemaya mashina peremennogo toka (Controllabl ACMachine), Moscow: Nauka 1969.
Onishchenko, G.B. and Lokteva, I.L., Asinkhronnye ventil’nye kaskady i dvigateli dvoinogo pitaniya (Induction Valve Cascades and Double-Feed Motors), Moscow: Energiya 1979.
Khvatov, S.V., Titov, V.G., and Poskobko, A.A., Asinkhronno-ventil’nye nagruzhayushchie ustroistva (Induction-Valve Loading Devices), Moscow: Energoizdat 1986.
Bulgakov, A.A., Novaya teoriya upravlyaemykh vypryamitelei (The New Theory for Controllable Rectifiers), Moscow: Nauka 1970.
Rozanov, Yu.K., Silovaya elektronika (Power Electronics), Moscow: National Research Univ. MPEI 2007.
Bogalecka, E., Zagadnienia sterowania maszyn dwustronnie zasilan pracuj c jako pr dnica w systemie elektroenergetycznym, in Prace Naukowe Wyïszej Szkoiy Morskiej w Gdyni, Gdynia 1997.
Kaz-mierkowski, M.P. and Tunia, H., Automatic Control of Converter-Fed Drives, Amsterdam–London–New York–Tokyo: Elsevier 1994.
German-Galkin, S.G., Virtual’nye laboratorii poluprovodnikovykh sistem v srede Matlab-Simulink (Virtual Laboratories of Semiconductor Systems in MatlabSimulink Environment), St. Petersburg: Lan’, 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.G. German-Galkin, 2015, published in Elektrotekhnika, 2015, No. 7, pp. 58–65.
About this article
Cite this article
German-Galkin, S.G. An analytic and simulation study of a wound-rotor asynchronous machine at positive slides. Russ. Electr. Engin. 86, 418–424 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068371215070056
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068371215070056