Abstract
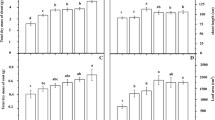
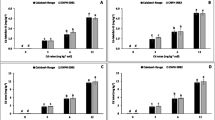
The influence of cadmium on the morphometric and biochemical indicators of the development of lettuce of the Moscow greenhouse variety, on productivity and also on metal accumulation in plant biomass during cultivation on sod-podzolic soil polluted with this toxicant in the doses range from 2 to 100 mg/kg was studied. It was shown that cadmium has a toxic effect on the development of lettuce: the plant height was reduced by 29.7–77.5%, the number of leaves was reduced by 16.4–61.3%, and the leaf surface area decreased by 34.5–99% depending on the level of contamination. The presence of metal in the soil in concentrations 5–100 mg/kg caused a decrease of the content of chlorophyll a by 15.6–38.1% in plants; chlorophyll b content decreased by 18–20% at cadmium concentration 10–100 mg/kg; carotenoids decreased by 40% at concentrations 20–50 mg/kg. Cadmium contributed to a decrease in free proline content by 20–26% with Cd concentrations at 5–100 mg/kg of soil; at a concentration of 2 mg/kg, on the contrary, Cd caused an increase of proline content of 66.2% and malondialdehyde content of 59.9% in comparison with the control. Productivity of plants decreased by 49.6–99.6% at all studied concentrations, and the level of metal accumulation in plants was significantly higher than the permissible level of cadmium (0.03 mg/kg) for lettuce.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kabata-Pendias, A., Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, CRC Press, 2010, 4th ed.
Ul’yanenko, L.N., Filipas, A.S., Loi, N.N., Stepanchikova, N.S., and Kruglov, S.V., Influence of cadmium contamination of sod-podzolic soil on the growth and development of barley plants, Agrokhimiya, 2009, no. 6, pp. 56–60.
Loi, N.N., Gubareva, O.S., Stepanchikova, N.S., and Sanzharova, N.I., Effect of cadmium pollution of sodpodzolic soil on growth and development of broad beans, Russ. Agric. Sci., 2012, vol. 38, nos. 5–6, pp. 374–376.
Zhurbitskii, Z.I., Teoriya i praktika vegetatsionnogo metoda (Theory and Practice of the Vegetative Method), Moscow: Nauka, 1968.
Metodicheskie ukazaniya po provedeniyu kompleksnogo monitoringa plodorodiya pochv zemel' sel’skokhozyaistvennogo naznacheniya (Methodical Instructions for Conducting Integrated Monitoring of Soil Fertility of Agricultural Lands), Moscow: Rosinformagrotekh, 2003.
Larsson, H.E., Bornman, J.F., and Asp, H., Influence of UV-B radiation and Cd2+ on chlorophyll fluorescence, growth and nutrient content in Brassica napus, J. Exp. Bot., 1998, vol. 49, no. 323, pp. 1031–1039.
Heath, R.L. and Packer, L., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 1968, vol. 125, no.1.
Bates, L.S., Waldern, R.P., and Teare, I.D., Plant Soil, 1973, vol. 39, no.1.
Metodicheskie ukazaniya po opredeleniyu tyazhelykh metallov v kormakh i rasteniyakh i ikh podvizhnykh soedinenii v pochvakh (Methodological Guidelines for the Determination of Heavy Metals in Feed and Plants and Their Mobile Compounds in Soils), Moscow: TsINAO, 1993, p.4.
Titov, A.F., Talanova, V.V., and Kaznina, N.M., Fiziologicheskie osnovy ustoichivosti rastenii k tyazhelym metallam: Uchebnoe posobie (Physiological Basics of Plant Resistance to Heavy Metals: Textbook), Petrozavodsk: KarNTs RAN, 2011.
Kuznetsov, Vl.V. and Shevyakova, N.I., Proline under stress: A biological role, metabolism, and regulation, Fiziol. Rast., 1999, vol. 46, pp. 321–336.
Seregin, I.V. and Ivanov, V.B., Physiological aspects of the toxic effect of cadmium and lead on higher plants, Fiziol. Rast., 2002, vol. 48, no. 4, pp. 606–630.
Shevyakova, N.I., Metabolism and physiological role of proline in plants under water and salt stress, Fiziol. Rast., 1983, vol. 30, pp. 768–783.
Sanitary Rules and Norms SanPiN 2.3.2.560-96 Hygienic Requirements for the Quality and Safety of Food Raw Materials and Food Products (approved by the decree of the State Committee for Sanitary Epidemiological Surveillance of the Russian Federation from October 24, 1996 no. 27) (as amended on October 11, 1998; March 21, 2000; January 13, 2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.N. Loi, N.I. Sanzharova, N.I. Shchagina, M.P. Mironova, 2017, published in Rossiiskaya Sel’skokhozyaistvennaya Nauka, 2017, No. 6, pp. 14–17.
About this article
Cite this article
Loi, N.N., Sanzharova, N.I., Shchagina, N.I. et al. The Effect of Cadmium Toxicity on the Development of Lettuce Plants on Contaminated Sod-Podzolic Soil. Russ. Agricult. Sci. 44, 49–52 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068367418010111
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068367418010111