Abstract
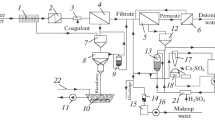
A low-waste combined technology for water softening, desalination, and deionization is proposed. The low-waste nature of the method is achieved through H-cationization of water using carboxylic polyacrylic ion exchange resin, followed by its deionization via reverse osmosis. If the requirements for desalinated water are high, such as when purified liquid is used for feeding supercritical pressure once-through boilers (SPB), it is additionally treated using ion exchange. The preconcentrate from reverse osmosis is processed through electrodialysis or electrolysis to yield acidic and alkaline solutions. These solutions are then used in conjunction with spent regeneration solutions from deep deionization ion exchange filters to regenerate the filter containing carboxylic polyacrylic ion exchange resin. The paper outlines the advantages of carboxylic cation exchange resins compared to sulfonated cation exchangers. A two-chamber H+,Na+-cation exchange filter operation circuit is proposed. Recirculation of the acidic portion of the spent regeneration solution from the BC storage reservoir through the H+Na+-cation exchange filter is planned to maximize the recovery of the cation exchange resin’s working capacity. The specifics of regenerating carboxylic cation exchange resin with acid solution in a fluidized bed mode are presented. The acidic solution storage tank should be constructed as a reservoir with a conical bottom and a cylindrical upper part. Such tank design enables its use as a gypsum particle crystallizer and settler. This circuit of separate water H+,Na+-cationization with a decarbonizer significantly expands technological capabilities. Intermediate water decarbonization decreases the alkalinity of the Na+-cation exchange filter effluent, thereby hindering the hydrolysis of the salt form of the cation exchanger. Water obtained through magnesium ionization is advisable to be directed into the softened water stream. To prevent an increase in liquid pressure drop across the filter and a sharp decrease in filtration rate, it is proposed to pass the alkaline regeneration solution from bottom to top.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
DBN V.2.5-74:2013. Water Supply. External Networks and Structures, Kyiv, 2013.
Dow Water Solutions DOWEX™ Ion Exchange Resins Water Conditioning Manual, Lenntech: Dow Chemical, 1995.
Goh, P.S. and Ismail A.F., A review on inorganic membranes for desalination and wastewater treatment, Desalination, 2018, vol. 434, no. 5, pp. 60–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.07.023
Ayol, A., Demiral, Y.O., and Güneş, S., Efficient treatment of domestic wastewaters by using a dynamic membrane bioreactor system, J. Membr. Sci. Res., 2021, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 55–58. https://doi.org/10.22079/JMSR.2020.120244.1330
Choi, J. Dorji, P., Shon, H.K., and Corrigendum, S.H., Applications of capacitive deionization: Desalination, softening, selective removal, and energy efficiency, Desalination, 2019, vol. 468, no. 10, pp. 118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.114096
DSTU 7525:2014. Drinking Water. Requirements and Methods of Quality Control, Kyiv, 2014.
GKD 34.20.507-2003: Rules for Technical Operation of Electrical Stations and Networks, Kyiv, 2003.
GOST (State Standard) 20298-74: Ion-Exchange Resins. Cation Exchangers. Specifications, Moscow, 1991.
TU U 02071045-001-98: Cation Exchange Resins. Cation Compounds. Requirements for the Quality of Cations of the Purolite Company. Introduction, 1997.
TU U 02071045-001-98: Cation Exchange Resins. Cationites. Requirements for the Quality of Cations of the Rohm and Haas Company. Introduction, 1998.
TU U 00013579-001-99: Cation-Exchange Resins. Cations. Requirements for the Quality of Cations of the Dow Chemical Company. Introduction, 1999.
Crittenden, J.C., Trussell, R.R., Hand, D.W., Howe, K.J., Tchobanoglous, G., Water Treatment: Principles and Design, New York: Wiley, 2012, 3rd ed.
Mamchenko, O.V. and Valuyskaya, Ye.A., A model of acidbase equilibrium for weakly dissociated ion exchangers, J. Water Chem. Technol., 1998, vol. 20, no. 5, pp. 10–18.
Mamchenko, A.V. and Valuiskaya, E.A., Analysis of potentiometric titration curves for carboxyl ion exchangers in terms of the exchange equilibrium theory, J. Water Chem. Technol., 1998, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 1–10.
Mamchenko, A.V. and Valuiskaya, E.A., H+Mg2+ exchange on carboxylic ion exchanges from the viewpoint of the exchange equilibria theory, J. Water Chem. Technol., 1999, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 1–14.
Funding
This work was supported by ongoing institutional funding. No additional grants to carry out or direct this particular research were obtained.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The autors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Allerton Press remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Mamchenko, O.V., Pakhar, T.A. Combined Technology of Water Softening, Desalination, and Deionization. J. Water Chem. Technol. 46, 125–131 (2024). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X24020103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X24020103