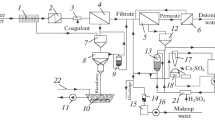
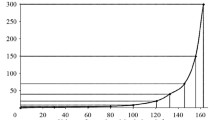
Abstract
Make-up water is treated at thermal power stations (TPS) with high-pressure or superhigh pressure boilers using membrane processes implemented in ultrafiltration, microfiltration, or reverse-osmosis (RO) units. Among the criteria of the efficiency of reverse osmosis units is the amount of highly mineralized effluents (or concentrate). At present, the RO concentrate is disposed of at TPSs by discharging it into an industrial sewage system in accordance with the applicable standards on the salt content limit of waste water, routing it into a district heating network, or returning it into recirculation water supply systems, decreasing as far as possible the volume of the discharged concentrate which is to be reused, for example, in regeneration of Na-cation exchangers installed upstream of the reverse-osmosis unit. The adsorption process is proposed for treatment of the reverse-osmosis concentrate using sludge from the makeup water treatment. The characteristics of carbonate sludge are presented. The regularities of adsorption of sulfate- and chloride-anions from the RO concentrate by carbonate sludge are described. An adsorption isotherm was obtained. The mechanism of adsorption on a sorption material is proposed. The effect of pH on adsorption of sulfate- and chloride-ions by a sorption material was investigated. A system is proposed for the treatment of the concentrate from the RO units at the Kazan Cogeneration Power Station TETs-2 to remove sulfate- and chloride anions using a three-stage adsorption method with a counter-current injection of the sorbent, namely, the carbonate sludge. The calculated values of the consumption of the sorption material required to achieve the desired residual concentration of sulfate- and chloride-anions in the treated water are presented. The economic effectiveness from implementation at the Kazan TETs-2 of the adsorption treatment of the RO concentrate by carbonate sludge to remove sulfate- and chloride-ions is estimated.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
I. A. Malakhov, A. A. Askerniya, I. I. Borovkova, G. I. Malakhov, V. A. Rogovoi, V. Yu. Lebedev, and N. N. Velichkina, “Technology for deep demineralization of makeup water at thermal power stations with utilization of wastewaters,” Therm. Eng 53, 596–599 (2006).
SanPin 2.1.4.1074-01. Potable Water (Minzdrav Rossii, Moscow, 2002).
T. G. Lupeiko, E. M. Bayan, and M. O. Gorbunova, “Use of carbonate-containing industrial waste for treatment of aqueous solutions to remove nickel(II) ions,” J. Appl. Chem. 77, 83–87 (2004).
MU 08-47/250. Thermal Waters. Methods of Sulfates Mass Concentration Estimation (With Change No. 1) (Sib-Strim, Tomsk, 2010).
Modernization of the Water Treatment Unit at “Kazanskaya TETs-2” Thermal Power Plant. http://www1. ta-tgencom.ru/.
Sewerage of Populated Places and Industrial Enterprises. Designer’s Handbook, Ed. by V. N. Samokhin (Stroiizdat, Moscow, 1981) [in Russian].
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work was performed within the scope of the basic part of the state assignment in the field of scientific activities (no. 13.6384.2017/BCh).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by T. Krasnoshchekova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolaeva, L.A., Minneyarova, A.R. Adsorption Treatment of Reverse-Osmosis Concentrate from Water-Treatment Units at Thermal Power Stations. Therm. Eng. 66, 372–376 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601519050069
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040601519050069