Abstract
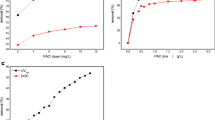
Optimization of coagulation and ozonation processes for removal of disinfection by–products (DBP) formation potential in raw water was conducted by a pilot scale system. Proper poly–aluminum–chloride–sulfates (PACS), pre–ozone and post–ozone dosages are required for improving the removal performance of DBP formation potential to guarantee the safety of drinking water. Considering the treatment performances and economic costs, the optimum PACS, pre–ozone and post–ozone dosages for treating raw water with high organic concentration should be around 8.9 mg/L Al2O3, 0.5 and 2.5 mg/L, respectively. The combined drinking water treatment system of pre–ozonation, coagulation/sedimentation, sand filtration, post–ozonation, granular activated carbon filtration and disinfection is a promising process to reduce DBP formation potential from raw water in southern China. Under the optimum conditions, this combined system removed total trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids formation potential 50.16 and 69.10%, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singer, P.C., J. Environ. Eng., ASCE, 1994, vol. 120, pp. 727–744.
Uyguner, C.S., Bekbolet, M., and Selcuk, H., Sep. Sci. Technol., 2007, vol. 42, pp. 1405–1419.
Jacangelo, J.G., DeMarco, J., Owen, D.M., and Randtke, S.J., J. Amer. Water Works Assoc., 1995, vol. 87, pp. 64–77.
Gao, B.Y., Abbt–Braun, G., and Frimmel, F.H., Acta Hydrochem. Hydrobiol., 2006, vol. 34, pp. 491–497.
Selcuk, H., Vitosoglu, Y., Ozaydin, S., and Bekbolet, M., Desalination, 2005, vol. 176, pp. 211–217.
Yavich, A.A. and Masten S.J., J. Amer. Water Works Assoc., 2003, vol. 95, pp. 159–171.
Zhang, Q., Liu, Y., Wei, Y., et al., Desalination and Water Treatment, 2012, vol. 48, pp. 221–231.
APHA/AWWA/WEF. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, [20th ed.], Washington, 1998.
Singer, P.C. and Chang, S.D., J. Amer. Water Works Assoc., 1989, vol. 81, pp. 61–65.
Iriarte–Velasco, U., Alvarez–Uriarte, J.I.,and Gonzalez–Velasco, J.R., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 368–380.
Gerrity, D., Mayer, B., Ryu, H., et al., Water Res., 2009, vol. 43, pp. 1597–1610.
Kim, W.H., Nishjima, W., Shoto, E., and Okada, M., Water Sci. Technol., 1997, vol. 35, pp. 21–28.
Tskeuchi, Y., Mochidzuki, K., Matsunobu, N., et al., Ibid., 1997, vol. 35, pp. 171–178.
Nishjima, W., Kim, W.H., Shoto, E., and Okada, M., Ibid., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 163–169.
Xie, S.G., Shi, D.W., Wen, D.H., et al., Biomed. Environ. Sci., 2007, vol. 20, pp. 217–225.
Chiang, P.C., Chang, E.E., Chang, P.C., and Huang, C.P., Sci. Total Environ., 2009, vol. 407, pp. 5735–5742.
Benschoten, J.E.V. and Edzwald J.K., Water Res., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 1527–1535.
Camel. V. and Bermond, A., Ibid., 1998, vol. 32, pp. 3208–3222.
Becker, W.C. and O’Melia, C.R., Ozone Sci. Eng., 1996, vol. 18, pp. 311–324.
Rueter, J. and Johnson, R., Aquacult. Eng., 1995, vol. 14, pp. 123–141.
Odegaard, H., Brattebo, H., Eikebrokk, B., and Thorsen, T., Water Supply, 1986, vol. 4, pp. 129–158.
Jammes, C., Hochereau, C., and Bruchet, A., In Proc. of the First Int. Res. Symp. on Water Treatment By–Products(Poitiers, France, 29–30 September, 1994), Poitiers, 1994, vol. 1, pp. 10.1–10.17.
De Laat, J., Dore, A. M., and Mallevialle, J., Water Res., 1991, vol. 25, pp. 151–164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Liu, B., Liu, Y. et al. Optimization of Coagulation and Ozonation Processes for Disinfection by–Products Formation Potential Reduction. J. Water Chem. Technol. 40, 246–252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X18040112
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X18040112