Abstract
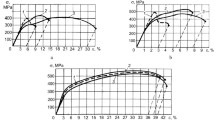
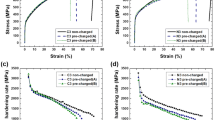
The introduction of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen in steel is analyzed in terms of the electron structure, dislocation properties, hardening, and failure of the steel. The similarity and differences in the mechanical properties of the corresponding solution solutions are discussed in relation to the influence of these elements on the density of electron states at the Fermi level of iron and correspondingly on the concentration of free electrons. Carbon reduces the concentration of free electrons, while nitrogen and hydrogen have the opposite effect. Hence, the atomic interaction is changed: specifically, its covalent or metallic component will be intensified. The dislocation rate in deformation is analyzed in the approximation of mobile and immobile interstitial atoms. In the first case, the interstitial atoms obstruct dislocational slip; the mobility of the dislocations is determined by the binding enthalpy of the dislocations with impurity atoms. If the interstitial atoms may accompany dislocations, the atomic bond is locally changed in dislocational atmospheres. That affects the unit energy of the dislocations and the distance between them in the slip planes. On the basis of the research results, the significant similarity between the hydrogen brittleness of austenitic steel and the ductile–brittle transition in alloying with nitrogen is explained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frehser, J. and Kubisch, Ch., BergHuettenmaenn. Monatsh., 1963, vol. 108, no. 11, pp. 369–380.
Norstroöm, L.A., Met. Sci., 1977, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 208–212.
Degallaix, S., Foct, J., and Hendry, A., Mater Sci. Technol., 1986, vol. 2, no. 9, pp. 946–950.
Gavriljuk, V.G., Berns, H., Escher, Ch., Glavatskaya, N.I., Sozinov, A., and Petrov, Yu.N., Grain boundary strengthening in austenitic nitrogen steels, Mater. Sci. Forum, 1999, vol. 318, pp. 455–460.
Sanbström, R. and Bergqvist, H., Scand. J. Metall., 1977, no. 6, pp. 156–169.
Nyilas, A., Obst, B., and Nakajima, H., in Proc. High Nitrogen Steels Conf., HNS-93, Gavriljuk, V.G. and Nadutov, V.M., Eds., Kiev: Inst. Met. Phys., 1993, pp. 339–344.
Gavriljuk, V.G., Sozinov, A.L., Foct, J., Petrov, Yu.N., and Polushkin, Yu.A., Effect of nitrogen on the temperature dependence of the yield strength of austenitic steels, Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 1157–1163.
Uggowitzer, P.J. and Harzenmoser, M., in Proc. High Nitrogen Steels Conf., HNS-88, Foct, J. and Hendry, A., Eds., London: Inst. Met., 1989, pp. 174–179.
Gavriljuk, V.G., Duz’, V.A., and Yephimenko, S.P., in Proc. High Nitrogen Steels Conf., HNS-90, Stein, G. and Witulsi, H., Eds., Dusseldorf: Stahl & Eisen, 1990, pp. 100–103.
Nilsson, J.O., The effect of slip behavior on the low cycle fatigue behavior of two austenitic stainless steels, Scr. Metall., 1983, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 593–596.
Vogt, J.B., Magnin, T., and Foct, J., Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 1993, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 555–564.
Briant, C.L., Effects of nitrogen and cold work on the sensitization of austenitic stainless steels, in Report NP-2457 on the Research Project 1574-1, New York: Gen. Electric Comp., 1982.
Mudali, U.K., Dayal, R.K., Gnanamoorthy, J.B., and Rodrigez, P., Relationship between pitting and intergranular corrosion of nitrogen-bearing austenitic stainless steels, ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 799–806.
Azuma, S., Miyuki, H., and Kudo, T., Effect of alloying nitrogen on crevice corrosion of austenitic stainless steels, ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 793–798.
Berns, H., Lueg, J., Trojan, W., and Zoch, H.W., in Proc. High Nitrogen Steels Conf., HNS-90, Stein, G. and Witulski, H., Eds., Dusseldorf: Stahl & Eisen, 1990, pp. 425–429.
Gavriljuk, V.G., Shanina, B.D., and Berns, H., Ab initio development of a high-strength corrosion-resistant austenitic steel, Acta Mater., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 5071–5082.
Tobler, R.L. and Meyn, D., Cleavage-like fracture along slip planes in Fe18Cr3Ni13Mn0.3N austenitic stainless steel at liquid helium temperature, Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 1626–1631.
Tomota, Y., Xia, Y., and Inoue, K., Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 1577–1587.
Hohenberg, P. and Kohn, W., Phys. Rev. B, 1964, vol. 136, pp. 864–871.
Kohn, W. and Sham, L.J., Phys. Rev. B, 1964, vol. 136, pp. 864–871.
Blaha, P., Schwarz, K., Madsen, G.K.H., Kvasnicka, D., and Luitz, J., WIEN2k, An Augmented Plane Wave Local Orbitals Program for Calculating Crystal Properties, Wien, Austria: Karlheinz Schwarz Techn. Univ., 2001. ISBN 3-9501031-1-2
Teus, S.M., Shyvanyuk, V.N., Shanina, B.D., and Gavriljuk, V.G., Effect of hydrogen on electronic structure of fee iron in relation to hydrogen embrittlement of austenitic steels, Phys. Status Solidi A, 2007, vol. 204, no. 12, pp. 4249–4258.
Gavriljuk, V.G., Shanina, B.D., Syvanyuk, V.N., and Teus, S.M., Electronic effect on hydrogen brittleness of austenitic steels, J. Appl. Phys., 2010, vol. 108, pp. 1–9.
Berns, H., Gavriljuk, V.G., Riedner, S., and Tyshchenko, A., High strength stainless austenitic CrMnCN steels. Part I: alloy design and properties, Steel Res. Int., 2007, vol. 787, no. 9, pp. 710–715.
Berns, H., Gavriljuk, V.G., and Riedner, S. High Interstitial Stainless Austenitic Steels, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2013.
Gavriljuk, V.G., Duz’, V.A., Efimenko, S.P., and Kvasnevskii, O.G., Interaction of carbon atoms and nitrogen with dislocations in austenite, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 1987, vol. 64, no. 6, pp. 1132–1135.
Atrens, A., Fiore, N.F., and Miura, K., J. Appl. Phys., 1977, vol. 48, no. 10, pp. 4247–4251.
Gavriljuk, V.G., Kushnareva, N.P., and Prokopenko, V.G., On the nature of structural changes during the tempering of lower bainite, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 1976, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 1288–1293.
Zelinski, A., Lunarska, E., and Smialowski, M., Acta Metall., 1977, vol. 25, pp. 305–308.
Schoeck, G., Bisogni, E., and Shyne, J., Acta Metall., 1964, vol. 12, no. 12, pp. 1466–1468.
Rivière, A., Amirault, J.P., and Woirgard, J., II Nuovo Cimento, 1976, vol. 33, pp. 398–407.
Schoeck, G., Acta Metall., 1963, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 617–622.
Seeger, A., Phys. Status Solid. A, 1979, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 457–468.
Takita, K. and Sakamoto, K., Scr. Metall., 1976, vol. 10, pp. 399–403.
Gavriljuk, V.G., Shanina, B.D., Shyvanyuk, V.N., and Teus, S.M., Hydrogen embrittlement of austenitic steels: electron approach, Corros. Rev., 2013, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 33–50.
Birnbaum, H.K. and Sofronis, P., Hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity-a mechanism for hydrogen-related fracture, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1994, vol. 176, pp. 191–202.
Larikov, L.N., Fal’chenko, V.M., Mazanko, V.F., Gurevich, S.M., Kharchenko, G.I., and Ignatenko, A.I., Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1975, vol. 221, no. 5, pp. 1073–1075.
Pogorelov, A.E., Ryaboshapka, K.P., and Zhuravlev, A.F., Mass transfer mechanism in real crystals by pulsed laser irradiation, J. Appl. Phys., 2002, vol. 92, p. 5766.
Harzenmoser, M.A.E., Massive aufgestickte anustenitisch–rostfreie Sraähle und Duplexstaähle, Doctoral Thesis, Zuärich: Eidgenoössische Tech. Hochschule, 1990.
Gavriljuk, V.G. and Berns, H., in High Nitrogen Steels, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.G. Gavriljuk, 2015, published in “Izvestiya VUZ. Chernaya Metallurgiya,” 2015, No. 10, pp. 761–768.
About this article
Cite this article
Gavriljuk, V.G. Influence of interstitial carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen on the plasticity and brittleness of steel. Steel Transl. 45, 747–753 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091215100046
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091215100046