Abstract
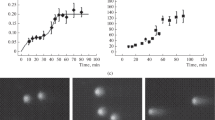
Results of the kinetics of DNA exit in neutral and alkaline variants of single cell gel electrophoresis are compared. It is shown that preincubation of samples in an alkaline buffer makes DNA exit in neutral electrophoresis impossible and, in contrast, effectively facilitates it within such buffers. We conclude that the alkali disrupts interactions between the loop domains of the DNA and the matrix proteins. We discuss the hypothetical nature of these interactions. The results obtained suggest that the mechanisms of DNA exit in the course of neutral and alkaline electrophoresis are substantially different. In the case of neutral electrophoresis, comet tails are formed by relaxed loop domains; during alkaline electrophoresis, they are formed by single-strand DNA fragments that are extracted, by the force of the electric field, from coils not yet bound to matrixes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins, A.R., The Comet Assay for DNA Damage and Repair: Principles, Applications, and Limitations, Mol. Biotechnol., 2004, vol. 26, pp. 249–261.
Olive, P.L., The Comet Assay. An Overiew of Techniques, Meth. Mol. Biol., 2002, vol. 203, pp. 179–194.
Møller, P., The Alkaline Comet Assay: Towards Validation in Biomonitoring of DNA Damaging Exposures, Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 2006, vol. 98, pp. 336–345.
Collins, A.R., Oscoz, A.A., Brunborg, G., Gaivao, I., Giovannelli, L., Kruszewski, M., Smith, C.C., and Stetina, R., The Comet Assay: Topical Issues, Mutagenesis, 2008, vol. 23, pp. 143–151.
Afanas’eva, K.S., Shuvalova, T.A., Zazhitskaya, M.O., and Sivolob, A.V., Reversibility of DNA Loop Release during Comet Electrophoresis of Isolated Cells, Biopolym. Cell, 2008, vol. 24, pp. 105–111.
Yendle, J.E., Tinwell, H., Elliott, B.M., and Ashby, J., The Genetic Toxicity of Time to the Outcome of Singe-Cell Gel Electrophoresis Assays, Mutat. Res., 1997, vol. 375, pp. 125–136.
Cook, P.R., Brazell, I.A., and Jost, E., Characterization of Nuclear Structures Containing Superhelical DNA, J. Cell Sci., 1976, vol. 22, pp. 303–324.
Hartmann, A., Agurell, E., Beevers, C., Brendler-Schwaab, S., Burlinson, B., Clay, P., Collins, A., Smith, A., Speit, G., Thybaud, V., and Tice, R.R., Recommendations for Conducting the in vivo Alkaline Comet Assay, Mutagenesis, 2003, vol. 18, pp. 45–51.
Kohwi-Shigematsu, T. and Kohwi, Y., Torsional Stress Stabilizes Extended Base Unpairing in Suppresser Sites Flanking Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Enhancer, Biochemistry, 1990, vol. 29, pp. 9551–9560.
Bode, J., Kohwi, Y., Dickinson, L., Joh, T., Klehr, D., Mielke, C., and Kohwi-Shigematsu, T., Biological Significance of Unwinding Capability of Nuclear Matrix-Associating DNAs, Science, 1992, vol. 255, pp. 195–197.
Probst, H. and Herzog, R., DNA Regions Associated with the Nuclear Matrix of Ehrlich Ascites Cells Expose Single-Stranded Sites After Deproteinization, Eur. J. Biochem., 1985, vol. 146, pp. 167–171.
Dickinson, L.A., Joh, T., Kohwi, Y., and Kohwi-Shigematsu, T., A Tissue-Specific MAR/SAR DNA-Binding Protein with Unusual Binding Site Recognition, Cell, 1992, vol. 70, pp. 631–645.
Lichtenstein, A.V., Zaboikin, M.M., Sjakste, N.I., and Alechina, R.P., Differential Dissociation of Chromatin Digests: A Novel Approach Revealing a Hierarchy of DNA-Protein Interactions within Chromatin Domains, J. Cell Sci., 1991, vol. 99, pp. 603–513.
Collins, A.R., Dobson, V.L., Dusinska, M., Kennedy, G., and Stetina, R., The Comet Assay: What Can It Really Tell Us?, Mutat. Res., 1997, vol. 375, pp. 183–193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K.S. Afanasieva, M.O. Zazhytskaya, A.V. Sivolob, 2009, published in Tsitologiya i Genetika, 2009, Vol. 43, No. 6, pp. 3–7.
About this article
Cite this article
Afanasieva, K.S., Zazhytskaya, M.O. & Sivolob, A.V. Mechanisms of DNA exit during neutral and alkaline comet assay. Cytol. Genet. 43, 367–370 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452709060012
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452709060012