Abstract
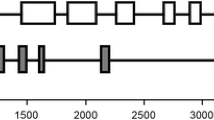
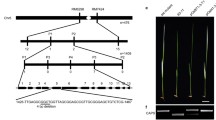
The chloroplast ATP synthase (ATPase) utilizes the energy of a transmembrane electrochemical proton gradient to drive the synthesis of ATP from ADP and phosphate. The chloroplast ATPase α and β subunits are the essential components of multisubunit protein complex. In this paper, the full-length cDNA and genomic DNA of ATPase α (designated as GbatpA) and β (designated as GbatpB) subunit genes were isolated from Ginkgo biloba. The GbatpA and GbatpB genes were both intronless. The coding regions of GbatpA and GbatpB were 1530 bp and 1497 bp long, respectively, and their deduced amino acid sequences showed high degrees of identity to those of other plant ATPase α and β proteins, respectively. The expression analysis by RT-PCR revealed that GbatpA and GbatpB both expressed in tissue-specific manners in G. biloba and might involve in leaf development. The recombinant GbATPB protein was successfully expressed in E. coli strain using pET28a vector with ATPase activity as three times high as the control, and the results showed that the molecular weight of the recombinant protein was about 54 kDa, a size that was in agreement with that predicted by bioinformatics analysis. This study provides useful information for further studying on overall structure, function and regulation of the chloroplast ATPase in G. biloba, the so-called “living fossil” plant as one of the oldest gymnosperm species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATPase:
-
ATP synthase
- CF0 :
-
coupling factor 0
- CF1 :
-
coupling factor 1
- H+-ATPase:
-
proton-translocating ATPase
- IPTG:
-
isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside
- PSI:
-
photosystem I
- PSII:
-
photosystem II
- RACE:
-
rapid amplification of cDNA ends
References
Abdallah F., Salamini F. & Leister D. 2000. A prediction of the size and evolutionary origin of the proteome of chloroplasts of Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 5: 141–142.
Altschul S.F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E.W. & Lipman D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410.
Avni A., Anderson J.D., Holland N., Rochaix J.D., Gromet-Elhanan Z. & Edelman M. 1992. Tentoxion sensitivity of chloroplasts determined by codon 83 of β subunit of proton-ATPase. Science 257: 1245–1247.
Benson D.A., Karsch-Mizrachi I., Lipman D.J., Ostell J. & Wheeler D.L. 2007. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 35(Database issue): D21–D25.
Boekema E.J. & Böttcher B. 1992. The structure of ATP synthase from chloroplasts: conformational changes of CF1 studied by electron microscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1098: 131–143.
Bradford M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Chen Z., Wu I., Richter M.L. & Gegenheimer P. 1992. Over-expression and refolding of β-subunit from the chloroplast ATP synthase. FEBS Lett. 298: 69–73.
de Boer A.D. & Weisbeek P.J. 1991. Chloroplast protein topogenesis: import, sorting, and assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1071: 221–253.
Deno H., Shinozaki K. & Sugiura M. 1983. Nucleotide sequence of tobacco chloroplast gene for the α subunit of proton-translocating ATPase. Nucleic. Acids Res. 11: 2185–2191.
Dever T.E., Glynias M.J. & Merrick W.C. 1987. GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 1814–1818.
Drapier D., Girard-Bascou J. & Wollman F. 1992. Evidence for nuclear control of the expression of the atpA and atpB chloroplast genes in chiamydomonas. Plant Cell 4: 283–295.
Felsenstein J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39: 783–791.
Fromme P., Boekema E.J. & Gräber P. 1987. Isolation and characterization of a supramolecular complex of subunit III of the ATP synthase from chloroplasts. Z. Naturforsch. 42c: 1239–1245.
Fry D.C., Kuby S.A. & Mildvan A.S. 1986. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: 907–911.
Futai M., Noumi T. & Maeda M. 1989. ATP synthase (H+-ATPase): result by combined biochemical and molecular biological approaches. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 58: 111–136.
Gogarten J.P., Starke T., Kibak H., Fishman J. & Taiz L. 1992. Evolution and isoforms of V-ATPase subunits. J. Exp. Biol. 172: 137–147.
Green C.D. & Hollingsworth M.J. 1994. Tissue specific expression of the large ATP synthase gene cluster in spinach plastids. Plant Mol. Biol. 25: 369–376.
Groth G. & Strotmann H. 1999. New results about structure, function and regulation of the chloroplast ATP synthase (CF0CF1). Physiol. Plant. 106: 142–148.
Groth G. & Pohl E. 2001. The structure of the chloroplast F1-ATPase at 3.2? resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 1345–1352.
Jang L. & Cai L.H. 2000. A method for extracting DNA of Ginkgo biloba. Plant Physiol. Commun. 36: 340–342.
Komine Y., Kwong L., Anguera M.C., Schuster G. & Stern D.B. 2000. Polyadenylation of three classes of chloroplast RNA in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. RNA 6: 598–607.
Kramer D.M., Cruz J.A. & Kanazawa A. 2003. Balancing the central roles of the thylakoid proton gradient. Trends Plant Sci. 8: 27–32.
Kudla J., Hayes R. & Gruissem W. 1996. Polyadenylation accelerates degradation of chloroplast mRNA. EMBO J. 15: 7137–7146.
Kumar A. & Ellis B.E. 2001. The phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene family in raspberry. Structure, expression, and evolution. Plant Physiol. 127: 230–299.
Leebens-Mack J., Raubeson L.A., Cui L., Kuehl J.V., Fourcade M.H., Chumley T.W., Boore J.L., Jansen R.K. & dePamphilis C.W. 2005. Identifying the basal angiosperm node in chloroplast genome phylogenies: sampling one’s way out of the Felsenstein zone. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22: 1948–1963.
Levva J.A. Bianchet M.A. & Amzel M. 2003. Understanding ATP synthesis: structure and mechanism of the F1-ATPase. Mol. Membr. Biol. 20: 27–33.
Li W., Fan J., Zhao N. & Liu J. 2001. cDNA cloning, sequencing andcharacterization of radish chloroplast ATPase beta subunit. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology) 41: 36–40. (in Chinese)
Liao Z.H., Chen M., Guo L., Gong Y.F., Tang F., Sun X.F. & Tang K.X. 2004. Rapid isolation of high-quality total RNA from Taxus and Ginkgo. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 34: 209–214.
Lisitsky I., Klaff P. & Schuster G. 1996. Addition of destabilizing poly(A)-rich sequences to endonuclease cleavage sites during the degradation of chloroplast mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 13398–13403.
Maier R.M., Neckermann K., Igloi G.L. & Kossel H. 1995. Complete sequence of the maize chloroplast genome: gene content, hotspots of divergence and fine tuning of genetic information by transcript editing. J. Mol. Biol. 251: 614–628.
Maiwald D., Dietzmann A., Jahns P., Pesaresi P., Joliot P., Joliot A., Levin J.Z., Salamini F. & Leister D. 2003. Knock-out of the genes coding for the rieske protein and the ATP-synthase δ-subunit of Arabidopsis. Effects on photosynthesis, thylakoid protein composition, and nuclear chloroplast gene expression. Plant Physiol. 133: 191–202.
Moller W. & Amons R. 1985. Phosphate-binding sequences in nucleotide-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 186: 1–7.
Muller P., Li X.P. & Niyogi K.K. 2001. Non-photochemical quenching: a response to excess light energy. Plant Physiol. 125: 1558–1566.
Nelson N. 1992. Evolution of organellar proton-ATPases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1100: 109–124.
Nickrent D.L., Parkinson C.L., Palmer J.D. & Duff R.J. 2000. Multigene phylogeny of land plants with special reference to bryophytes and the earliest land plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 17: 1885–1895.
Saitou N. & Nei M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4: 406–425.
Sambrook J. & Russell D.W. 2001. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor.
Saraste M., Sibbald P.R. & Wittinghofer A. 1990. The P-loop — a common motif in ATP-and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 15: 430–434.
Savolainen V., Chase M.W., Hoot S.B., Morton C.M., Soltis D.E., Bayer C., Fay M.F., de Bruijin A.Y., Sullivan S. & Qiu Y.L. 2000. Phylogenetics of flowering plants based on combined analysis of plastid atpB and rbcL gene sequences. Syst. Biol. 49: 306–362.
Schuettpelz E., Korall P. & Pryer K.M. 2006. Plastid atpA data provide improved support for deep relationships among ferns. Taxon 55: 897–906.
Shi Q.H., Li M.Y., Xu J.B. & Tan X.M. 2006. Effects of high temperature stress on ATPase activity of plasma membrane and NH +4 absorption rate in roots of early rice. Acta Agronomica Sinica 32: 1044–1048. (in Chinese)
Stock D., Leslie A.G. & Walker J.E. 1999. Molecular architecture of the rotary motor in ATP synthase. Science 286: 1700–1705.
Tang J., Xia H., Cao M., Zhang X., Zeng W., Hu S., Tong W., Wang J., Wang J., Yu J., Yang H. & Zhu L. 2004. A comparison of rice chloroplast genomes. Plant Physiol. 135: 412–420.
Thompson J.D., Gibson T.J., Plewniak F., Jeanmougin F. & Higgins D.G. 1997. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 2876–4882.
van Walraven H.S, Lutter R & Walker J.E. 1993. Organization and sequence of genes for the subunits of ATP synthase in the thermophilic cyanobacterium Synechococcus 6716. Biochem. J. 294: 239–251.
Wakasugi T., Tsudzuki J., Ito S., Nakashima K., Tsudzuki T. & Sugiura M. 1994. Loss of all ndh genes as determined by sequencing the entire chloroplast genome of the black pine Pinus thunbergii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 9794–9798.
Walker J.E., Saraste M. Runswick M.J. & Gay N.J. 1982. Distantly related sequences in the alpha-and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1: 945–951.
Woessner J.P., Masson A., Harrls E.H., Bennoun P., Gillham N.W. & Boynton J.E. 1984. Molecular and genetic analysis of the chloroplast ATPase of Chlamydomonas. Plant Mol. Biol. 3: 177–190.
Wolf P.G., Karol K.G., Mandoli D.F., Kuehl J., Arumuganathan K., Ellis M.W, Mishler D.D, Kelch D.G., Olmstead R.G & Boore J.L. 2005. The first complete chloroplast genome sequence of a lycophyte, Huperzia lucidula (Lycopodiaceae). Gene 350: 117–128.
Zurawski G., Bottomley W. & Whitfeld P.R. 1982. Structures of the genes for the β and ε subunits of spinach chloroplast ATPase indicate a dicistronic mRNA and an overlapping translation stop/start signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79: 6260–6264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Cai, R., Cheng, Sy. et al. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of atpA and atpB genes from Ginkgo biloba . Biologia 63, 526–534 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0093-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0093-0