Abstract
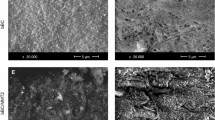
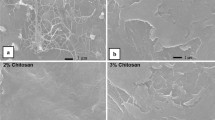
Antimicrobial packaging protects the product from the external environment and microbial contamination, conferring numerous advantages on human health. Interest in biopolymers as packaging materials has considerably increased recently. Bacterial cellulose is an interesting biomaterial produced as nanofibrils by Acetobacter xylinium and is a promising candidate due to its remarkable properties. New composite materials with antimicrobial properties were developed in this work, containing poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) as polymer matrix and ground bacterial cellulose (BC) as reinforcing fibres. Sorbic acid was used as an antimicrobial agent because it is a preservative recognised in the food industry. The materials obtained were studied using Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The swelling rate of the composites was also measured. Release experiments of sorbic acid from the composite films into water were performed and the mass transfer phenomena were investigated using Fick’s law of diffusion. The antimicrobial effect was tested against Escherichia coli K12-MG1655. The results obtained indicated that the new biocomposite films could be promising antimicrobial food packaging materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buonocore, G. G., Del Nobile, M. A., Panizza, A., Bove, S., Battaglia, G., & Nicolais, L. (2003). Modeling the lysozyme release kinetics from antimicrobial films intended for food packaging applications. Journal of Food Science, 68, 1365–1370. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2003.tb09651.x.
Choi, J. H., Choi, W. Y., Cha, D. S., Chinnan, M. J., Park, H. J., Lee, D. S., & Park, J. M. (2005). Diffusivity of potassium sorbate in κ-carrageenan based antimicrobial film. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 38, 417–423. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2004.07.004.
Crank, J. (1975). The mathematics of diffusion. Bristol, UK: Oxford University Press.
Czaja, W. K., Young, D. J., Kawecki, M., & Brown, R. M., Jr. (2007). The future prospects of microbial cellulose in biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules, 8, 1–12. DOI: 10.1021/bm060620d.
Del Nobile, M. A., Conte, A., Incoronato, A. L., & Panza, O. (2008). Antimicrobial efficacy and release kinetics of thymol from zein films. Journal of Food Engineering, 89, 57–63. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.04.004.
Flores, S., Haedo, A. S., Campos, C., & Gerschenson, L. (2007). Antimicrobial performance of potassium sorbate supported in tapioca starch edible films. European Food Research and Technology, 225, 375–384. DOI: 10.1007/s00217-006-0427-5.
Gemili, S., Yemenicioğlu, A., & Altınkaya, S. (2009). Development of cellulose acetate based antimicrobial food packaging materials for controlled release of lysozyme. Journal of Food Engineering, 90, 453–462. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.07.014.
Han, J. H. (2003). Antimicrobial food packaging. In R. Ahvenainen (Ed.), Novel food packaging techniques (pp. 50–70). Cambridge, UK: Woodhead Publishing Ltd.
Han, J. H., & Floros, J. D. (2007). Active packaging: A nonthermal process. In G. Tewari, & V. K. Juneja (Eds.), Advances in thermal and non-thermal food preservation (pp. 167–183). Ames, IA, USA: Blackwell Publishing.
Iguchi, M., Yamanaka, S., & Budhiono, A. (2000). Bacterial cellulose-a masterpiece of nature’s arts. Journal of Materials Science, 35, 261–270.
Jonas, R., & Farah, L. F. (1998). Production and application of microbial cellulose. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 59, 101–106. DOI: 10.1016/S0141-3910(97)00197-3.
Kačuráková, M., Smith, A. C., Gidley, M. J., & Wilson, R. H. (2002). Molecular interactions in bacterial cellulose composites studied by 1D FT-IR and dynamic 2D FT-IR spectroscopy. Carbohydrate Research, 337, 1145–1153. DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6215(02)00102-7.
Markin, V. S., Iordanskii, A. L., & Kosenko, R. Yu. (1998). Benzoic acid release from strongly swelling PVA films. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 3, 54–56. DOI: 10.1007/BF02539231.
Mastromatteo, M., Barbuzzi, G., Conte, A., & Del Nobile, M. A. (2009). Controlled release of thymol from zein based film. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 10, 222–227. DOI: 10.1016/j.ifset.2008.11.010.
Mastromatteo, M., Lecce, L., De Vietro, N., Favia, P., & Del Nobile, M. A. (2011). Plasma deposition processes from acrylic/methane on natural fibres to control the kinetic release of lysozyme from PVOH monolayer film. Journal of Food Engineering, 104, 373–379. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.12.032.
Min, S., & Krochta, J. M. (2007). Edible coatings containing bioactive antimicrobial agents. In J. H. Han (Ed.), Packaging for nonthermal processing of food (pp. 29–52). Ames, IA, USA: Blackwell Publishing and the Institute of Food Technologists.
Petersen, K., Nielsen, P. V., Bertelsen, G., Lawther, M., Olsen, M. B., Nilsson, N. H., & Mortensen, G. (1999). Potential of biobased materials for food packaging. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 10, 52–68. DOI: 10.1016/S0924-2244(99)00019-9.
Redl, A., Gontard, N., & Guilbert, S. (1996). Determination of sorbic acid diffusivity in edible wheat gluten and lipid based films. Journal of Food Science, 61, 116–120. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1996.tb14739.x.
Rothstein, S. N., Federspiel, W. J., & Little, S. R. (2009). A unified mathematical model for the prediction of controlled release from surface and bulk eroding polymer matrices. Biomaterials, 30, 1657–1664. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.12.002.
Souza, M. P., Cerqueira, M. A., Souza, B. W. S., Teixeira, J. A., Porto, A. L. F., Vicente, A. A., & Carneiro-da-Cunha, M. G. (2010). Polysaccharide from Anacardium occidentale L. tree gum (Policaju) as a coating for Tommy Atkins mangoes. Chemical Papers, 64, 475–481. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-010-0017-7.
Uz, M., & Altınkaya, S. A. (2011). Development of mono and multilayer antimicrobial food packaging materials for controlled release of potassium sorbate. LWT — Food Science and Technology. Article in press. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.05.003.
Watanabe, K., Tabuchi, M., Morinaga, Y., & Yoshinaga, F. (1998). Structural features and properties of bacterial cellulose produced in agitated culture. Cellulose, 5, 187–200. DOI: 10.1023/A:1009272904582.
Yoshida, C. M. P., Bastos, C. E. N., & Franco, T. T. (2010). Modeling of potassium sorbate diffusion through chitosan films. LWT — Food Science and Technology, 43, 584–589. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2009.10.005.
Zhu, G.-Q., Gao, Q.-C., Li, Z.-H., Wang, F.-G., & Zhang, H. (2010). Modification of poly(vinyl alcohol) membrane via blending with poly(γ-benzyl l-glutamate)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymer. Chemical Papers, 64, 776–782. DOI:10.2478/s11696-010-0069-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobre, LM., Stoica-Guzun, A., Stroescu, M. et al. Modelling of sorbic acid diffusion through bacterial cellulose-based antimicrobial films. Chem. Pap. 66, 144–151 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-011-0086-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-011-0086-2