Abstract
Background
The aim of the study was to analyse the predictive host and viral factors of sustained virological response (SVR) in Estonian patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1b.
Methods
A total of 76 outpatients (44 males and 32 females, aged 21–63 years) were enrolled in the single-centre prospective study. The patients received 180 µg of Peg-IFN α-2α weekly plus daily weight-based ribavirin (1000–1200 mg/day).
Results
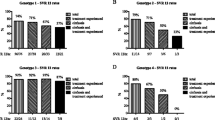
The SVR was achieved in 50% of the patients, 43.4% of the patients were referred to as non-SVR. The SVR and the non-SVR patients differed significantly in terms of age (p=0.012), stage of fibrosis (p=0.012), grade of inflammatory activity (p=0.002), platelet count (p=0.005), gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) level (p=0.028), as well as a decrease of the viral load at weeks 4 and 12 more than 3.59 log10 IU/ml and 5.98 log10 IU/ml (P<0.01), respectively.
Conclusion
Age below 40 years, absence of or mild and moderate fibrosis, absence of severe inflammation activity, normal platelet count and normal GGT level, and pronounced changes in viral kinetics at weeks 4 and 12, were valuable predictors of better response to peginterferon alfa plus ribavirin treatment in Estonian patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1b.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization Viral Cancers: Hepatitis C virus. Accessed 2010 May 28. Available from: URL: http://www.who.int/vaccine_research/diseases/viral_cancers/en/index2.html#disease%20burden
Simmonds P., Bukh J., Combet C., Deleage G., Enomoto N., Feinstone S., et al., Consensus proposals for a unified system of nomenclature of hepatitis C virus genotypes, Hepatology, 2005, 42(4), 962–973
Lavanchy D., Evolving epidemiology of hepatitis C virus, Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 2011, 17(2), 107–115
Esteban J.I., Sauleda S., Quer J., The changing epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection in Europe, J. Hepatol., 2008, 48, 148–162
Tallo T., Norder H., Tefanova V., Krispin T., Schmidt J., Ilmoja M., et al., Genetic characterization of hepatitis C virus strains in Estonia: fluctuations in the predominanting subtype with time, J. Med. Virol., 2007, 79(4), 374–382
Zusinaite E., Krispin T., Raukas E., Kiiver K., Salupere R., Ott K., et al., Hepatitis C virus genotypes in Estonia, APMIS, 2000, 108(11), 739–746
Tefanova V., Tallo T., Kutsar K., Priimgi L., Urgent action needed to stop spread of hepatitis B and C in Estonian drug users, Euro Surveill., 2006, 11, E060126.3
Ghany M.G., Strader D.B., Thomas D.L., Seeff L.B., Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update, Hepatology, 2009, 49, 1335–1374
EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of hepatitis C virus infection, J. Hepatol., 2011, 55, 245–264
Shiffman M.L., Chronic hepatitis C: treatment of pegylated interferon/ribavirin nonresponders, Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep., 2006, 8(1), 46–52
Manns M.P., McHutchison J.G., Gordon S.C., Rustgi V.K., Shiffman M., Reindollar R., et al., Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial, Lancet, 2001, 358, 958–965
Fried M.W., Shiffman M.L., Reddy K.R., Smith C., Marinos G., Gonçales F.L. Jr, et al., Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection, N. Engl. J. Med., 2002, 347, 975–982
Hadziyannis S.J., Sette H.Jr., Morgan T.R., Balan V., Diago M., Marcellin P., et al., Peginterferon-alfa2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose, Ann. Intern. Med., 2004, 140(5), 346–355
McHutchison J.G., Lawitz E.J., Shiffman M.L., Muir A.J., Galler G.W., McCone J., et al., Peginterferon alfa-2b or alfa-2a with ribavirin for treatment of hepatitis C infection, N. Engl. J. Med., 2009, 361(6), 580–593
Ferenci P., Optimal treatment duration for patients with HCV genotype 1 infection, J. Viral. Hepat., 2012, 19(Suppl 1), 7–13
Yu J.W., Sun L.J., Zhao Y.H., Kang P., Yan B.Z., Impact of sex on virologic response rates in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C patients with peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin treatment, Int. J. Infect. Dis., 2011, 15(11), 740–746
Berg T., Sarrazin C., Herrmann E., Hinrichsen H., Gerlach T., Zachoval R., et al., Prediction of treatment outcome in patients with chronic hepatitis C: significance of baseline parameters and viral dynamics during therapy, Hepatology, 2003, 37(3), 600–609
Zeuzem S., Heterogeneous virologic response rates to interferon-based therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C: who responds less well? Ann. Intern. Med., 2004, 140(5), 370–381
Foster G.R., Fried M.W., Hadziyannis S.J., Messinger D., Freivogel K., Weiland O., Predicting of sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a (40 KD)/ribavirin, Scand. J. Gastroenterol., 2007, 42(2), 247–255
Hoofnagle J.H., Wahed A.S., Brown R.S.Jr., Howell C.D., Belle S.H., Virahep-C Study Group, Early changes in hepatitis C virus (HCV) levels in response to peginterferon and ribavirin treatment in patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 infection, J. Infect. Dis., 2009, 199(8), 1112–1120
Saludes V., Bracho M.A., Valero O., Ardevol M., Planas R., Gonzalez-Candelas F., et al., Baseline prediction of combination therapy outcome in hepatitis C virus 1b infected patients by discriminant analysis using viral and host factors, PloS One, 2010, 5(11), e14132
Puig-Basagoiti F., Forns X., Furcić I., Ampurdanés S., Giménez-Barcons M., Franco S., et al., Dynamics of hepatitis C virus NS5A quasispecies during interferon and ribavirin therapy in responder and non-responder patients with genotype 1b chronic hepatitis C, J. Gen. Virol., 2005, 86(Pt 4), 1067–1075
Villela-Nogueira C.A., Perez R.M., de Segadas Soares J.A., Coelho H.S., Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) as an independent predictive factor of sustained virologic response in patients with hepatitis C treated with interferon-alpha and ribavirin, J. Clin. Gastroenterol., 2005, 39(8), 728–730
Jacobson I.M., Brown R.S. Jr., Freilich B., Afdhal N., Kwo P.Y., Santoro J., et al., Peginterferon alfa-2b and weight-based or flat-dose ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients: a randomized trial, Hepatology, 2007, 46(4), 971–981
Poordad F., Reddy K.R., Martin P., Rapid virologic response: a new milestone in the management of chronic hepatitis C, Clin. Infect. Dis., 2008, 46(1), 78–84
Fried M.W., Hadziyannis S.J., Shiffman M.L., Messinger D., Zeuzem S., Rapid virological response is the most important predictor of sustained virological response across genotypes in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection, J. Hepatol., 2011, 55(1), 69–75
Clark P.J., Thompson A.J., McHutchison J.G., IL28B genomic-based treatment paradigms for patients with chronic hepatitis C infection: the future of personalized HCV therapies, Am. J. Gastroenterol., 2011, 106(1), 38–45
Bedossa P., Poynard T., An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group, Hepatology, 1996, 24(2), 289–293
Backus L.I., Boothroyd D.B., Phillips B.R., Belperio P., Halloran J., Mole L.A., A sustained virologic response reduces risk of all-cause mortality in patients with hepatitis C, Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 2011, 9, 509–516
Brjalin V., Salupere R., Tallo T., Kuznetsova T., Priimägi L., Tefanova V., Efficacy of peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin combination therapy in treatment-naïve Estonian patients with chronic hepatitis C, Cent. Eur. J. Public Health, 2012, 20(2), 150–155
Lee S.S., Bain V.G., Peltekian K., Krajeden M., Yoshida E.M., Deschenes M., et al., Treating chronic hepatitis C with pegylated interferon alfa- 2a (40 KD) and ribavirin in clinical practice, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther., 2006, 23, 397–408
Mauss S., Hueppe D., John C., Goelz J., Heyne R., Moeller B., et al., Estimating the likelihood of sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C therapy, J. Viral. Hepat., 2011, 18, 81–90
Weich V., Herrmann E., Chung T.L., Sarrazin C., Hinrichsen H., Buggisch P., et al., The determination of GGT is the most reliable predictor of nonresponsiveness to interferon-alpha based therapy in HCV type-1 infection, J. Gastroenterol., 2011, 46(12), 1427–1436
Marcellin P., Cheinquer H., Curescu M., Dusheiko G.M., Ferenci P., Horban A., et al., High sustained virologic response rates in rapid virologic response patients in the large realworld PROPHESYS cohort confirm results from randomized clinical trials, Hepatology, 2012, 56(6), 2039–2050
Navaneethan U., Kemmer N., Neff G.W., Predicting the probable outcome of treatment in HCV patients, Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol., 2009, 2(5), 287–302
Berg T., von Wagner M., Nasser S., Sarrazin C., Heintges T., Gerlach T., et al., Extended treatment duration for hepatitis C virus type 1: comparing 48 versus 72 weeks of peginterferon-alfa- 2a plus ribavirin, Gastroenteroly, 2006, 130, 1086–1097
Lindsay K.L., Morishima C., Wright E.C., Dienstag J.L., Shiffman M.L., Everson G.T., et al., Blunted cytopenias and weight loss: new correlates of virologic null response to re-treatment of chronic hepatitis C, Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 2008, 6(2), 234–241
Enomoto N., Sakuma I., Asahina Y., Kurosaki M., Murakami T., Yamamoto C., et al., Mutations in the nonstructural protein 5A gene and response to interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus 1b infection, N. Engl. J. Med., 1996, 334(2), 77–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Brjalin, V., Salupere, R., Tallo, T. et al. Predictors of treatment response in patients with hepatitis C 1b genotype. cent.eur.j.med 8, 822–829 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-013-0221-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-013-0221-2