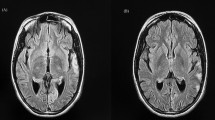
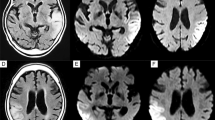
Abstract
Epilepsy is an associated feature of patients with the syndrome of mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS). A substitution at nucleotide position 3243 A>G of the mitochondrial DNA is the most common mutation encountered both in Caucasians and in Chinese/Taiwanese. We herein report a 38-year-old man with A3243G mutation of the mitochondrial DNA whom developed MELAS. The manifestation of his focal motor epilepsy was aggravated by use of sodium valproate (VPA). The mechanism of this paradoxical effect is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M. Shoffner: “Maternal inheritance and the evaluation of oxidative phosphorylation diseases”, Lancet, Vol. 348, (1996), pp. 1283–1288.
P.F. Chinnery, N. Howell, R.N. Lightowlers and D.M. Turnbull: “Molecular pathology of MELAS and MERRF: The relationship between mutation load and clinical phenotypes”, Brain, Vol. 120, (1997), pp. 1713–1721.
S. Dimauro and G. Davidzon: “Mitochondrial DNA and disease”, Ann. Med., Vol. 37, (2005), pp. 222–232.
S. DiMauro: “Mitochondrial diseases”, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Vol. 1658, (2004), pp. 80–88.
S.G.. Pavlakis, P.C. Phillips, S. DiMauro, D.C. DeVivo and L.P. Rowlan: “Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes: a distinctive clinical syndrome”, Ann. Neurol., Vol. 16, (1984), pp. 481–488.
P. Thajeb, D.F. Dai, M.F. Chiang and W.C. Shyu: “Genotype-phenotype correlation of maternally inherited disorders due to mutations of the mitochondrial DNA”, Taiwanese J. Obstet. Gynecol., Vol. 45(3), (2006), pp. 201–207.
C.C. Huang, R.S. Chen, C.M. Chen, H.S. Wang, C.C. Lee, C.Y. Pang, H.S. Hsu, H.C. Lee and Y.H. Wei: “MELAS syndrome with mitochondrial tRNALeu(UUR) gene mutation in a Chinese family”, J. Neurol. Neurosury. Psychiatry, Vol. 57, (1994), pp. 586–589.
C.W. Liou, C.C. Huang, E.C. Chee, Y.J. Jong, J.L Tsai, C.Y. Pang, H.C. Lee and Y.H. Wei: “MELAS syndrome: correlation between clinical features and molecular genetic analysis”, Acta Neurol. Scand., Vol. 90, (1994), pp. 354–359.
W. Fang, C.C. Huang, C.C. Lee, S.Y. Cheng, C.Y. Pang and Y.H. Wei: “Ophthalmologic manifestations in MELAS syndrome”, Arch. Neurol., Vol. 50, (1993), pp. 977–980.
P. Thajeb, M.C. Wu, B.F. Shih, C.Y. Tzen, M.F. Chiang and R.Y. Yuan: “Brain SPECT studies in patients with A3243G mutation of the mitochondrial DNA”, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., Vol. 1042, (2005), pp. 48–54.
C.Y. Tzen CY, P. Thajeb, T.Y. Wu and S.C. Chen: “MELAS with point mutations involving tRNALeu (A3243G) and tRNAGlu(14693G)”, Muscle Nerve, Vol. 28, (2003), pp. 575–581.
Y. Zhang, J.F. Li, F.Y. Wang and C.X. Li: “The study of A3243G and G13513A mitochondria DNA point mutation in patients with cerebral infarction”, Chin. Med. J. (Beijing), Vol. 114, (2001), pp. 129–135.
U. Altrup, H. Reith and E.J. Speckmann: “Effects of valproate in a model nervous system (buccal ganglia of Helix pomatia): II. Epileptogenic actions”, Epilepsia, Vol. 33, (1992), pp. 753–759.
B. Chabrol, J. Mancini, D. Chretien, P. Rustin, A. Munnich and N. Pinsard: “Valproate-induced hepatic failure in a case of cytochrome c oxidase deficiency”, Eur. J. Pediatr., Vol. 153, (1994), pp. 133–135.
S. Ponchaut, F. Van Hoof and K. Veitch: “Cytochrome c oxidase depletion is the cause of the deficient mitochondrial respiration induced by chronic valproate administration”, Biochem. Pharmacol., Vol. 43, (1992), pp. 644–647.
S. Ponchaut, F. Van Hoof and K. Veitch: “Valproate and cytochrome c oxidase deficiency”, Eur. J. Pediatr., Vol. 154, (1995), p. 79.
C.W. Lam, C.H. Lau, J.C. Williams, Y.W. Chan and L.J. Wong: “Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) triggered by valproate therapy”, Eur. J. Pediatr., Vol. 156, (1997), pp. 562–564.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YM., Lin, CM. & Thajeb, P. Paradoxical effect of sodium valproate that aggravates epilepsy of MELAS in a patient with A3243G mutation of the mitochondrial DNA. cent.eur.j.med 2, 103–107 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-007-0007-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-007-0007-5