Abstract
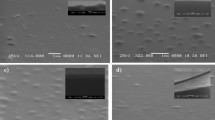
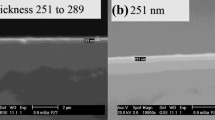
The effect of pulsed laser treatment of metal, and metal blacks, was studied. Gold and black gold thin films were fabricated by thermal evaporation of gold in a vacuum and nitrogen atmosphere respectively. Black gold films were grown in a nitrogen atmosphere at pressures of 200 Pa and 300 Pa. UV pulsed laser radiation (λ = 266 nm, τ = 4 ns), with fluence ranging from 1 mJ·cm−2 to 250 mJ·cm−2 was used for the film treatment in a vacuum and nitrogen atmosphere. The nitrogen pressure was varied up to 100 kPa. Surface structure modifications were analyzed by optical microscopy, atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) was used for chemical characterization of the samples. A significant dependence of the film optical and structural properties on laser treatment conditions (laser fluence, ambient pressure and number of applied pulses) was found. The threshold for observable damage and initiation of changes of morphology for gold and black gold surfaces was determined. Distinct modifications were observed for fluences greater than 106 mJ·cm−2 and 3.5 mJ·cm−2 for the gold and black gold films respectively. Absorbtivity of the black gold film is found to decrease with an increase in the number of laser pulses. Microstructural and nanostructural modifications after laser treatment of the black gold film were observed. EDX analysis revealed that no impurities were introduced into the samples during both the deposition and laser treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. V. Teperiketal, Nature Photonics 2, 299 (2008)
A. H. Pfund, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1, 397 (1930)
W. Becker, R. Fettig, W. Ruppel, Infrared Phys. Techn. 40, 431 (1999)
J. Lehman, E. Theocharous, G. Eppeldauer, C. Pannell, Meas. Sci. Technol. 14, 916 (2003)
K. Snail, A. Morrish, L. M. Hanssen, Proc. SPIE 692, 143 (1986)
H. Jiang, Z. Li, L. Hong, Z. Liu, B. Guo, Appl. Surf. Sci. 223, 279 (2004)
A. Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 7272 (2007)
A. Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 59, 579 (2007)
A. Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, J. Appl. Phys. 104, 053516 (2008)
J. Mauletal, Appl. Phys. A 82, 43 (2006)
U. Kreibig, M. Vollmer, Optical Properties of Metal Clusters (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1995)
S. Altshulin, J. Zahavi, A. Rosen, S. Vadiv, J. Mater. Sci. 25, 2259 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Novotný, M., Fitl, P., Sytchkova, A.K. et al. Pulsed laser treatment of gold and black gold thin films fabricated by thermal evaporation. centr.eur.j.phys. 7, 327–331 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11534-009-0027-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11534-009-0027-7